
Types of Data Masking: How to Protect Sensitive Data

Introduction
Protecting sensitive data is a critical part of maintaining security and regulatory compliance. Data masking is the practice of hiding real data with fake but realistic values to reduce the risk of exposure in non-production and even production environments. This article explores the main types of data masking, common masking methods, and how dedicated platforms like DataSunrise provide flexible, secure, and scalable masking solutions.
Types of Data Masking
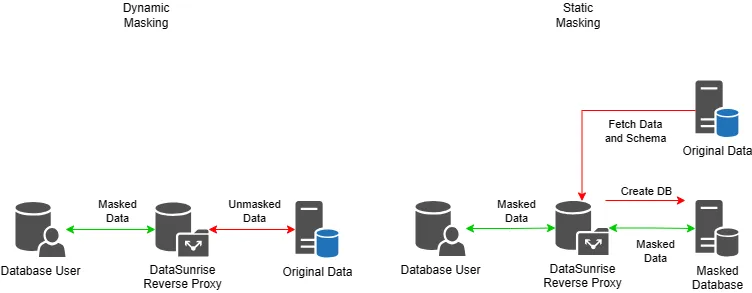
Static Data Masking (SDM)
Static Data Masking transforms data in-place or during export to create a sanitized version for use in test or development environments. It modifies sensitive data before it leaves the production system.
Example: Patient names and IDs in a healthcare dataset are replaced with fictitious values, allowing developers to use the dataset without exposing real personal information.
Dynamic Data Masking (DDM)
Dynamic Data Masking hides data at query time. The original data remains unchanged, but unauthorized users only see masked output based on their access level. This method works best in live environments where real-time protection is needed.
Example: A support agent queries a customer record, but sees only the last four digits of the customer’s phone number and an obfuscated email address.
In-Place Masking
This technique masks data directly in the production environment. While sometimes necessary, it introduces higher risk and should be used with caution. Unlike SDM, there’s no safe backup of the original values.
When and How Masking Happens
- Static masking: One-time masking applied before data leaves the production database.
- Dynamic masking: Real-time, rule-based masking at query execution, typically through a proxy.
Reversible vs. Irreversible Masking
- Reversible: Encryption or tokenization methods allow access to original values when necessary.
- Irreversible: Substitution or shuffling removes the ability to recover original data, ideal for dev/test.
Popular Data Masking Methods
Substitution
Replaces real values with fabricated ones that look realistic. Used when the data format must remain valid.
Original: John Doe Masked: James Smith
Shuffling
Randomizes the order of data within a column to maintain statistical properties without retaining actual values.
Original: Alice, Bob, Charlie Masked: Charlie, Alice, Bob
Encryption
Applies cryptographic algorithms to convert data into unreadable formats, reversible with a key.
Original: John Doe Masked: Xk9fTm1pR2w=
Tokenization
Replaces data with a token. The original data is stored securely in a token vault and retrieved via authorized access.
Original: 4111-1111-1111-1111 Masked: TOKEN12345
DBMS Tools vs Dedicated Masking Solutions
Some native DBMS platforms offer masking through views or stored procedures. While useful, these often lack flexibility, centralized management, and auditability.
| Feature | Native DBMS Tools | DataSunrise |
|---|---|---|
| Technique Variety | Basic substitution/view masking | Substitution, tokenization, FF3 encryption, conditional masking |
| Dynamic Masking | Rare or complex to implement | Built-in proxy-based DDM with rule engine |
| Audit & Logging | Manual | Centralized logs, masking audit per user/query |
| Policy Management | Scattered across scripts and views | Centralized via GUI or CLI |
| Multi-DB Support | Limited to vendor | Works across MS SQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, etc. |
Masking with DataSunrise
DataSunrise supports both static and dynamic masking with granular control. The Web UI and CLI offer flexibility for enterprise teams, test engineers, and DevOps pipelines alike.
Dynamic Masking via CLI
executecommand.bat addMaskRule -name script-rules -instance aurora \ -login aurorauser -password aurorauser -dbType aurora -maskType fixedStr \ -fixedVal XXXXXXXX -action mask \ -maskColumns 'test.table1.column2;test.table1.column1;'
This rule replaces specified columns with fixed values during runtime without altering the data at rest.
Conclusion
Data masking plays a vital role in protecting personal and regulated data in test, development, and production environments. Choosing the right type—static or dynamic—depends on your use case, compliance needs, and operational model.
While native tools can provide basic coverage, they fall short for modern enterprises that require cross-platform, audited, and policy-driven data protection. DataSunrise offers a mature, scalable masking solution with support for multiple masking techniques and seamless integration across environments.
Request a demo to explore how DataSunrise can help secure your sensitive data and enforce masking policies across your organization.
