Secure Federated Learning
As organizations race to train smarter AI models together, federated learning (FL) has become one of the most promising techniques for collaboration without compromising data privacy. Instead of pooling data into a central server, each participant trains a local model and shares only its updates.
While this setup reduces exposure, it also introduces new attack surfaces. Vulnerabilities such as gradient inversion and data poisoning can still reveal private information or manipulate outcomes. Ensuring secure federated learning requires a combination of cryptography, monitoring, and strong data compliance frameworks.
Federated learning is not inherently secure — privacy-preserving mechanisms must be designed into every layer of the process.
Understanding Secure Federated Learning
In federated systems, participants — often hospitals, banks, or research institutions — collaboratively train a shared model. Each node computes updates locally and sends only model parameters or gradients to an aggregator.
However, attackers can still reverse-engineer sensitive data from these gradients. Researchers from Google AI first introduced the concept, but later studies demonstrated that even encrypted gradients can leak identifiable information when not properly managed.
That’s where secure federated learning comes in — introducing:
End-to-end encryption
Activity monitoring for auditability
Anomaly detection using behavior analytics
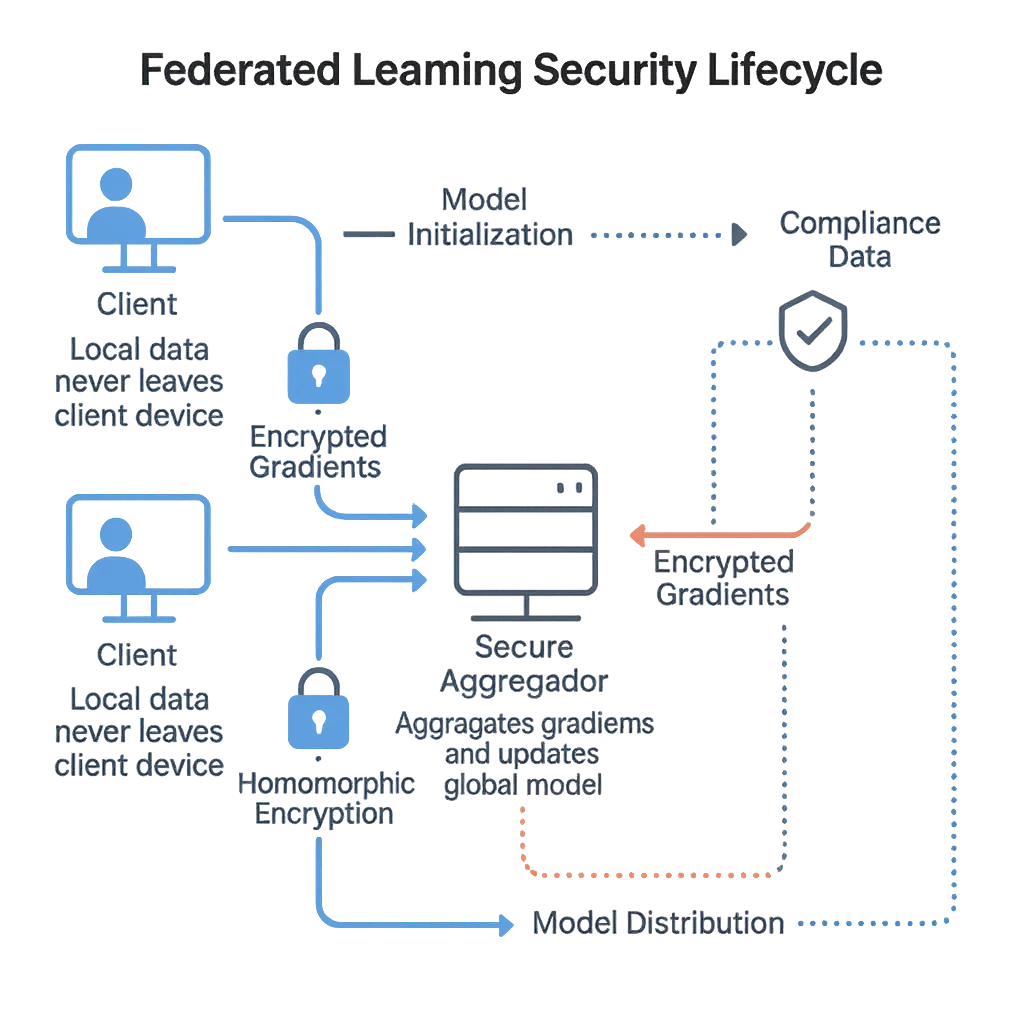
These measures ensure that model updates remain verifiable, encrypted, and compliant across all participants.
Always assume that even “trusted” nodes might be compromised — design your system for zero trust.
Key Security Challenges
Gradient Inversion Attacks – Adversaries reconstruct private samples from shared gradients, exposing PII.
Model Poisoning – Malicious contributors can inject biased data or backdoors, bypassing firewall defenses.
Untrusted Aggregators – Without strict role-based access control, central nodes become single points of failure.
Compliance Drift – Multi-jurisdictional data flows challenge ongoing GDPR and HIPAA alignment.
Recent academic reviews, like Zhu et al. (2023), emphasize that federated models require not only encryption but also behavioral governance — validating contributions, access control, and logging across the model lifecycle.
Implementing Secure Aggregation
The following Python snippet demonstrates a simplified secure aggregation mechanism that validates trust and filters malicious updates before integration:
from typing import Dict, List
import hashlib
class FederatedSecurityAggregator:
def __init__(self, threshold: float = 0.7):
self.threshold = threshold
self.trust_registry: Dict[str, float] = {}
def hash_gradient(self, gradient: List[float]) -> str:
"""Generate a hash for integrity verification."""
return hashlib.sha256(str(gradient).encode()).hexdigest()
def validate_node(self, node_id: str, gradient: List[float]) -> Dict:
"""Evaluate node reliability and detect anomalies."""
gradient_hash = self.hash_gradient(gradient)
trust_score = self.trust_registry.get(node_id, 0.8)
malicious = trust_score < self.threshold
return {
"node": node_id,
"hash": gradient_hash,
"trust_score": trust_score,
"malicious": malicious,
"recommendation": "Exclude" if malicious else "Accept"
}
def aggregate(self, updates: Dict[str, List[float]]):
"""Aggregate only verified updates."""
return {
node: self.validate_node(node, grad)
for node, grad in updates.items()
}
This logic can be integrated into audit logs and data activity history for traceability and compliance validation.
Use cryptographically secure hashes (like SHA-3) and digital signatures to verify contributor authenticity before model merging.
Implementation Best Practices
For Organizations
Privacy-by-Design – Apply dynamic and static data masking before training.
Unified Audit Strategy – Maintain continuous audit trails across nodes using data discovery tools.
Regulatory Compliance – Validate adherence to regional frameworks (GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS).
Encrypted Collaboration – Employ database encryption for inter-organization channels.
For Technical Teams
Trust Scoring – Maintain node reliability metrics via behavior analytics.
Reverse Proxy Security – Route all traffic through a reverse proxy for controlled data flows.
Centralized Monitoring – Combine database activity monitoring with adaptive security policies.
Continuous Validation – Re-evaluate model updates periodically and apply the principle of least privilege.
Automate compliance checks — tools like DataSunrise’s Compliance Manager can continuously validate settings across all participants.
FAQ: Secure Federated Learning
Q1. What is federated learning in one sentence?
Federated learning lets multiple parties train a shared model by keeping raw data local and sharing only model updates.
Q2. Does FL make data sharing compliant by default?
No—FL reduces exposure but you still need policy, logging, and controls to satisfy frameworks like GDPR and HIPAA; use continuous data compliance checks.
Q3. How do I prevent gradient inversion leaks?
Combine secure aggregation (e.g., multi-party computation or homomorphic encryption) with differential privacy noise on updates, plus strict access control and audit trails.
Q4. TLS vs. Secure Aggregation—what’s the difference?
TLS protects updates in transit; secure aggregation ensures the server can’t see individual updates even if transport is secure. Use both.
Q5. How are poisoned or backdoored updates detected?
Use trust scoring and anomaly detection (e.g., cosine-similarity outliers, loss-based filters), quarantine suspicious nodes, and enforce role-based access control.
Q6. What does an aggregator actually do?
It verifies, aggregates encrypted updates, produces a global model, and redistributes it; it should not access raw data or unblinded client updates.
Q7. Where does compliance fit in the loop?
As an oversight layer: it monitors logs, configurations, and evidence (DP settings, key lifecycles, policy matches) rather than receiving gradients. See database activity monitoring and audit logs.
Q8. Do I need differential privacy in every round?
Preferably yes for sensitive data; per-round noise with privacy accounting limits cumulative leakage while retaining utility.
Q9. Can I mask sensitive fields before training?
Yes—apply dynamic or static data masking at the edge so sensitive fields never enter the feature pipeline.
Q10. How do I log without leaking data?
Log metadata (rule hits, DP budgets, node IDs, hashes) and store to tamper-evident audit storage; avoid raw payloads.
Q11. What’s the model lifecycle in secure FL?
Initialization → distribution to clients → local training → encrypted update → secure aggregation → validation → global model update → redistribution; repeat with versioning and rollback.
Q12. How does DataSunrise help?
It provides proxy-based monitoring, encryption, behavior analytics, policy enforcement, and compliance evidence across the federated pipeline.
Building Trust in Collaborative AI
Federated learning demonstrates that collaboration and privacy can coexist — but only with transparent auditing, encryption, and governance. Without these, it risks becoming a blind spot for exploitation.
By combining secure aggregation, behavior analytics, and regulatory alignment, DataSunrise provides a foundation for trustworthy collaborative AI. Its Data Protection and Audit modules ensure every model contribution remains verifiable, traceable, and compliant.
Recommended Reading:
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now