Amazon OpenSearch Data Activity History
Amazon OpenSearch Data Activity History is a core visibility layer for organizations that use Amazon OpenSearch to store, analyze, and search operational telemetry, application logs, and event-driven data. In practice, OpenSearch clusters often ingest sensitive attributes such as user identifiers, IP addresses, timestamps, request metadata, and structured application payloads. Each indexing or search request therefore represents a concrete data access event that must be traceable.
Unlike relational databases, OpenSearch does not operate with persistent SQL sessions or transactional query contexts. Instead, it exposes REST endpoints that accept stateless HTTP requests. Applications, log shippers, and automation tools may generate thousands of such requests per minute, often on behalf of multiple users or backend services. As a result, traditional database activity tracking models fail to provide sufficient context or continuity.
Amazon OpenSearch Data Activity History addresses this gap by recording how data is written, queried, and accessed over time while preserving request context and execution order. This article explains how DataSunrise implements data activity history for OpenSearch, focusing on rule definition, live traffic capture, transactional correlation, and validation of recorded actions.
Why Data Activity History Matters in Amazon OpenSearch
OpenSearch clusters typically operate behind application services, log collectors, SIEM pipelines, or data ingestion frameworks. Requests arrive through REST endpoints and frequently represent business actions rather than direct user queries. For example, a single API call from an application may result in multiple index writes, updates, or search operations executed by OpenSearch.
Because these interactions are stateless and distributed, relying solely on native OpenSearch logs makes it difficult to reconstruct who accessed which data and in what sequence. This limitation becomes critical during incident investigations, access reviews, or regulatory audits, where organizations must demonstrate a complete and consistent history of data activity.
This architecture introduces several challenges when tracking data activity:
- REST requests lack session-based execution context
- Single user actions may trigger multiple API calls
- Indexing and search operations occur continuously
- Native logs do not provide end-to-end activity correlation
Without centralized database activity monitoring, reconstructing historical data access becomes unreliable.
Defining Data Activity Rules for OpenSearch
Amazon OpenSearch Data Activity History in DataSunrise starts with explicit activity rules that define the scope and depth of monitoring. These rules specify which OpenSearch instances are subject to monitoring, which HTTP methods and endpoints are captured, and how recorded activity is stored and retained.
Unlike basic logging, activity rules allow organizations to control monitoring granularity. For example, teams may choose to track only write operations on sensitive indices, administrative API calls, or access originating from specific network segments. This selective approach ensures that activity history remains actionable without overwhelming storage or analysis pipelines.
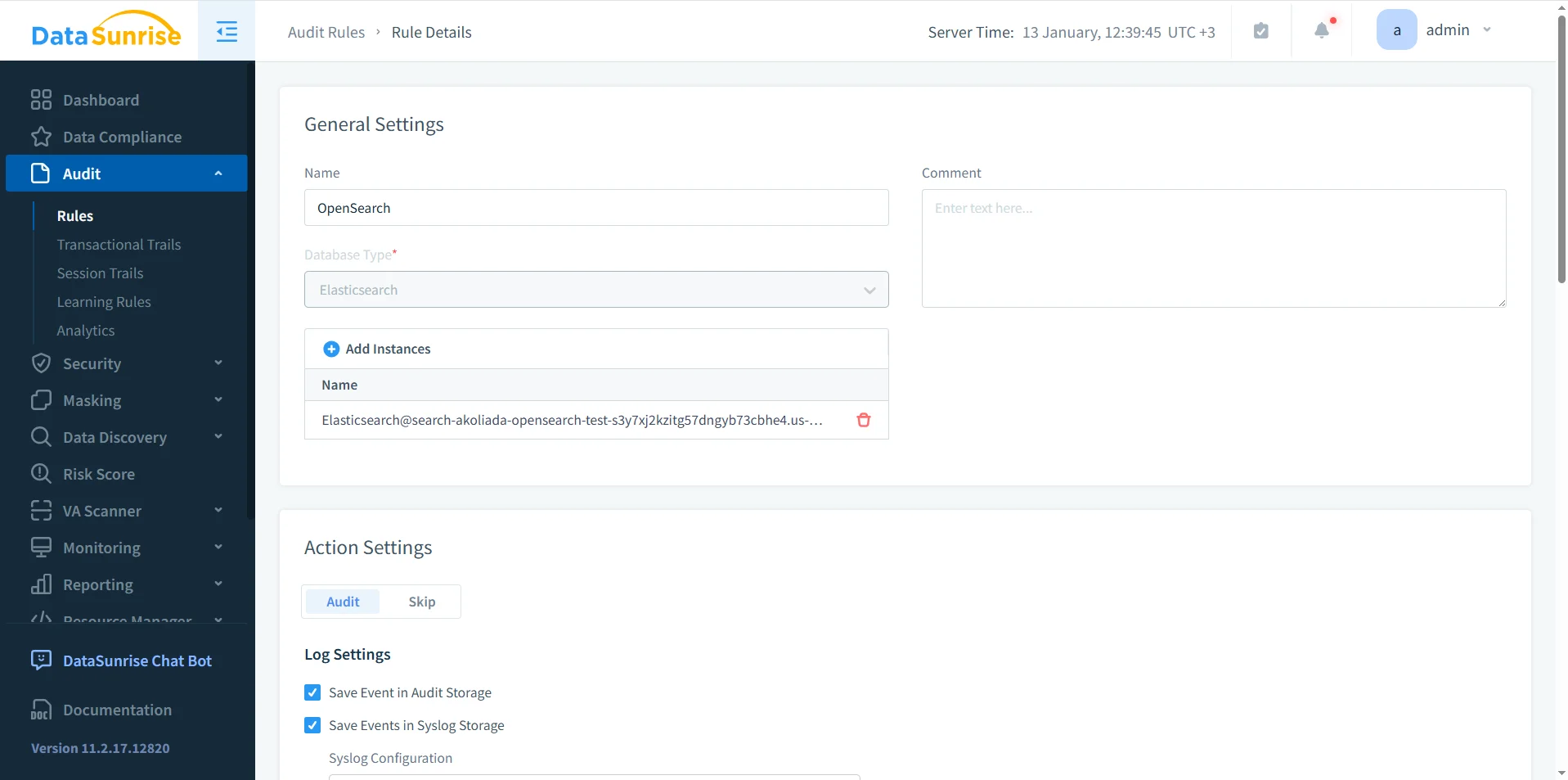
Rule evaluation follows the rules priority model, which ensures predictable enforcement even in complex environments with overlapping policies.
Capturing Real OpenSearch Data Activity
Once activity rules are enabled, DataSunrise begins capturing live OpenSearch traffic transparently. This includes document indexing, updates, deletions, and search operations executed by applications or automated services. Each captured request is enriched with contextual metadata such as source address, request timing, operation type, and target index.
For example, when an application sends a document indexing request, DataSunrise records the full interaction as part of the OpenSearch data activity history, even though OpenSearch itself treats the request as a stateless operation.
Example: Writing Data to OpenSearch
curl -X POST "http://localhost:9201/audit-demo/_doc" \
-H "Host: search-your-opensearch-domain.us-east-2.es.amazonaws.com" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"user": "alice",
"action": "login",
"ip": "10.0.0.5",
"timestamp": "2026-01-13T09:35:00Z"
}'
This request is intercepted by DataSunrise and stored as a structured activity record, including client identity, request timing, and operation type.
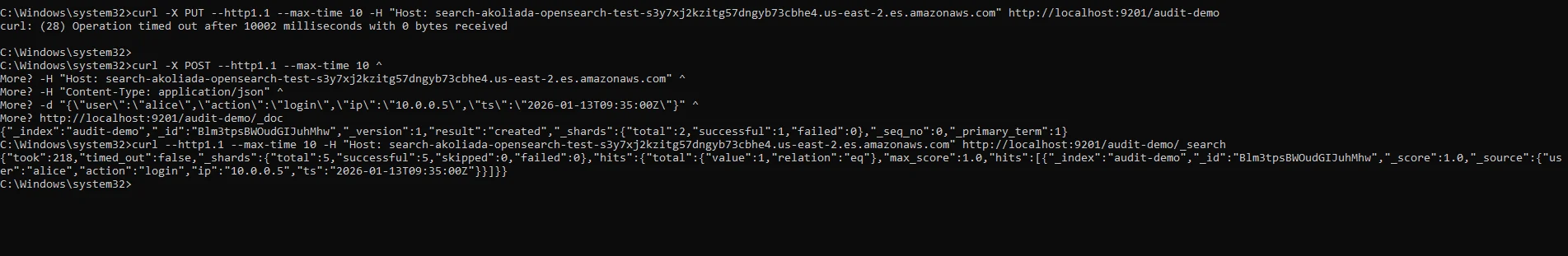
Unlike native OpenSearch logs, DataSunrise preserves contextual metadata required for historical analysis, investigation, and audit reconstruction.
Session-Level Activity and Transactional Correlation
By default, OpenSearch processes each REST request independently and does not maintain session context across operations. This design improves scalability but complicates historical analysis. During investigations, security teams often need to understand the full sequence of operations triggered by a single user or service.
DataSunrise resolves this limitation by correlating related REST requests into logical activity sessions and transactional trails. Correlation is based on connection metadata, timing, and request attributes, allowing analysts to trace a complete interaction chain rather than isolated events.
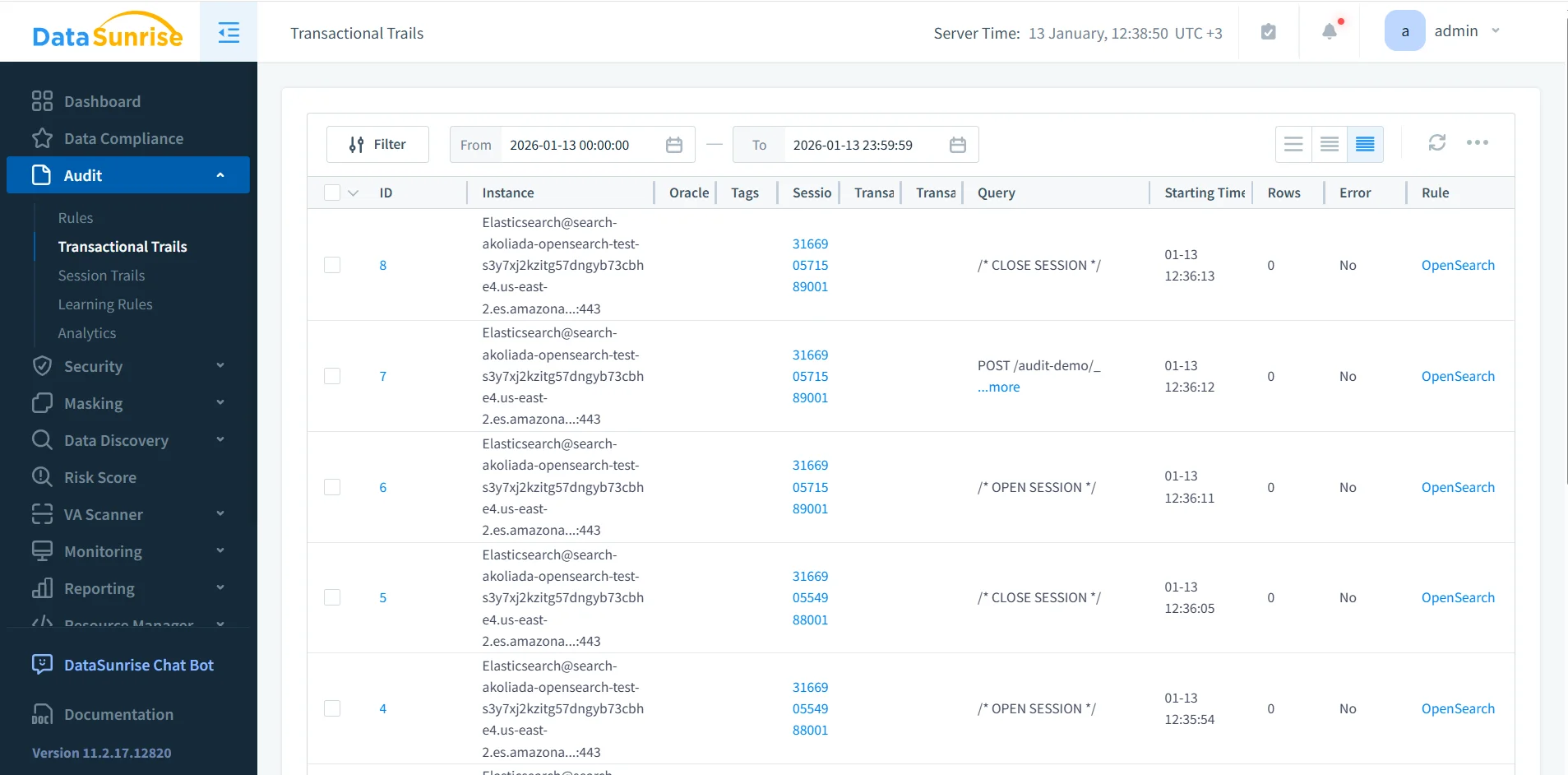
Session-aware correlation significantly improves incident response, root-cause analysis, and long-term activity auditing.
Verifying Data Activity History Inside OpenSearch
Data activity history provides value only when recorded events accurately reflect real data changes. Verification ensures that captured activity corresponds to actual indexing and search operations executed by OpenSearch.
In practice, verification involves confirming that documents referenced in activity records exist in the target index and match the recorded request parameters. This step is especially important during audits.
Example: Querying Indexed Activity Data
curl -X GET "http://localhost:9201/audit-demo/_search" \
-H "Host: search-your-opensearch-domain.us-east-2.es.amazonaws.com" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"query": {
"match": {
"user": "alice"
}
}
}'
This query confirms that the indexed document exists and aligns with the captured data activity record.
Operational Visibility: Native Logs vs Data Activity History
| Capability | Native OpenSearch Logs | DataSunrise Activity History |
|---|---|---|
| Request visibility | Basic REST metadata | Full request context with client attribution |
| Session correlation | Not supported | Transactional activity trails |
| Historical analysis | Limited | Queryable activity history |
| Retention control | Cluster-dependent | Centralized storage with retention policies |
Compliance Use Cases for Data Activity History
Many OpenSearch deployments process regulated data, which makes data activity history essential for compliance and audit readiness.
| Regulation | Activity Tracking Requirement | How DataSunrise Supports It |
|---|---|---|
| GDPR | Track access to personal data | Centralized activity history and retention control |
| HIPAA | Monitor access to healthcare-related data | Session-aware activity reporting |
| PCI DSS | Record access to payment-related events | Granular activity rules and evidence generation |
| SOX | Accountability for system interactions | Immutable transactional activity records |
When working with high-volume OpenSearch clusters, begin with activity rules that focus on sensitive indices and administrative endpoints. Expand coverage gradually to balance performance with historical visibility.
Conclusion: Building Reliable OpenSearch Data Activity History
Amazon OpenSearch delivers powerful search and analytics functionality, but it does not provide a complete, context-aware data activity history by default. Native logs capture isolated events but lack session awareness, correlation, and long-term analytical consistency.
By introducing an external activity tracking layer, DataSunrise converts OpenSearch interactions into structured, verifiable data activity history. This approach supports investigations, compliance audits, and long-term operational governance without disrupting existing workflows.
As OpenSearch adoption grows, organizations that treat data activity history as a core infrastructure component gain stronger visibility, improved security posture, and clearer regulatory confidence.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now