Generative AI for Threat Intelligence
Introduction
Cyber threats are evolving faster than traditional security intelligence systems can interpret and react. From phishing kits to supply-chain breaches, the modern attack surface grows wider by the day.
Generative AI for Threat Intelligence changes this paradigm — introducing real-time pattern generation, automated correlation, and predictive modeling that help defenders stay several steps ahead of adversaries.
Instead of waiting for analysts to manually interpret fragmented threat feeds, AI models can synthesize indicators, map relationships, and forecast emerging threats in seconds.
Platforms like DataSunrise complement this intelligence with autonomous compliance management, continuous data monitoring, and zero-touch protection across enterprise data ecosystems.
Generative AI transforms threat intelligence from reactive investigation to predictive orchestration — learning continuously and acting autonomously.
1. Understanding Generative AI for Threat Intelligence
Traditional threat-intelligence workflows rely on human analysts correlating Indicators of Compromise (IoCs), such as IP addresses, file hashes, and attack signatures.
While effective, these approaches are limited by human bandwidth and data silos. Generative AI enhances these processes with self-learning architectures capable of contextual reasoning and pattern simulation.
According to MITRE ATT&CK, most cyberattacks follow identifiable patterns — but their variations are endless. Generative models trained on vast telemetry data can create synthetic attack scenarios, helping defenders anticipate new tactics before they are seen in the wild.
By combining Large Language Models (LLMs) with Machine Learning Audit Rules, Generative AI systems can:
- Summarize thousands of raw alerts into coherent narratives.
- Detect hidden correlations across database activity logs, user behavior, and network flows.
- Produce automated risk evaluations aligned with NIST, ISO 27001, and SOC 2 frameworks.
The result is an adaptive intelligence ecosystem that improves accuracy while reducing response latency and analyst fatigue.
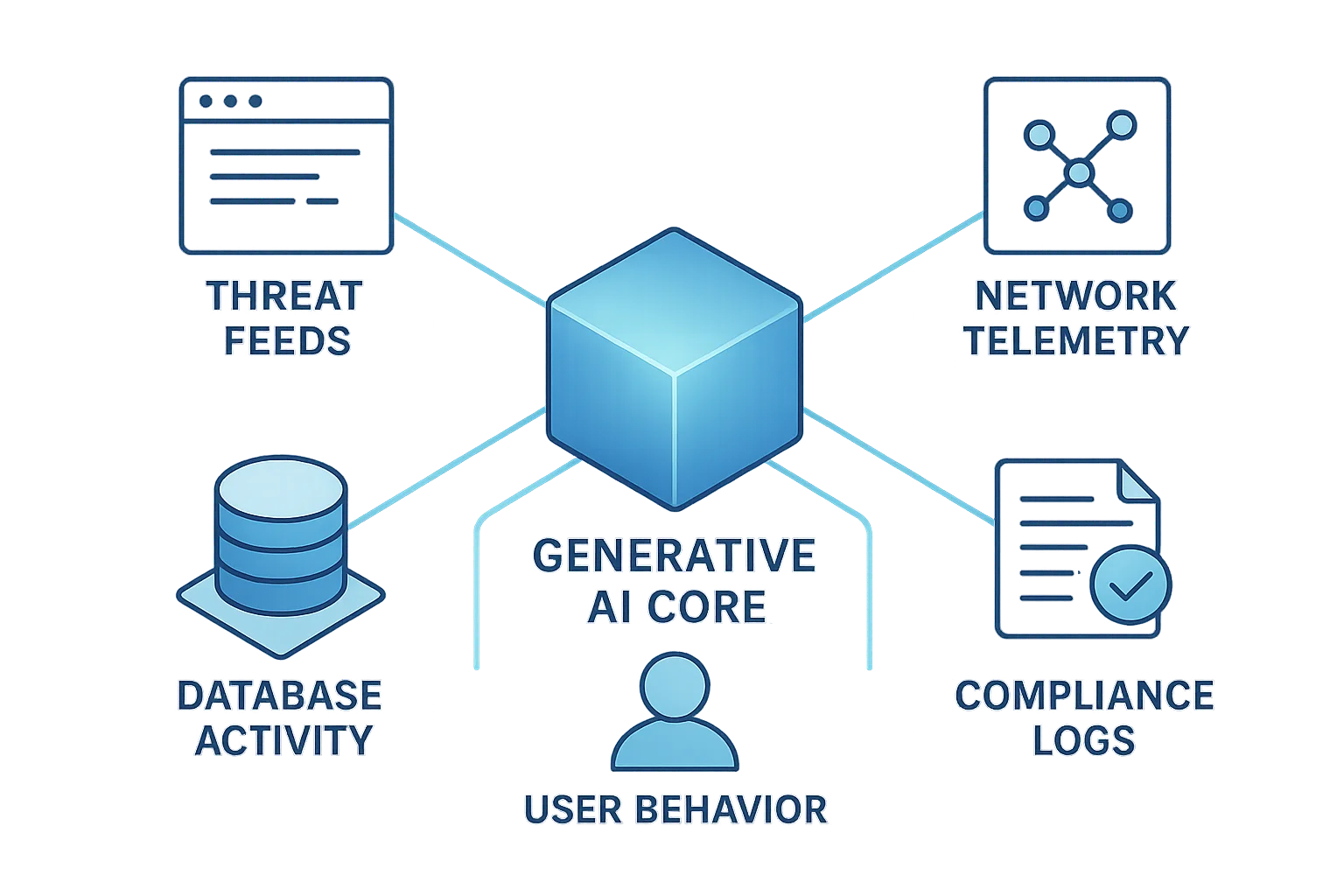
2. How Generative AI for Threat Intelligence Enhances Detection
Unlike traditional rule-based detectors, generative models don’t just recognize threats — they hypothesize them.
They learn adversarial behavior from historical incidents, generate variations of known exploits, and anticipate unseen intrusion paths.
When integrated with Database Activity Monitoring and Behavior Analytics, these models can visualize multi-stage attack campaigns, connecting isolated events into a single threat narrative.
Example: Generative Simulation for Threat Forecasting
from random import choice
attack_patterns = ["phishing", "ransomware", "credential_stuffing", "supply_chain", "cloud_key_exfiltration"]
def simulate_threat():
threat = choice(attack_patterns)
print(f"Simulating {threat} attack scenario...")
return {
"threat": threat,
"counter": f"Deploy automated mitigation for {threat} via adaptive rule engine"
}
simulate_threat()
This lightweight simulation illustrates how AI can automatically explore potential attack strategies.
When coupled with monitoring and masking layers, these generated insights form the foundation for proactive mitigation and fine-tuned security controls.
For further exploration, see Microsoft’s Security Copilot which uses generative reasoning to analyze large-scale enterprise threats in real time.
3. Generative AI and Data Governance
Generative AI thrives on data — but the same data can contain sensitive or regulated information.
Without governance, models risk exposing personal details, business secrets, or compliance-sensitive records.
Effective data governance provides the structural safeguards that ensure AI-driven intelligence operates responsibly and ethically:
- Data Classification: Identify and tag PII, PHI, and proprietary assets before model training.
- Data Minimization: Restrict training to only necessary information while excluding irrelevant sensitive content.
- Access Controls: Apply strict RBAC and attribute-based rules to govern who can view AI outputs and datasets.
- Continuous Auditing: Maintain immutable logs of all AI model interactions and automated decisions.
- Regulatory Alignment: Map AI workflows to privacy frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS to ensure global compliance.
Strong governance transforms raw data into trustworthy intelligence.
It ensures that AI-powered security insights remain actionable without crossing ethical or regulatory boundaries.
4. From Detection to Prediction: The Evolution of Threat Intelligence
The true strength of Generative AI for Threat Intelligence lies in its predictive capability.
It enables organizations to simulate adversary evolution — anticipating tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) before they are operationalized by attackers.
Paired with Threat Detection engines and continuous Data Activity History analysis, AI continuously refines baselines and detects deviations that precede actual compromises.
Use case:
A financial institution correlates phishing campaigns, anomalous logins, and abnormal API requests. Generative AI identifies a new phishing strategy targeting cloud credentials, then triggers an automatic rule update through the organization’s Security Policies module — mitigating the risk before exploitation.
Predictive threat modeling works only when supported by high-quality, masked, and compliant data sources. Governance remains essential for effective AI security.
5. Architecture of Generative AI for Threat Intelligence
An end-to-end architecture for AI-driven threat intelligence typically includes:
- Data Collection Layer: Aggregates sensor data, endpoint telemetry, and dark-web feeds.
- Generative Core: Transformer-based models for summarization, correlation, and scenario generation.
- Security Orchestration Layer: Access control and dynamic masking to manage sensitive information.
- Compliance and Audit Layer: Automated reporting aligned with NIST and ENISA standards.
This layered design ensures operational scalability while keeping sensitive datasets compliant and verifiable.
6. Business Impact of Generative AI in Threat Intelligence
By merging AI reasoning with strong governance and automated policy frameworks, organizations experience tangible improvements:
| Objective | Traditional Systems | Generative AI-Based Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Detection Speed | Hours – Days | Seconds – Minutes |
| Analyst Workload | High manual triage | Reduced by up to 70% |
| Compliance Alignment | Manual verification | Automated reporting and validation |
| Regulatory Evidence | Fragmented logs | Unified, audit-ready records |
| Threat Coverage | Known signatures | Predictive simulation of unknown vectors |
According to IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025, AI-augmented security can reduce detection and response times by over 40%, translating directly into reduced financial and reputational impact.
7. Building a Resilient Threat Intelligence Framework
To fully realize the benefits of Generative AI for Threat Intelligence, organizations should focus on sustainable, auditable design principles:
- Integrate Data Discovery for classifying sensitive assets before AI training.
- Apply Continuous Data Protection for encrypted telemetry and log storage.
- Enforce Role-Based Access Controls (RBAC) to restrict access to AI outputs and training pipelines.
- Run periodic Vulnerability Assessments based on generated threat patterns.
- Implement behavioral monitoring to flag anomalous AI actions and mitigate drift.
Each element ensures that AI-powered insight remains reliable, explainable, and compliant — even as the underlying data landscape evolves.
8. The Future of Generative AI for Threat Intelligence
The next generation of threat intelligence will be fully autonomous and adaptive.
Future systems will integrate with frameworks like MITRE D3FEND and Zero Trust Architectures, generating counter-strategies in real time as attacks unfold.
Generative AI will not only simulate attacker intent but also propose defensive automation — patching vulnerabilities, updating firewall rules, or issuing compliance reports autonomously.
When paired with machine-learning–based auditing and automated governance, these systems will form self-healing cybersecurity infrastructures — capable of protecting data before, during, and after an incident.
The convergence of AI and data governance marks the emergence of “living defense systems” — infrastructures that think, learn, and adapt faster than adversaries.
Conclusion
Generative AI for Threat Intelligence represents a pivotal shift in cybersecurity — from static detection to dynamic prediction.
By merging AI-driven reasoning with strong governance and continuous monitoring, organizations achieve a dual advantage: smarter threat prevention and compliance by design.
As AI continues to evolve, its role in cybersecurity will only deepen.
Combining intelligent analytics with transparent oversight ensures that innovation never compromises trust — and that the defenders of tomorrow remain one step ahead of the threats of today.
To explore related topics, visit the Data Compliance Overview.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now