How to Apply Static Masking in Percona Server
Static masking in Percona Server for MySQL is a practical approach to protecting sensitive information before data leaves production environments. Percona Server is widely used for transactional workloads, analytics pipelines, and customer-facing applications, which often store regulated data such as personal identifiers, contact details, and financial attributes. In this context, static masking acts as a foundational control within broader data security strategies.
Once production datasets are copied into development, testing, analytics, or support environments, traditional access controls lose their effectiveness. At that point, permanent data transformation becomes the most reliable way to prevent exposure while still preserving schema integrity and relational consistency. This approach directly supports modern database security practices, where protection must persist even outside production boundaries. Percona Server for MySQL itself is commonly chosen for these scenarios due to its performance and enterprise features, as described in the official Percona Server documentation.
This article explains how static masking can be applied in Percona Server for MySQL using native SQL techniques, and how centralized platforms such as DataSunrise extend these capabilities with policy-driven, repeatable masking workflows aligned with modern data compliance requirements.
When Static Masking Is Required in Percona Server for MySQL
Percona environments often serve several operational purposes at the same time. A single database instance may support application debugging, quality assurance and regression testing, business analytics, data science experimentation, and routine support investigations. Although these activities rely on realistic schemas and data relationships, they do not require access to real personal or financial values. In practice, static masking becomes a key control within broader data security strategies that aim to reduce unnecessary exposure.
Once production data is reused outside its original environment, retaining original values introduces significant risks. Even when role-based permissions are enforced, copied datasets are often accessed by a wider range of users and stored in less controlled systems. At that stage, traditional access controls alone are no longer sufficient, which is why static masking is commonly applied as part of comprehensive database security practices.
Static masking becomes mandatory when production data is replicated into non-production environments, shared with third-party vendors or contractors, or used for testing and analytical workloads without a clear business need for real values. In addition, regulatory frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS explicitly require minimizing the use of real sensitive data outside production systems, aligning static masking with established data compliance principles.
Unlike dynamic masking, static masking permanently replaces sensitive values in the dataset. This irreversible transformation ensures that even if access controls fail or data is copied again, the original information cannot be recovered. As a result, static masking complements other protection mechanisms, including dynamic data masking, by removing exposure risks at the data level itself.
Native Static Masking Techniques in Percona Server for MySQL
Percona Server for MySQL does not include a built-in static masking engine. As a result, static masking is usually implemented through explicit SQL transformations executed against copied datasets in non-production environments. These operations permanently modify the data and are typically performed immediately after replication or export.
Column-Level Static Masking with UPDATE Statements
The most common static masking technique involves overwriting sensitive columns with deterministic or partially obfuscated values. This approach preserves schema structure and data types while removing real content.
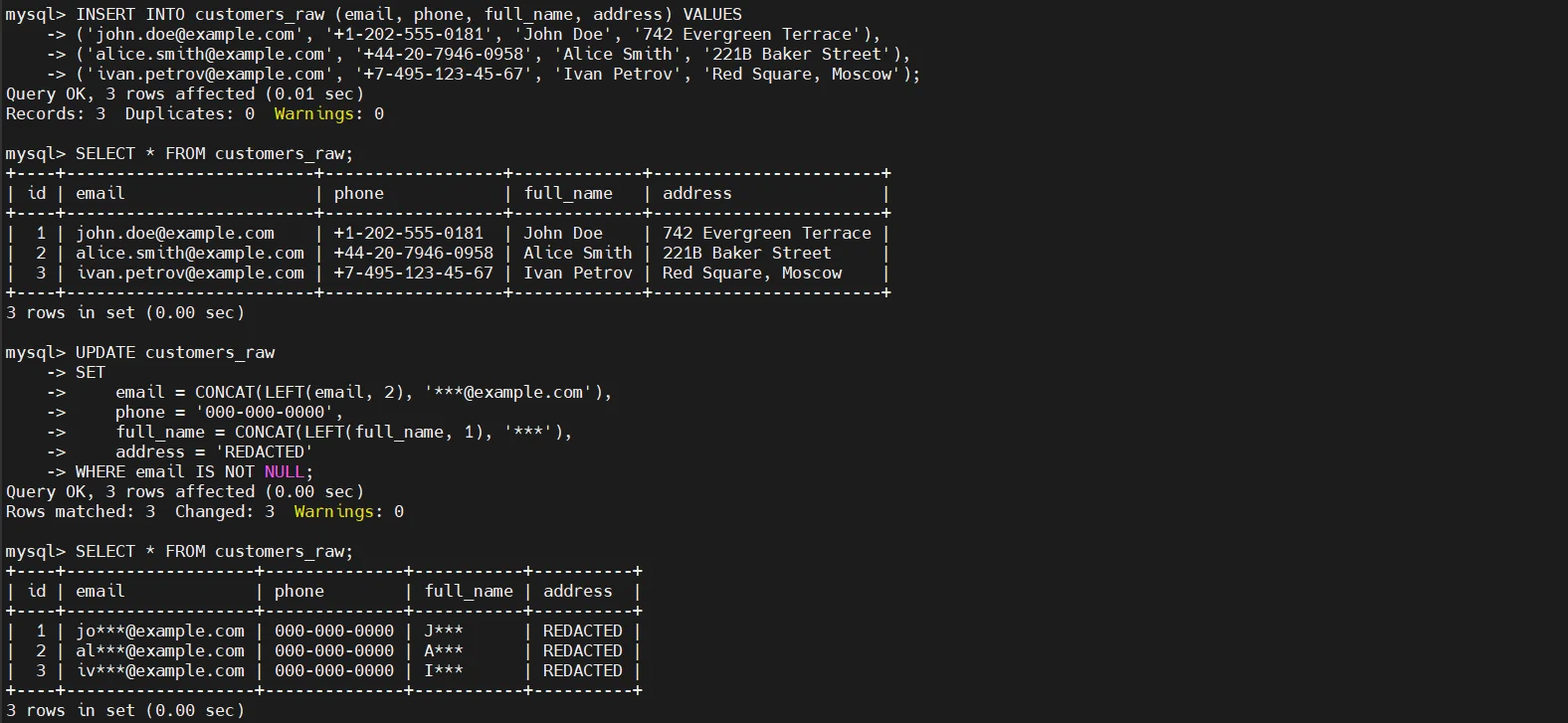
This method is simple and effective, but it permanently alters the dataset. Once executed, original values cannot be restored, which makes this approach suitable only for non-production copies.
Hash-Based Masking for Identifiers
When uniqueness and referential integrity must be preserved, hashing provides a reliable static masking technique. Hashed values remain consistent across tables, allowing joins and comparisons to continue functioning.
UPDATE users
SET
national_id = SHA2(national_id, 256),
passport_number = SHA2(passport_number, 256)
WHERE national_id IS NOT NULL;
Because hashing is one-way, original identifiers cannot be reconstructed, while relational logic remains intact across dependent tables.
Randomized Masking for Numeric and Date Fields
For financial amounts, metrics, or timestamps, randomization within controlled ranges helps maintain realistic data distributions without exposing real values.
UPDATE payments
SET
amount = FLOOR(RAND() * 1000) + 10,
tax_amount = FLOOR(RAND() * 200),
payment_date = DATE_SUB(
CURDATE(),
INTERVAL FLOOR(RAND() * 365) DAY
),
settlement_date = DATE_ADD(
payment_date,
INTERVAL FLOOR(RAND() * 5) DAY
);
This approach is commonly used in testing and analytics environments, where trends and distributions matter, but real transactional data does not.
Practical Considerations
While native SQL-based static masking offers flexibility, it requires careful coordination. Dependencies between tables must be handled manually, masking logic must be kept consistent across environments, and execution errors can easily lead to incomplete or broken datasets. As masking scope grows, these scripts become harder to maintain and govern.
Centralized Static Masking for Percona Server for MySQL with DataSunrise
DataSunrise introduces an external, policy-driven security layer that automates static masking without embedding transformation logic into SQL scripts or database objects. Instead of maintaining custom UPDATE statements or stored procedures, masking rules are defined centrally and executed consistently across environments. This ensures that the same transformation logic is applied every time production data is prepared for non-production use.
By externalizing masking logic, this approach aligns static masking with broader data security and database security strategies, where protection is enforced independently of application code and database schema design.
Sensitive Data Discovery and Classification
Before any masking operation begins, DataSunrise automatically scans Percona Server for MySQL schemas to identify sensitive data. The discovery process detects personally identifiable information, financial attributes, credentials, and other regulated data elements based on actual content patterns rather than column names or metadata alone. This capability builds on modern data discovery techniques that focus on real data content rather than schema assumptions.
Because discovery relies on content analysis, it remains effective even in poorly documented or inconsistently named schemas. As a result, sensitive fields are identified reliably before masking rules are applied, reducing the risk of accidental data exposure and strengthening overall data security controls.
- Automatic identification of PII, financial data, and credentials based on data content, aligned with PII protection practices
- Independence from column naming conventions or schema documentation quality
- Continuous discovery as schemas evolve over time
- Reduced risk of missing sensitive fields prior to masking
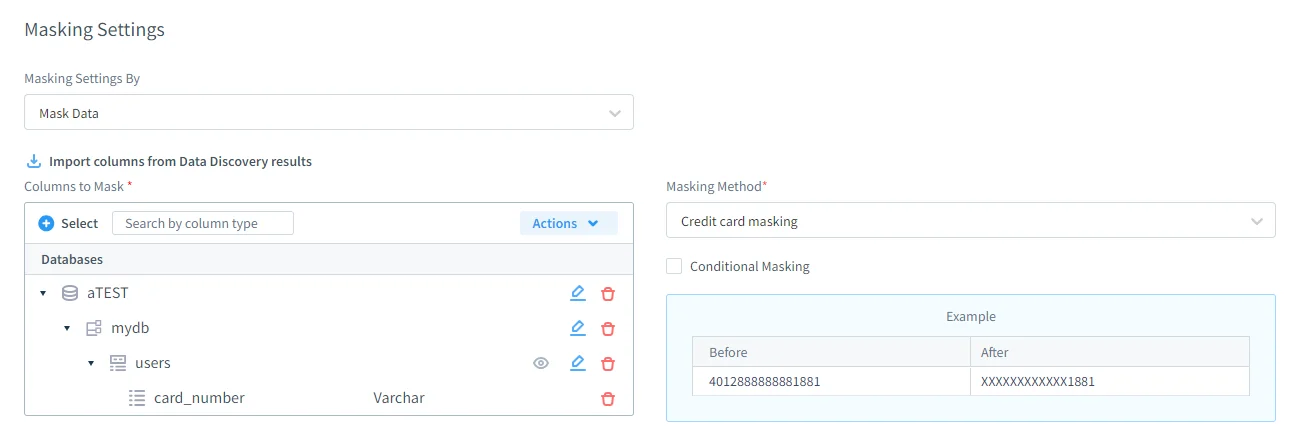
Defining Static Masking Rules
Static masking rules in DataSunrise provide fine-grained control over how data is transformed. Administrators can precisely define which databases, schemas, tables, and columns are subject to masking, as well as the masking method applied to each field. Supported techniques include substitution, hashing, randomization, and nulling, following established static data masking principles.
Importantly, masking rules can preserve referential integrity across related tables, ensuring that foreign key relationships remain valid after transformation. Rules are reusable and version-controlled, which eliminates the need for one-off SQL scripts and helps maintain consistency across multiple environments while supporting centralized database security policies.
- Centralized rule definition across databases and schemas
- Support for multiple masking techniques per data type
- Referential integrity preservation across related tables
- Version-controlled rules reusable across environments
Executing Static Masking Jobs
Once masking rules are configured, execution becomes a controlled operational process rather than a manual task. Static masking jobs can be run on demand, scheduled to execute automatically, or integrated into CI/CD and data provisioning pipelines. This operational model aligns with broader test data management practices used in modern DevOps workflows.
As a result, non-production environments receive consistently masked datasets without relying on manual SQL execution or ad-hoc scripting, reducing operational risk and human error while improving data management efficiency.
- On-demand execution for ad-hoc dataset preparation
- Scheduled masking for recurring refresh cycles
- Integration with CI/CD and data provisioning workflows
- Elimination of manual SQL-based masking steps
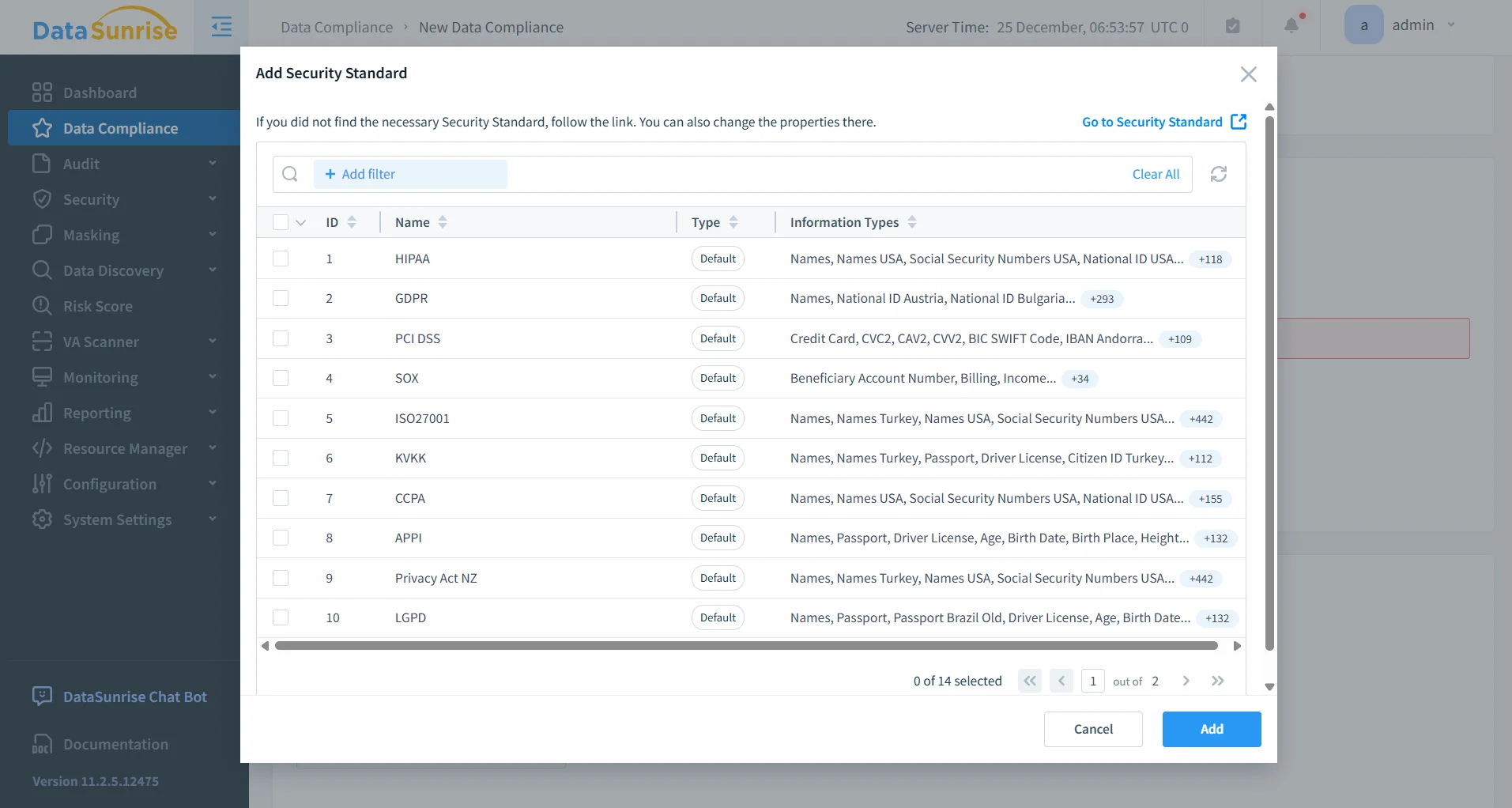
Auditability and Compliance Alignment
Every static masking operation performed by DataSunrise is logged and traceable. These records create a clear history of when masking was executed, which rules were applied, and which data assets were affected. This level of visibility directly supports structured data compliance programs.
By turning static masking into a documented, repeatable process, organizations move away from ad-hoc data handling and toward a governed compliance workflow that stands up to internal reviews and external audits, complementing centralized compliance management initiatives.
- Full traceability of masking operations and rule usage
- Alignment with GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX requirements
- Evidence-ready records for audits and compliance reviews
- Transition from ad-hoc masking to governed compliance processes
Business Impact of Static Masking in Percona Server for MySQL
| Business Area | Operational Impact |
|---|---|
| Data exposure risk | Reduced likelihood of sensitive data leakage outside production environments |
| Test data provisioning | Faster creation of compliant datasets for development, QA, and analytics |
| Audit readiness | Lower effort required to prepare evidence for security and compliance audits |
| Operational consistency | Uniform masking rules applied across teams and environments |
| Data sharing confidence | Safer collaboration with internal teams and external partners |
Static masking shifts the focus from restricting access to enabling secure and controlled data reuse, making non-production workflows both safer and more efficient.
Conclusion
Percona Server for MySQL provides the flexibility to implement static masking using native SQL techniques. These approaches are suitable for small, controlled scenarios where manual enforcement is acceptable and basic static data masking requirements can be met with custom scripts.
However, organizations that require scalable governance, consistency across environments, and audit-ready masking workflows benefit from centralized platforms such as DataSunrise. By formalizing static masking into structured policies rather than fragile scripts, sensitive data protection becomes predictable, repeatable, and compliant by design, strengthening overall data security posture.
Static masking stops being a workaround — and becomes an operational control.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now