Data Masking Tools and Techniques for MongoDB
Modern applications built on MongoDB frequently process personally identifiable information, financial records, authentication data, and operational telemetry. As regulatory pressure increases under frameworks such as GDPR and HIPAA, protecting sensitive data inside MongoDB collections becomes a strategic requirement rather than an optional safeguard.
MongoDB provides encryption, role-based access control, and client-side encryption mechanisms. These features strengthen overall database security and help enforce structured access controls. However, encryption alone does not control how data appears once access is granted. If a user has valid permissions, full values are still returned. That is where structured data masking strategies become essential.
This article explains how MongoDB’s native capabilities relate to masking, how practical masking techniques can be applied in development and analytics environments, how enterprise-grade masking platforms automate policy orchestration, and what business impact Zero-Touch Data Masking delivers in terms of measurable risk reduction and compliance efficiency.
Importance of Data Masking Tools and Techniques
Sensitive data does not become a risk only when it is stolen. It becomes a risk when it is unnecessarily exposed. In MongoDB environments, developers, analysts, DevOps engineers, and third-party integrations often require access to production-like datasets. Without structured masking controls, these users may view full PII, payment details, authentication tokens, or confidential business records during routine operations.
Encryption protects data at rest and in transit. Role-based access control limits who can connect. However, once legitimate access is granted, neither mechanism controls how sensitive fields are displayed in query results. This creates a visibility gap. Data masking tools close that gap by transforming sensitive values in real time while keeping datasets usable.
Modern masking techniques support several operational goals. First, they protect production environments by enforcing context-aware visibility rules. Second, they enable secure data provisioning for development and testing without copying live PII. Third, they support compliance frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX by limiting exposure and generating defensible audit evidence.
In addition, automated masking platforms integrate with broader data security strategies and centralized compliance management programs. Instead of relying on manual query modifications or application logic, organizations can enforce consistent policies across MongoDB clusters, hybrid infrastructures, and cloud environments.
Ultimately, data masking tools are not only technical controls. They are governance mechanisms that reduce insider risk, minimize compliance gaps, and maintain operational usability without sacrificing protection.
Native Data Masking Techniques in MongoDB
MongoDB does not include a built-in centralized masking engine. However, it offers several mechanisms that can be adapted to support masking-related use cases. These approaches rely on query logic, aggregation transformations, or encryption features rather than dedicated masking controls.
1. Projection-Based Field Redaction
Projection allows developers to exclude specific fields from query results. By explicitly omitting sensitive attributes such as social security numbers or credit card details, applications can prevent those fields from appearing in returned documents.
db.users.find(
{},
{
ssn: 0,
creditCardNumber: 0
}
)
This method hides selected fields at query time and reduces unnecessary exposure in application responses. However, it requires direct query modification inside application code. There is no centralized enforcement mechanism, which means every query must be manually adjusted. It also cannot dynamically apply masking conditions based on user roles or contextual factors. In addition, projection does not provide compliance reporting or governance-level visibility.
Projection-based redaction works for simple application-level filtering, but it is not designed for enterprise-wide governance or cross-environment consistency.
2. Aggregation Pipeline Redaction
MongoDB’s aggregation framework enables dynamic data transformation during query execution. Using operators such as $project, $substr, or $concat, developers can partially mask sensitive values. For example, only the first few characters of an email address may be displayed, while the remaining characters are replaced with placeholder symbols.
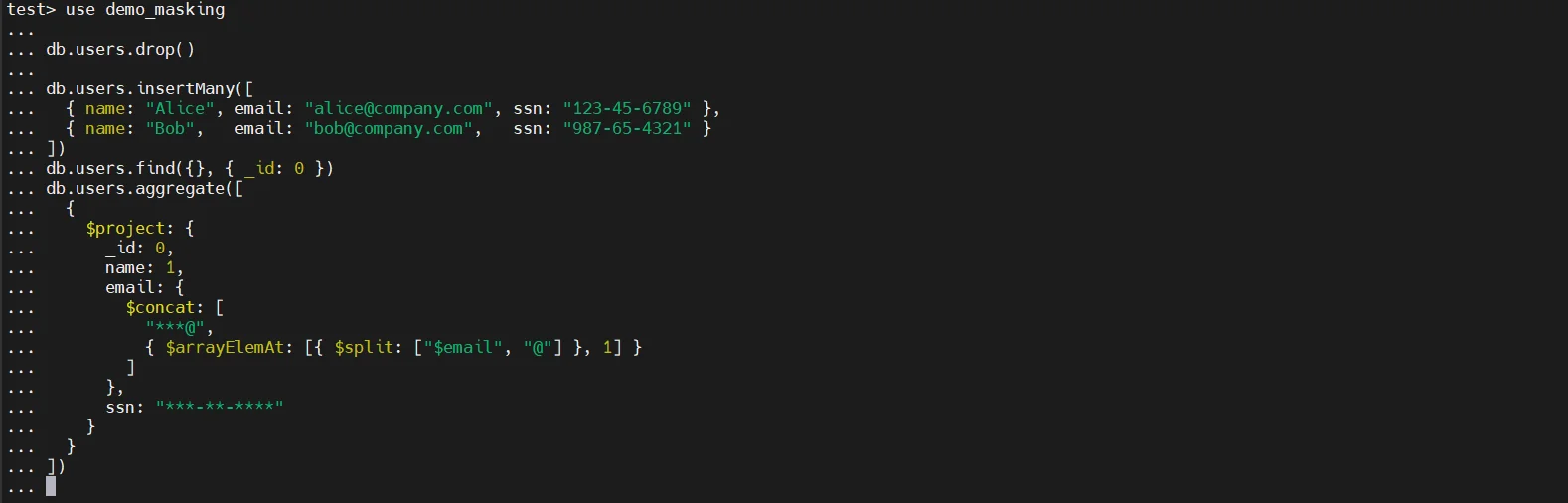
This technique offers more flexibility than basic projection because it transforms values instead of simply excluding them. However, it still requires manual implementation within each query. There is no built-in role-based conditional masking, and scaling this method across multiple services or applications quickly becomes operationally complex. Governance remains fragmented, and centralized control is absent.
Aggregation-based masking can be effective for specific analytical workloads, yet it does not provide sustainable policy management in larger environments.
3. Client-Side Field Level Encryption (CSFLE)
MongoDB supports Client-Side Field Level Encryption (CSFLE), which encrypts designated fields before they are written to the database. Encrypted fields remain protected both at rest and in transit, strengthening confidentiality at the storage layer.
{
encryptedFields: {
fields: [
{
path: "ssn",
bsonType: "string",
algorithm: "AEAD_AES_256_CBC_HMAC_SHA_512-Deterministic"
}
]
}
}
While encryption improves overall security posture, it does not implement contextual masking. Users who have decryption privileges will still see the full original values. Encryption focuses on protecting stored data and data in transit rather than controlling visibility at query time.
In practical terms, encryption secures where data is stored and how it travels. Masking controls how data appears once access is granted.
Advanced Masking Capabilities
Dynamic Data Masking
Dynamic Data Masking transforms sensitive fields in real time during query execution. When a user submits a request, masking rules are applied before results are returned. The original data stored in MongoDB collections remains unchanged.
This approach enables context-aware protection aligned with broader data security strategies. Masking policies can be defined using dynamic data masking controls and integrated with structured access controls to enforce role-based visibility.
For example, a support engineer may see partially masked email addresses, while a compliance officer with elevated privileges may view full values. Because masking occurs at runtime, no application changes are required, and production data integrity is preserved.
Dynamic masking is particularly valuable in operational environments where exposure must be minimized without disrupting business workflows.
Static Data Masking
Static Data Masking creates sanitized copies of production datasets. Sensitive fields are transformed before data is exported or replicated into development, testing, or analytics environments.
Unlike runtime transformation, static data masking modifies the copied dataset itself. This ensures that non-production systems never contain live PII or regulated information. Development teams can safely test application logic or perform analytics without exposing real customer data.
Static masking strengthens overall governance and supports compliance initiatives by limiting uncontrolled data distribution across environments.
In-Place Masking
In-Place Masking permanently transforms sensitive values directly within selected MongoDB collections. This method is often used for decommissioning, archival, or irreversible anonymization scenarios.
Through structured in-place masking controls, organizations can apply irreversible transformations when data no longer requires identifiable attributes. Once applied, original values cannot be restored.
In-place masking requires precise policy management and governance oversight because it alters stored production data directly.
Cross-Platform Coverage
Enterprise masking must extend beyond a single database platform. DataSunrise delivers centralized governance across MongoDB, relational databases, data warehouses, cloud storage systems, and file environments.
This unified model integrates with broader compliance management initiatives, ensuring consistent masking enforcement across structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data sources.
Cross-platform coverage reduces policy fragmentation, minimizes compliance gaps, and strengthens security posture in hybrid and heterogeneous infrastructures.
Business Impact of Automated Data Masking
Organizations implementing autonomous masking for MongoDB achieve measurable operational and compliance improvements. The following table summarizes the key business outcomes:
| Business Outcome | Impact Description |
|---|---|
| Quantifiable Risk Reduction | Eliminates exposure of live PII in production and non-production environments, reducing breach probability. |
| Streamlined Compliance Workflows | Automates reporting and evidence generation for regulatory audits. |
| Significant Reduction in Manual Effort | Removes the need for developers to manually rewrite queries or manage masking logic. |
| Optimized Total Cost of Compliance | Lowers operational overhead through no-code policy automation and centralized rule management. |
| Enhanced Audit Preparation | Provides audit-ready documentation and one-click compliance evidence for regulators. |
Zero-Touch Data Masking reduces the attack surface while preserving data usability for analytics, testing, and development teams.
Conclusion
MongoDB offers flexibility and scalability, but its native capabilities do not provide centralized, compliance-aligned data masking orchestration. While built-in mechanisms contribute to baseline database security, they are not designed for automated governance at scale.
Manual projection rules and aggregation pipelines can partially hide sensitive fields. However, they lack automated discovery, contextual enforcement, and regulatory automation. Without integrated data discovery and centralized policy management, organizations must rely on fragmented controls that increase operational risk.
DataSunrise delivers Autonomous Compliance Orchestration, dynamic data masking, and Unified Security Framework capabilities for MongoDB deployments across cloud and on-prem environments. Through centralized enforcement and alignment with structured compliance management programs, masking policies remain consistent across heterogeneous infrastructures.
By eliminating compliance gaps and reducing manual oversight, organizations strengthen their security posture while accelerating time-to-compliance.
To experience enterprise-grade masking for MongoDB, explore flexible deployment modes or request a live demonstration to see autonomous masking in action.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now