What Is IBM Db2 Audit Trail
Introduction — A Record That Tells a Story
Every action in a database tells part of a larger story. When users connect, modify tables, or adjust permissions, these traces form a continuous thread known as an audit trail. In IBM Db2, the audit trail is more than a simple log file — it is a verified record of how the system has been used, by whom, and under what context.
An IBM Db2 audit trail is a chronological record of events within the database engine. It documents activities such as user authentication, schema changes, privilege grants, and data manipulation. Administrators rely on it to identify suspicious actions, validate change history, and ensure compliance with internal and external regulations.
Unlike an audit log, which might represent a single event or transaction, an audit trail maintains the complete narrative. It allows Db2 administrators to reconstruct past activities, proving accountability and preserving data integrity across regulated environments.
Why Db2 Audit Trails Are Critical
A well-maintained audit trail transforms raw data events into actionable security insight. For organizations working with sensitive or regulated information, it serves several key purposes:
- Accountability – Every modification can be traced back to an authenticated user or process.
- Compliance – Regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS require accurate records of system activity.
- Forensics and Investigation – When anomalies or incidents occur, audit trails enable detailed reconstruction.
- Integrity Assurance – Detect unauthorized changes or policy violations early.
IBM Db2 supports these principles through a built-in auditing system designed to capture events across the database engine. For full implementation details, refer to IBM’s Security and Auditing documentation.
Inside the Native IBM Db2 Audit Trail
IBM Db2 includes a dedicated tool called db2audit, which manages audit trail configuration and data extraction. This facility records both instance-level and database-level activity, creating a comprehensive sequence of operations.
Main Audit Categories
Db2 administrators can choose which types of actions to monitor:
- SECMAINT – Security-related changes, such as user creation or privilege alteration.
- OBJMAINT – Object maintenance activities like table creation, deletion, or modification.
- CHECKING – Authorization checks performed when users attempt to access protected resources.
- CONTEXT – Session details, including client connection parameters and timestamps.
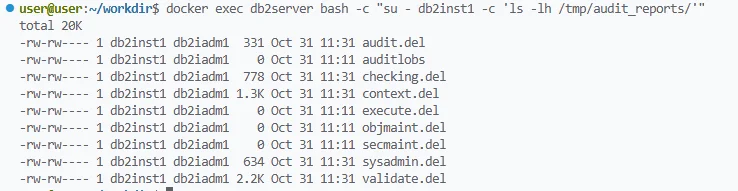
Configuration and Extraction Example
The db2audit utility lets administrators enable, control, and review audits with precision.
db2audit configure scope all status both
db2audit start
db2audit extract delasc to /audit/reports
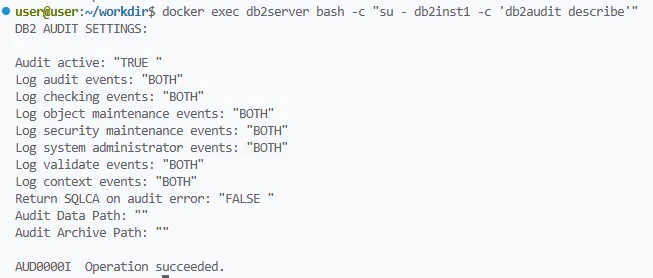
The configuration above enables full auditing, starts the process, and extracts results into a readable format. For reference, IBM provides detailed syntax and options in its Audit Facility command guide.
Schedule regular extraction and archiving of Db2 audit files to avoid overwriting or performance issues during peak activity.
Interpreting and Managing the Audit Trail
Once audit data is generated, it resides in binary form under the Db2 instance directory. Administrators use db2audit extract to convert these records into human-readable files. The extracted reports contain vital details such as:
- Executed SQL statements
- Affected objects
- User IDs and application names
- Connection timestamps
- Access outcomes (success or failure)
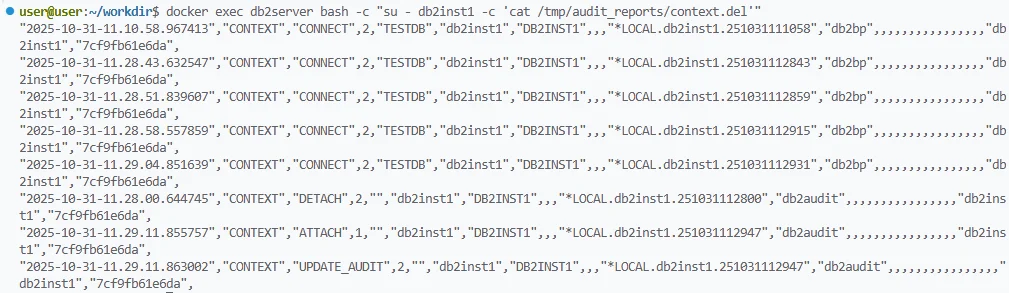
Effective management involves automating extraction, rotating archives securely, and periodically reviewing records for anomalies.
| Strength | Limitation |
|---|---|
| Integrated into Db2 engine | Manual extraction required |
| Category-based precision | No built-in visualization |
| Binary log integrity | Resource overhead on large systems |
| Fine-grained control | Limited correlation across instances |
These constraints are common across native database auditing tools — they provide complete raw data but lack centralized context, automation, and real-time response.
Beyond Native Auditing — Extending Db2 with DataSunrise
While db2audit provides essential insight into what happens within Db2, large infrastructures often involve multiple databases, applications, and storage systems. Managing these independently can become cumbersome.
DataSunrise extends Db2’s native auditing with centralized visibility, analytics, and automation.
DataSunrise integrates with Db2 through either proxy mode or native log trailing mode, capturing audit events in real time. It transforms raw audit trails into correlated, compliance-ready intelligence. Key capabilities include:
- Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts – Detect and respond to unusual query behavior instantly.
- Machine Learning Audit Rules – Identify anomalies in query frequency or access patterns.
- Unified Audit Dashboard – Consolidate activities from Db2 and other data platforms.
- Automated Compliance Reports – Generate audit-ready evidence aligned with frameworks such as SOX, HIPAA, or GDPR.
When integrating Db2 with DataSunrise, use proxy mode for maximum visibility and real-time analytics; use native log trailing mode when minimal intrusion is required.
This integration turns audit data into a dynamic control mechanism rather than a static record, allowing teams to react immediately to policy breaches or suspicious user actions.
Example: Configuring Audit Trails for Db2 in DataSunrise
Audit configuration in DataSunrise is performed through its graphical interface rather than command-line utilities. The workflow builds directly on Db2’s audit data but adds automation and visual analytics.
Typical workflow:
Connect IBM Db2 through the DataSunrise proxy or log trailing mode.
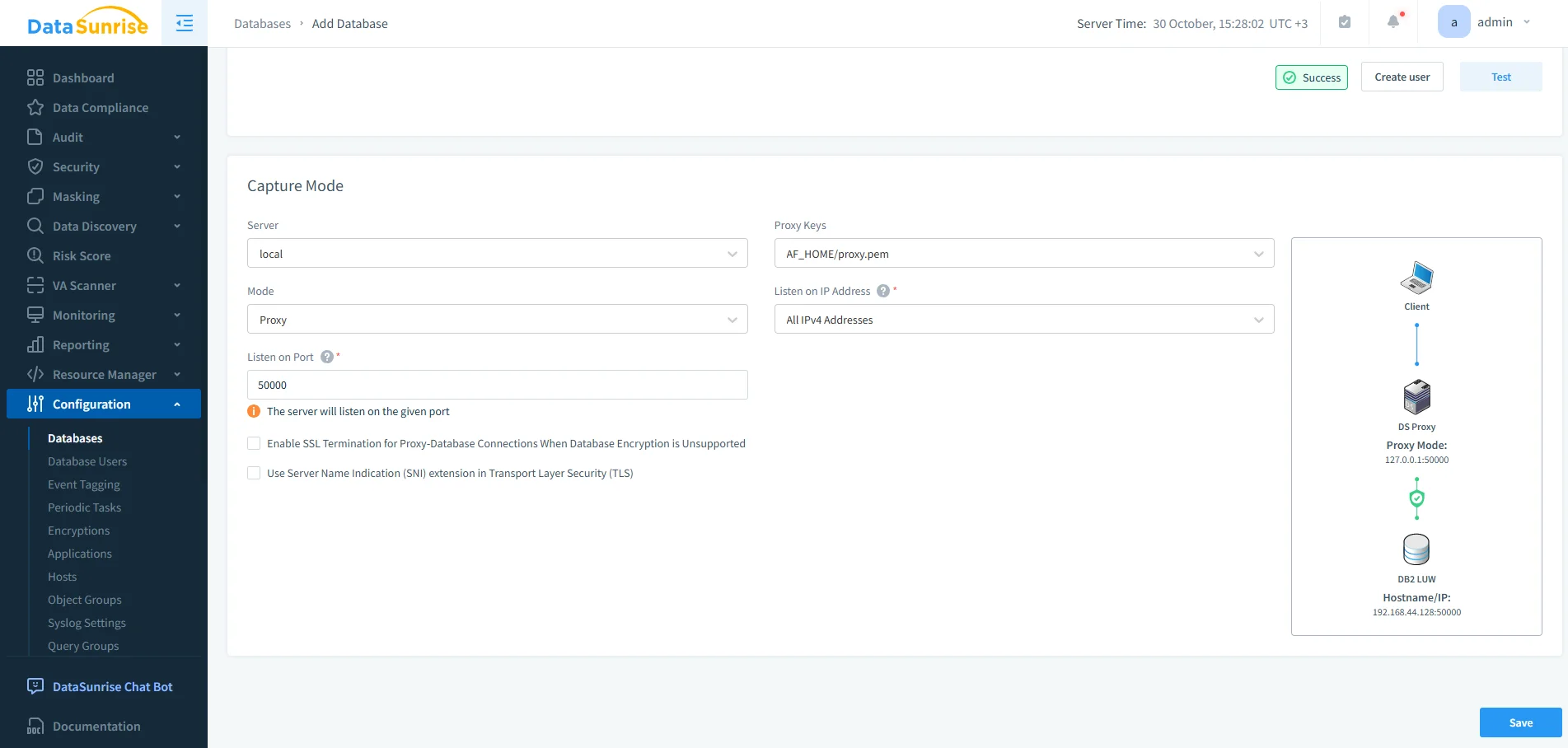
Configuring IBM Db2 in DataSunrise using Proxy mode with SSL key settings and a defined listener port for encrypted traffic monitoring. Open the Audit Module from the main dashboard and create a new rule.
Select Target Objects (schemas, tables, or databases) to monitor.

Creating a new Db2 audit configuration in DataSunrise, binding the Db2 LUW instance to an audit rule for continuous activity collection. Choose Operations to track — for example, SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, or DDL actions.
Define Conditions such as specific users, roles, or client IPs.
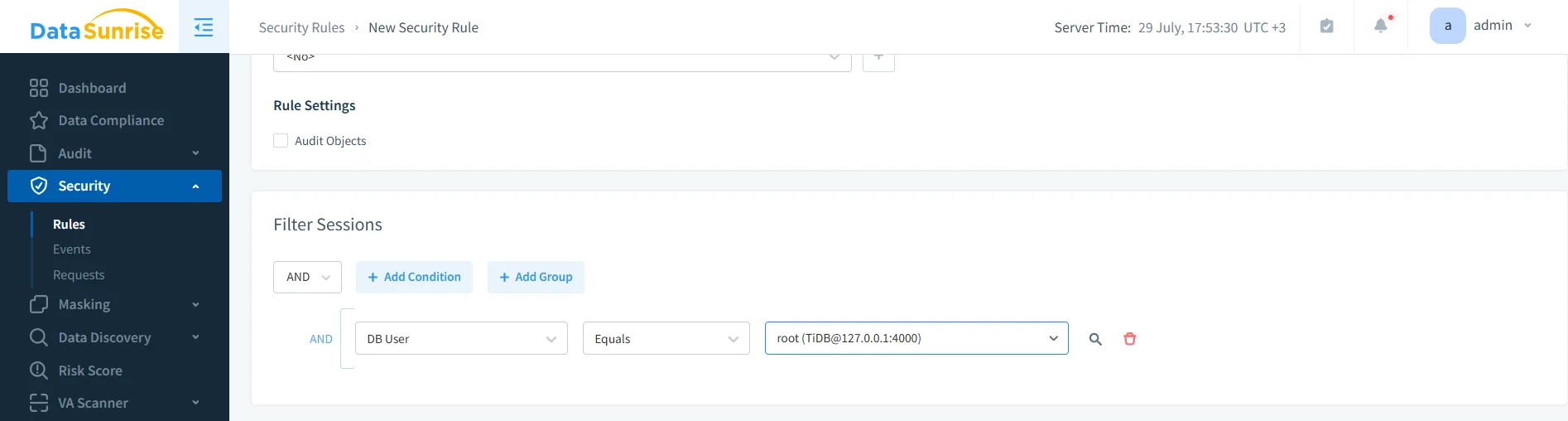
Building a DataSunrise security rule to audit sessions filtered by database user, illustrating fine-grained session monitoring setup. Enable Notifications or Forwarding to SIEM systems for real-time alerting.
Activate the Rule to begin collecting and correlating events.
After activation, DataSunrise displays all relevant Db2 activity in its unified dashboard. Administrators can search and filter records, correlate activity by user or object, and export reports directly in PDF or CSV formats.
This approach significantly reduces manual effort compared to parsing native logs while providing a continuous compliance view across multiple environments.
Compliance and Business Outcomes
Maintaining an audit trail isn’t only about technical accountability — it’s a business necessity. When organizations integrate Db2 with DataSunrise, they strengthen compliance alignment and reduce audit preparation time.
| Aspect | Native Db2 | Db2 + DataSunrise |
|---|---|---|
| Log management | Manual extraction | Centralized, automated |
| Alerting | Limited to manual review | Real-time ML-driven alerts |
| Reporting | Text-based output | Compliance-ready visual reports |
| Multi-database view | Single-instance | Unified across platforms |
By automating policy monitoring and evidence generation, DataSunrise ensures consistent regulatory alignment and minimizes operational risk. It also aligns with IBM’s security framework described in the Db2 Compliance documentation.
Conclusion — Building an Enduring Record
The IBM Db2 audit trail is a core mechanism for ensuring integrity and transparency within enterprise databases. It records every significant event, creating a verifiable chain of accountability that protects both data and reputation.
Yet, as data ecosystems expand, manual audit management becomes impractical. With DataSunrise, organizations can extend Db2’s native capabilities — transforming static audit trails into proactive compliance intelligence. The result is stronger governance, faster incident response, and a clearer view of every data interaction.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now