
Google Cloud SQL Audit Log

Introduction
A Google Cloud SQL Audit Log records who did what, where, and when in your database environment. It captures events such as logins, queries, schema changes, and permission modifications, giving you the visibility needed to secure data, prove compliance, and investigate incidents.
Google Cloud SQL offers native audit logging features through its supported database engines (MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server) and Google Cloud’s own Cloud Audit Logs service. While this provides a strong foundation, pairing it with DataSunrise adds granular control, real-time alerting, and compliance automation.
Why Google Cloud SQL Audit Logs Matter
- Security – Detect suspicious queries, failed logins, and abnormal behavior before they escalate.
- Compliance – Demonstrate adherence to standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX.
- Operational Insight – Hold users accountable, troubleshoot performance issues, and create a clear record for forensic investigations.
Without a reliable audit log, organizations run the risk of undetected breaches, incomplete compliance evidence, and slower incident response.
Native Google Cloud SQL Audit Log Capabilities
Google Cloud SQL combines database-native auditing features with Google Cloud’s platform-level logging and monitoring.
Supported audit logging by engine:
| Engine | Native Audit Features | Cloud Integration |
|---|---|---|
| MySQL | general_log for all queries, slow_query_log for performance |
Cloud Audit Logs, export to Cloud Storage / BigQuery |
| PostgreSQL | pg_stat_statements for query statistics, logging collector for activity |
Cloud Audit Logs, export to Cloud Storage / BigQuery |
| SQL Server | SQL Server Audit for event groups, logins, DDL/DML changes | Cloud Audit Logs, export to Cloud Storage / BigQuery |
Administrators can view Cloud Audit Logs directly in the Google Cloud Console, or export them to BigQuery for deeper analysis.
Example: Configuring and Viewing Google Cloud SQL Audit Logs
Part 1 — Enabling SQL Server Audit in Google Cloud SQL
You can configure native SQL Server Audit to capture key events:
CREATE SERVER AUDIT GCloudAudit
TO FILE (FILEPATH = '/var/opt/mssql/audit', MAXSIZE = 50 MB);
ALTER SERVER AUDIT GCloudAudit WITH (STATE = ON);
CREATE SERVER AUDIT SPECIFICATION AuditLoginFailures
FOR SERVER AUDIT GCloudAudit
ADD (FAILED_LOGIN_GROUP)
WITH (STATE = ON);
CREATE DATABASE AUDIT SPECIFICATION AuditTransactions
FOR SERVER AUDIT GCloudAudit
ADD (SELECT ON dbo.transactions BY public)
WITH (STATE = ON);
View the captured logs:
SELECT *
FROM sys.fn_get_audit_file('/var/opt/mssql/audit/*.sqlaudit', NULL, NULL);
Part 2 — Exploring Logs in Google Cloud Console
Open Logs Explorer and set
resource.typetocloudsql_database.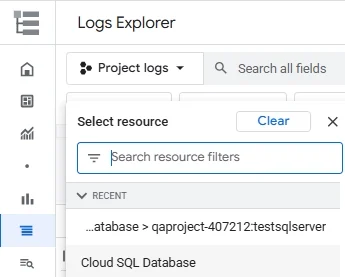
Selecting the Cloud SQL Database resource in Google Cloud Logs Explorer to filter audit log results for a specific instance. Filter by your instance ID and select a log type (e.g.,
sqlserver.err).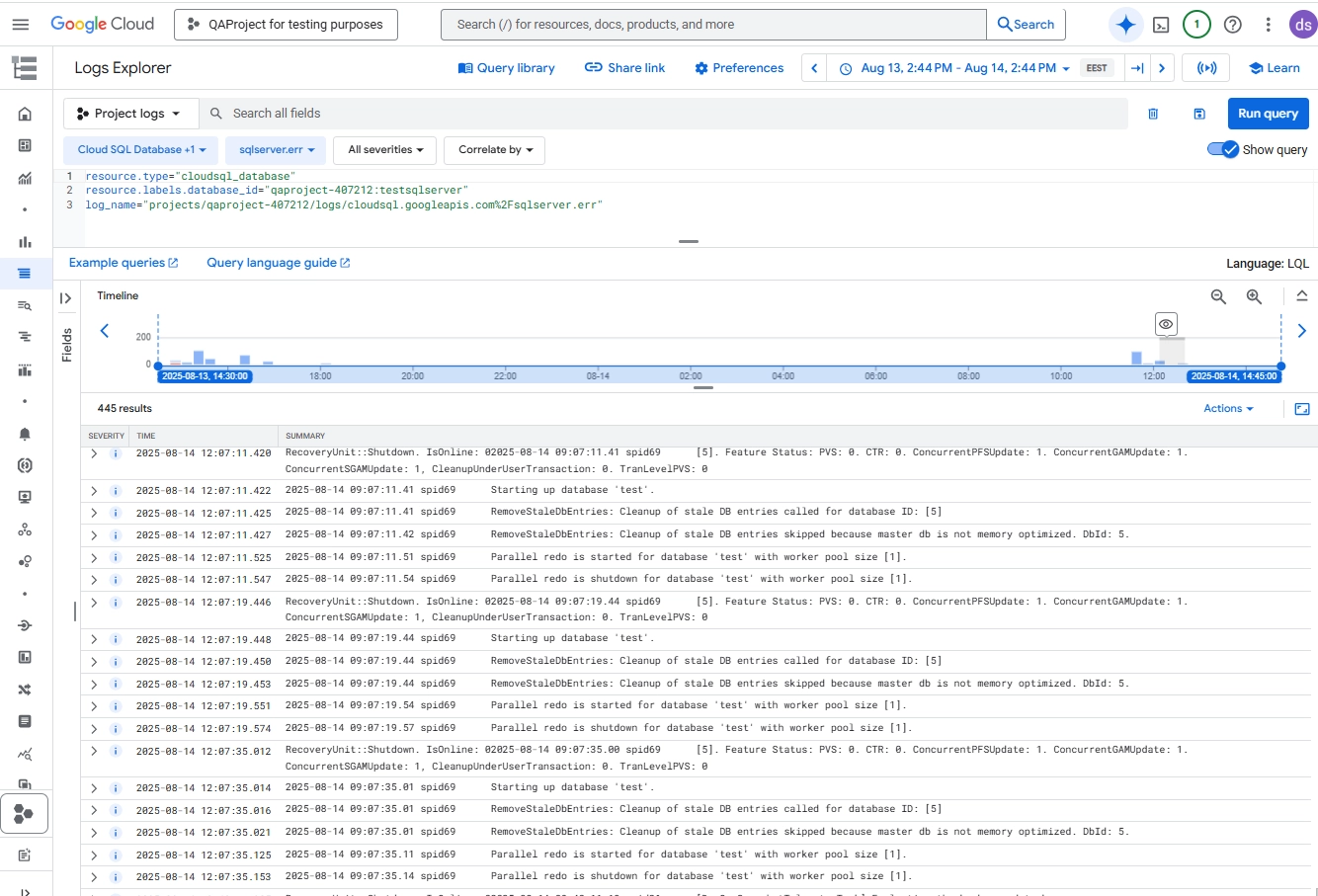
Logs Explorer view showing SQL Server error logs from a Cloud SQL instance, including startup, shutdown, and database recovery events.
Apply log name or severity filters to narrow results.
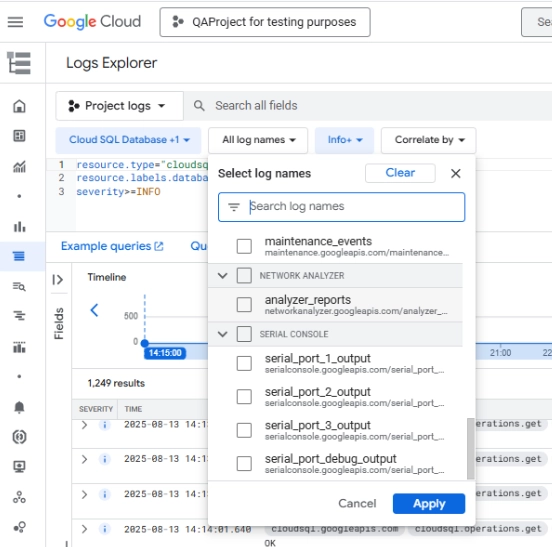
Filtering audit logs in Google Cloud Logs Explorer by log name categories to narrow down database-related events.
This combined approach lets you both capture events at the SQL Server level and analyze them through Google Cloud’s logging interface for rapid investigation and compliance reporting.
From Native Logging to Advanced Security
With SQL Server’s audit configuration and Google Cloud’s Logs Explorer, you get a reliable baseline for tracking activity. The combination lets you capture login attempts, query executions, schema changes, and system messages — all stored securely and exportable to BigQuery or Cloud Storage for further analysis.
However, these native capabilities have limits. Alerts are not generated in real time, sensitive data may appear in logs without masking, and correlating activity across multiple instances can require manual effort. Compliance reporting also remains a largely manual process.
This is where DataSunrise comes in — extending native logging with granular rules, real-time detection, masking, and automated compliance support.
Comparative Capabilities: Native SQL Server + Google Cloud vs. DataSunrise
Native SQL Server auditing in Google Cloud SQL offers a strong baseline, but some features are either limited or missing entirely. DataSunrise extends these capabilities into a full security and compliance platform.
| Feature | Native SQL Server + Google Cloud SQL | DataSunrise Enhancement |
|---|---|---|
| Event Logging | Yes – logins, queries, schema changes | Adds granular rules for specific users, IPs, query types |
| Cloud Audit Logs Integration | Yes | Centralized dashboard for multiple instances |
| Real-Time Alerts | No | Yes – instant notifications via email, Slack, SIEM |
| Data Masking in Logs | No | Yes – dynamic masking for PII, PHI, and financial data |
| Compliance Reporting | Manual export and formatting | Automated auditor-ready reports (GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, SOX) |
| Cross-Instance Correlation | Limited | Full correlation across all monitored databases |
| Log Analysis | Export to BigQuery or SIEM | Built-in analytics with rule-based filtering |
See DataSunrise in Action
Below are examples of how these enhanced capabilities look in the DataSunrise interface:
Audit Rule Creation – Define precise rules for tracking specific operations, objects, or users.
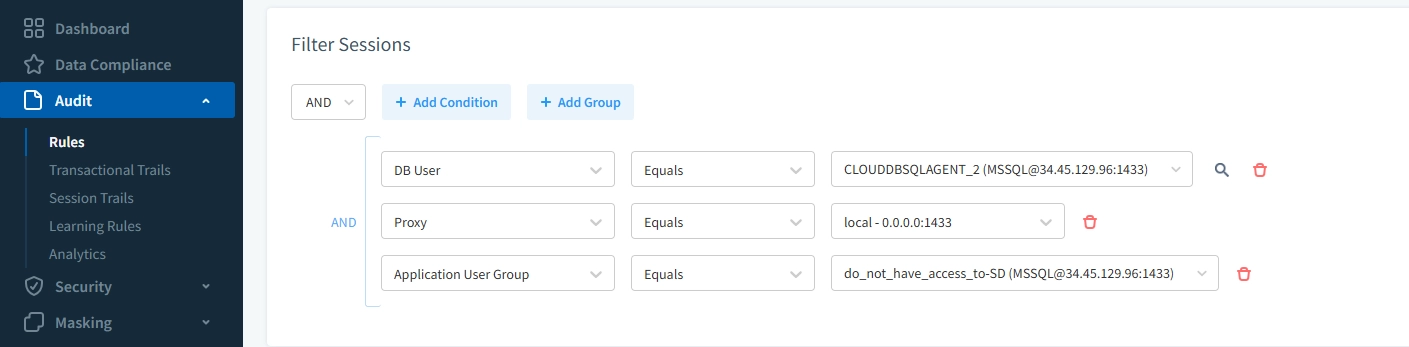
Configuring an audit rule in DataSunrise to track activity for a specific SQL Server instance in Google Cloud SQL based on user, proxy, and application group filters.
Dynamic Data Masking – Mask sensitive fields in real time to protect PII, PHI, or financial data.
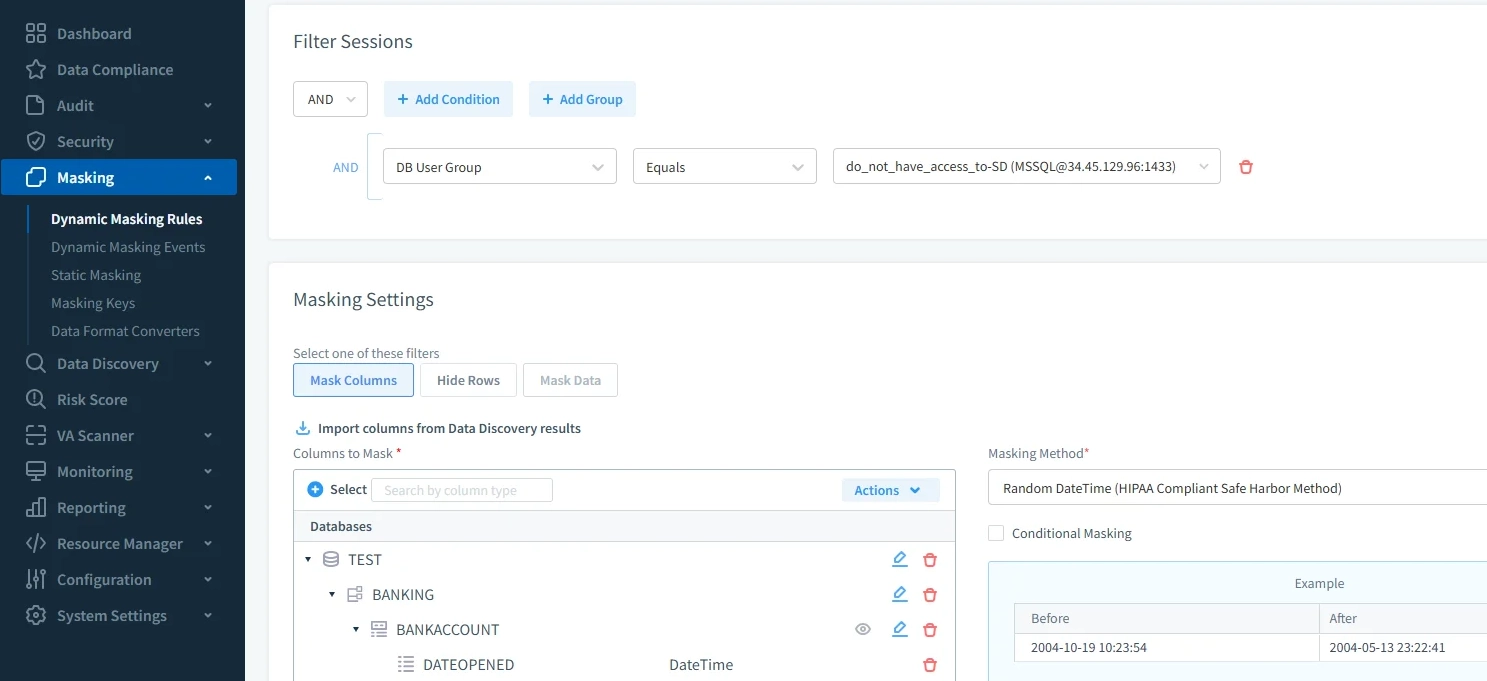
Setting up a dynamic data masking rule in DataSunrise to conceal sensitive date and account information in a Google Cloud SQL database.
Compliance Reporting – Generate ready-to-submit audit reports for major regulatory standards.
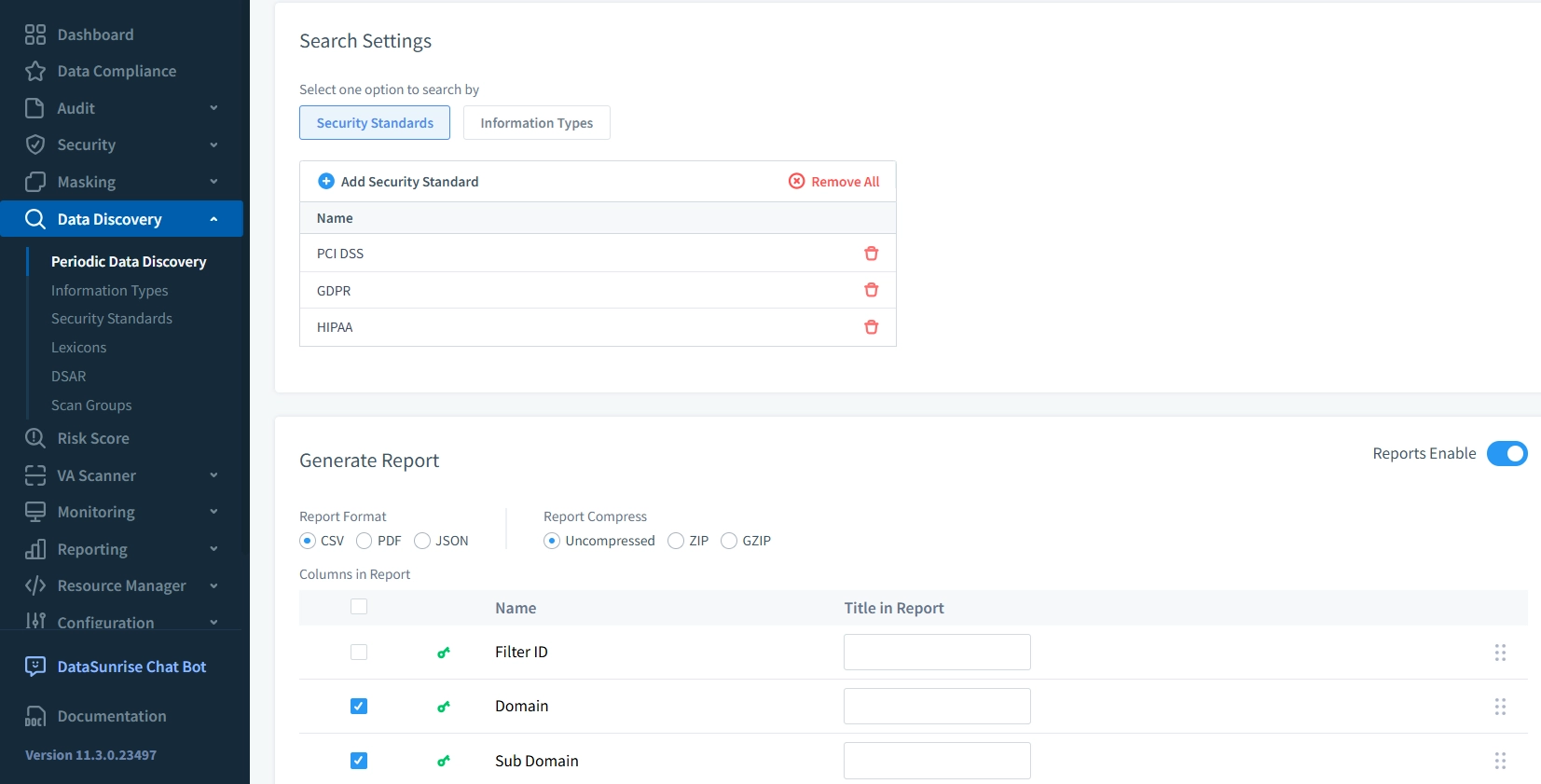
Running a periodic data discovery scan in DataSunrise to generate compliance reports for GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS.
Practical Applications and Implementation Tips
| Use Case | How to Apply |
|---|---|
| Investigating Suspicious Access Patterns | Enable detailed login and query logging in SQL Server Audit. In DataSunrise, create alert rules for failed logins followed by unusual queries. |
| Compliance Verification During Audits | Keep logs in Cloud Storage with lifecycle rules. Use DataSunrise’s compliance reports to meet GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX requirements. |
| Tracking Changes in Financial Data | Audit INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE on sensitive tables. Apply dynamic masking to hide sensitive fields in reports. |
| Cross-Instance Behavior Analysis | Export logs to BigQuery for basic correlation. Use DataSunrise’s dashboard to identify patterns across production, staging, and reporting. |
| Post-Incident Forensics | Preserve all logs after a breach. Correlate timestamps, IP addresses, and SQL statements to reconstruct the full sequence of events. |
Conclusion
A Google Cloud SQL Audit Log is essential for detecting security issues, ensuring compliance, and maintaining operational transparency. Native SQL Server and Google Cloud SQL provide a capable foundation, but DataSunrise transforms these logs into actionable intelligence with real-time alerts, masking, compliance automation, and cross-instance correlation.
By combining both approaches, you gain complete visibility into database activity while reducing manual workload and strengthening your security posture.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now