Amazon OpenSearch Audit Trail
Amazon OpenSearch audit trail becomes relevant when a cluster stops being used only for logging and starts serving as a source of business and security data. In a typical production environment, the same OpenSearch domain receives queries from application services, BI dashboards, support teams, and automated processes. These requests often hit the same indices and APIs, even though the users and systems behind them have different roles and intentions.
If teams do not maintain an audit trail, service logs scatter activity and fail to provide a coherent picture. During an incident, teams must reconstruct events indirectly: who accessed an index, which endpoint they used, whether they modified data, and what occurred within the same session. When OpenSearch stores customer identifiers, access logs, or security events, this approach quickly becomes unreliable.
Why an audit trail matters for Amazon OpenSearch
Amazon OpenSearch is not a relational database, but it stores persistent data and executes structured operations on that data. Clients create indices, update documents, run searches, and retrieve results that may include sensitive fields. From a governance perspective, these actions fall under the same audit expectations applied to databases.
Several factors make OpenSearch auditing different from auditing SQL-based systems:
-
API-based data access
Most OpenSearch operations arrive as HTTP requests with JSON payloads. Index management, document updates, and search operations rely on REST endpoints rather than SQL statements. An audit trail that only understands SQL will miss critical control-plane and data-plane activity. -
Many consumers in the same cluster
A single OpenSearch cluster often supports both production workloads and temporary access. Without an audit trail, teams struggle to separate normal application traffic from misconfigured jobs, support investigations, or index scans. -
Batch operations change large volumes
Bulk indexing and bulk update operations can modify large sets of documents in a single call. When issues occur, teams need the session context of the request, not just confirmation that a request happened. -
Regulated data ends up in indices
Once indices contain identifiers, IP addresses, customer records, or security incidents, access and modification history falls under GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX audit requirements.
Amazon OpenSearch audit log architecture
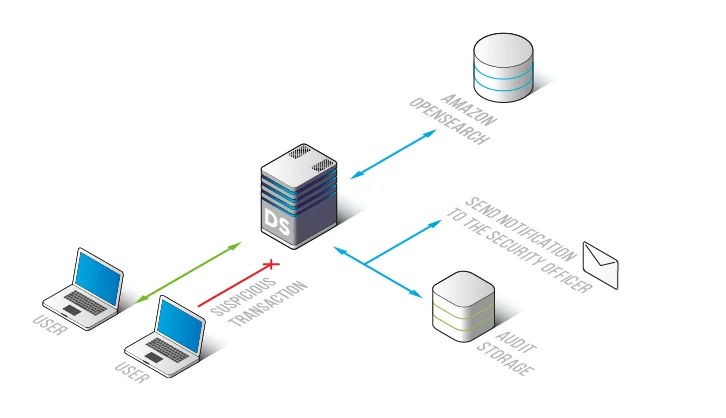
DataSunrise implements an Amazon OpenSearch audit log by placing a transparent control layer between client applications and the OpenSearch service. Requests pass through the DataSunrise layer, where the system evaluates operations and records audit events according to defined policies. This design avoids changes to OpenSearch indices and application code.
This traffic-based approach fits broader database activity monitoring workflows and lets teams review activity across users, endpoints, indices, and time ranges.
Each request becomes an audit record that teams can filter by user, index, action type, timestamp, and rule context. This filtering makes the audit log practical for incident investigation and compliance verification.
Defining audit logging rules for Amazon OpenSearch
An audit log is only effective when teams define clear rules for what the system records. DataSunrise uses rule-based auditing to track OpenSearch activity and store it in a consistent format.
Typical rule inputs include index or index pattern, HTTP method, user or service account, and source network. Rules can also capture session context and execution outcomes.
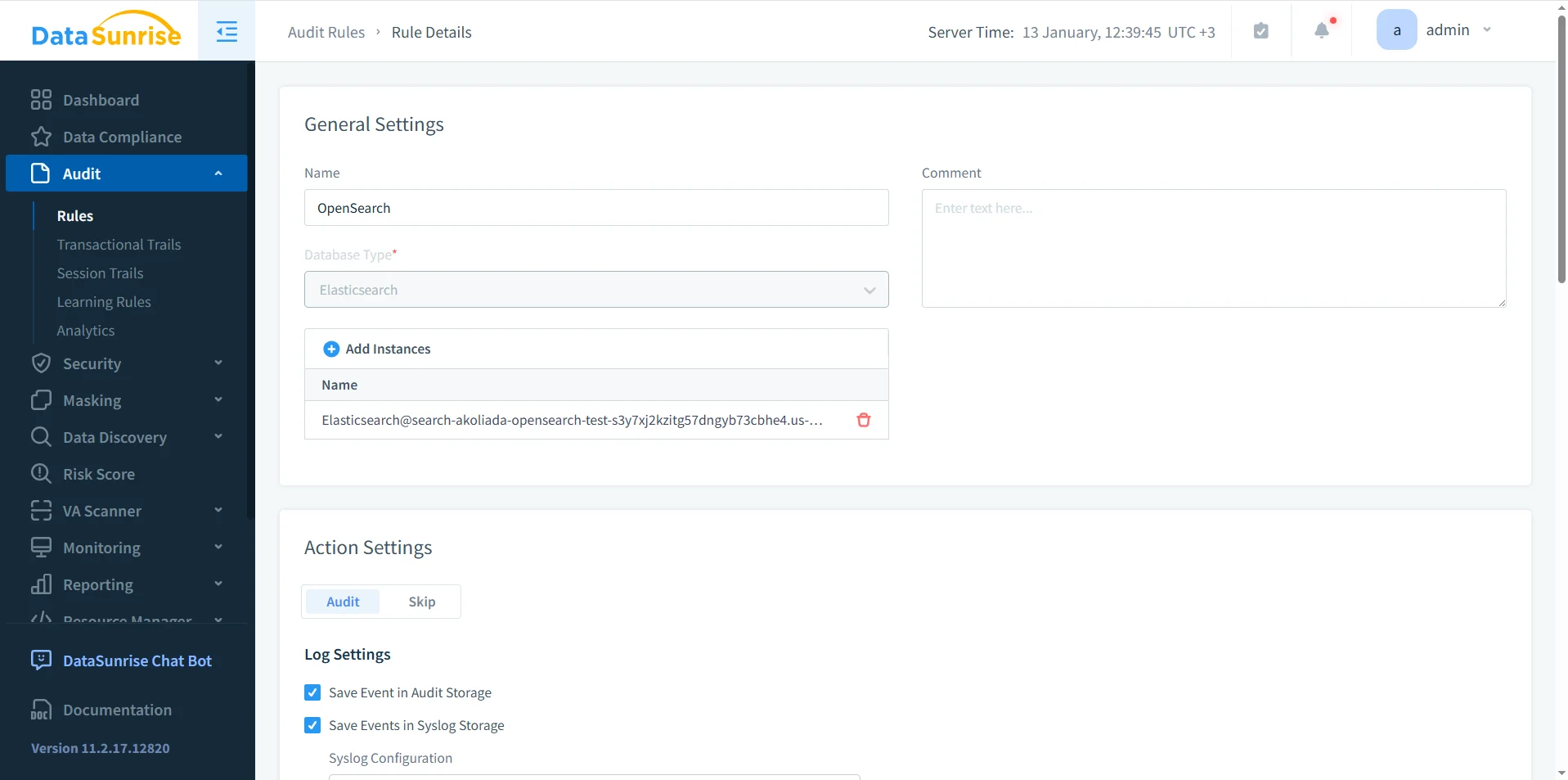
Rule prioritization allows stricter auditing for sensitive indices while reducing noise from low-risk operational traffic. In high-volume OpenSearch environments, this distinction determines whether audit data remains usable.
Transactional audit log and session context
After teams enable audit rules, DataSunrise records activity in transactional audit trails. Instead of treating each request as an isolated event, the system groups related actions into sessions and transactions.
This grouping changes how teams investigate incidents. Teams can review sessions that executed multiple searches, followed by bulk updates, before closing. This approach provides a clear sequence of actions rather than relying solely on timestamps.
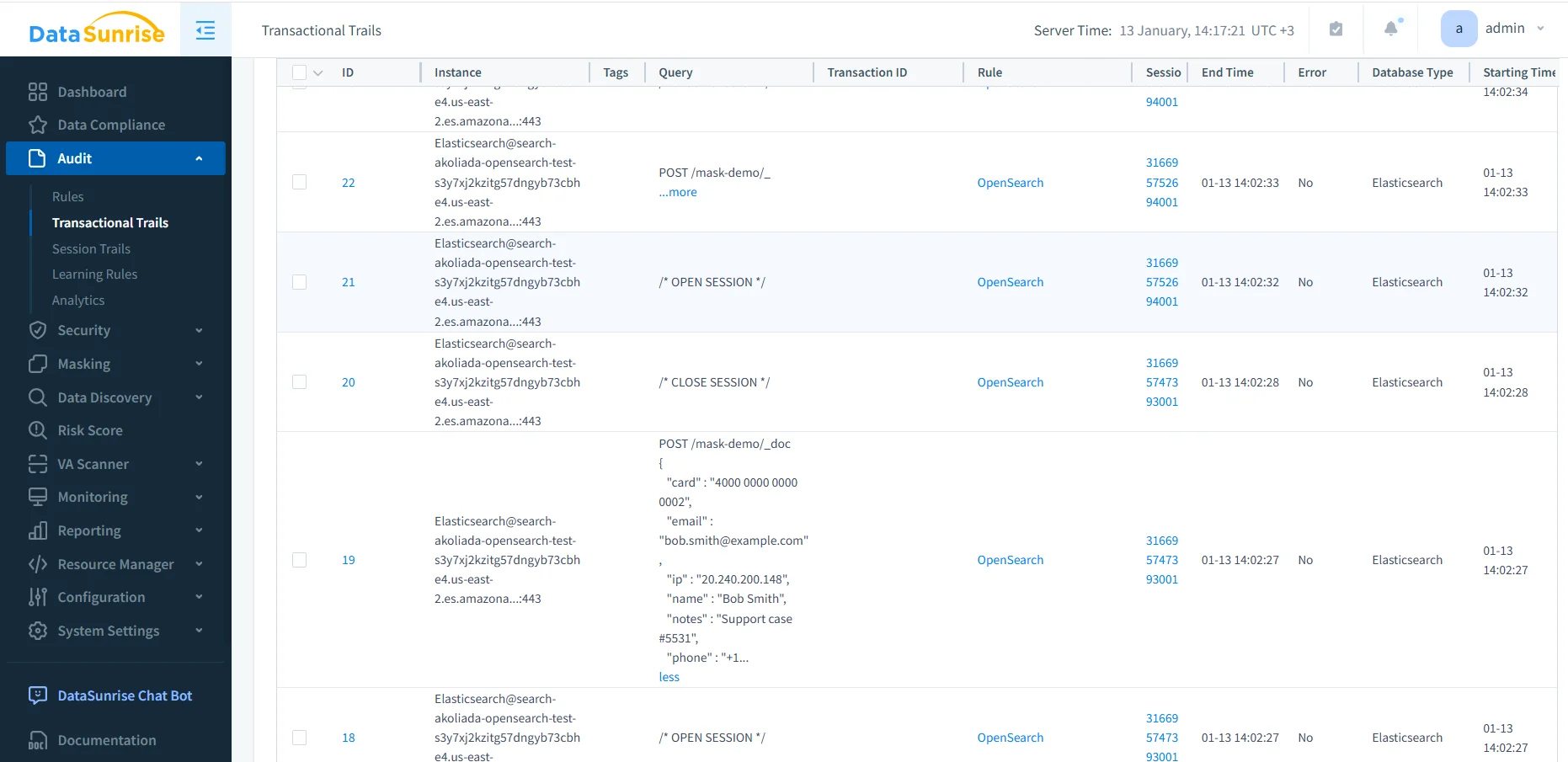
Each audit log entry typically includes:
- OpenSearch endpoint and index name
- HTTP method and request type
- Session and transaction identifiers
- Source IP address and user context
- Timestamps, execution time, and error status
This level of detail supports incident response, internal investigations, and compliance evidence collection.
Content collected using the Amazon OpenSearch audit log
Amazon OpenSearch audit log coverage includes index creation and deletion, configuration changes, document insert, update, and delete operations, search and aggregation queries, bulk requests, session open and close events, and failed or rejected operations.
Teams can store audit log data locally or forward it to external systems and integrate it into centralized data security workflows.
Start with bulk operations and access to indices that contain regulated fields. These events provide the highest investigation value with less noise than blanket logging.
Audit log and security controls
The audit log also acts as a control surface. By observing which endpoints identities use, teams can detect patterns such as repeated scans, unintended exports, or service accounts invoking administrative endpoints from new network segments.
DataSunrise can combine audit logs with security rules and behavior-based detection to flag suspicious OpenSearch activity early and route it into established investigation workflows.
Compliance adjustment and audit evidence
If regulated data is indexed, organizations must produce evidence that shows traceable access and modification. DataSunrise correlates audit log records with compliance workflows for GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX. Teams can generate reports using report generation when they need audit evidence.
| Regulation | Audit trail requirement | DataSunrise support |
|---|---|---|
| GDPR | Tracking access to personal data | Searchable audit trails with retention controls |
| HIPAA | Monitoring access to protected health data | Session-based audit log entries |
| PCI DSS | Logging access to payment-related data | Immutable audit storage and reporting |
| SOX | Accountability for administrative actions | Change tracking and compliance reporting |
Automated workflows through the Compliance Manager reduce manual effort when teams need repeatable audit evidence.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now