Amazon Redshift Audit Log
Amazon Redshift is widely used for large-scale analytical workloads, supporting BI dashboards, ETL pipelines, and data science queries across distributed clusters. As Redshift environments grow and become shared across teams, applications, and automated services, organizations must maintain reliable visibility into how data is accessed and modified. This requirement makes a structured Amazon Redshift audit log a foundational element of security, governance, and regulatory compliance, closely tied to broader practices such as database activity monitoring and data activity history.
Unlike transactional databases, Redshift executes queries across multiple compute nodes and maintains metadata in a combination of system tables and service logs. While these records contain valuable information, they are not designed to function as a complete audit log on their own. Reconstructing a clear sequence of events, correlating users to actions, and proving compliance often requires additional processing and correlation, especially in environments subject to strict data compliance regulations.
This article explains how Amazon Redshift audit logging works, referencing native capabilities described in the official Amazon Redshift documentation, and shows how centralized audit platforms extend Redshift audit logs into a complete, compliance-ready audit trail aligned with modern database audit trail requirements.
Importance of Audit Log
In analytical platforms like Amazon Redshift, data is often accessed by many users, services, and automated pipelines simultaneously. Queries may be generated by BI tools, scheduled jobs, machine learning workloads, or ad-hoc user activity. Without a reliable audit log, it becomes difficult to understand who accessed specific data, how it was used, and whether that access aligned with internal policies or regulatory requirements. This challenge becomes even more pronounced in environments that rely on continuous database activity monitoring to maintain visibility across distributed systems.
An audit log plays a critical role in establishing accountability. It allows organizations to trace database actions back to individual users or applications, making it possible to investigate incidents, validate proper data usage, and resolve disputes related to unauthorized access or unexpected data changes. In practice, this level of traceability is a core objective of a well-defined database audit trail.
Audit logs are also essential for operational visibility. When performance issues, data anomalies, or unexpected schema changes occur, audit records help teams reconstruct the sequence of events that led to the issue. This visibility reduces troubleshooting time and supports faster root-cause analysis in complex, distributed environments where maintaining a consistent data activity history is critical.
From a compliance perspective, audit logs serve as formal evidence during internal reviews and external audits. Regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX require organizations to demonstrate control over data access and processing. A well-maintained audit log provides the historical proof needed to show that sensitive data was accessed appropriately and monitored consistently.
In large-scale Redshift deployments, the audit log is not just a security artifact. It becomes an operational and governance tool that supports trust, transparency, and long-term control over analytical data platforms.
Native Amazon Redshift Audit Logging Capabilities
Amazon Redshift provides several native mechanisms for collecting audit-relevant data across query execution, user access, and administrative activity. These mechanisms expose low-level telemetry that can be used to reconstruct database activity, analyze usage patterns, and support security reviews. However, the data is distributed across multiple sources, each capturing a specific aspect of system behavior.
System Tables and Views
Redshift stores detailed historical information about queries, users, and sessions in internal system tables and views. These tables form the primary source of native audit visibility and are commonly queried for activity analysis and investigations.
Query Execution and Session Activity
The STL_QUERY table captures high-level query execution metadata, including execution timing, user identity, and error states.
SELECT
query,
userid,
starttime,
endtime,
aborted,
substring
FROM stl_query
ORDER BY starttime DESC
LIMIT 20;
This query allows administrators to review recent query executions, identify failed queries, and correlate execution time with user activity.
Session and authentication visibility is provided through STL_CONNECTION_LOG, which records both successful and failed connection attempts.
SELECT
recordtime,
remotehost,
username,
event,
pid
FROM stl_connection_log
ORDER BY recordtime DESC
LIMIT 20;
This data is commonly used to audit login behavior, detect repeated authentication failures, and identify unusual connection sources.
Schema and Object Changes (DDL)
Structural changes are tracked through the STL_DDLTEXT table, which records Data Definition Language statements executed against the cluster.
SELECT
xid,
starttime,
text
FROM stl_ddltext
ORDER BY starttime DESC
LIMIT 20;
This table is essential for auditing schema evolution, tracking table creation or deletion, and validating administrative changes.
Full SQL Text Reconstruction
For longer or complex SQL statements, Redshift splits query text across internal segments. The SVL_STATEMENTTEXT view reconstructs these fragments into readable statements.
SELECT
query,
sequence,
text
FROM svl_statementtext
WHERE query = 123456
ORDER BY sequence;
This capability is particularly useful when auditing generated SQL from BI tools or ETL frameworks that produce multi-part queries.
Data Access and Modification Activity
The STL_SCAN table provides visibility into which tables were read during query execution, including row counts and execution context.
SELECT
query,
tbl,
rows,
bytes
FROM stl_scan
ORDER BY query DESC
LIMIT 20;
For data modification operations, Redshift exposes insert and delete activity through dedicated system tables.
SELECT
query,
tbl,
rows
FROM stl_insert
ORDER BY query DESC
LIMIT 20;
SELECT
query,
tbl,
rows
FROM stl_delete
ORDER BY query DESC
LIMIT 20;
Together, these tables allow administrators to analyze read and write activity at the object level. However, all system tables are node-local and retention-limited. Older records are automatically purged as the system operates, and meaningful audit reconstruction requires manual correlation across multiple tables.
Database Audit Logging to Amazon S3
In addition to system tables, Amazon Redshift supports exporting audit logs directly to Amazon S3. When enabled, Redshift continuously delivers log files to an S3 bucket, providing durable storage outside the cluster lifecycle.
Audit logging to S3 is configured at the cluster level. Once enabled, Redshift automatically writes logs without requiring query-level configuration.
AuditLogging = Enabled
S3BucketName = redshift-audit-logs
Redshift delivers multiple log types to S3, including:
- User activity logs
- Connection logs
- User authentication logs
- DDL and administrative events
These logs are written as time-partitioned files and can be consumed by external systems. A common pattern is querying them through Athena or downstream analytics pipelines.
SELECT
user_name,
database_name,
query_text,
record_time
FROM redshift_audit_logs
WHERE record_time > current_timestamp - interval '1 day';
Storing audit logs in Amazon S3 enables longer retention, centralized storage, and integration with SIEM or compliance tooling. The logs preserve raw execution and access details and remain available independently of Redshift cluster lifecycle events.
At the same time, the exported logs remain uncorrelated flat files. They do not provide a unified execution timeline, cross-session context, or built-in mechanisms for compliance reporting and policy enforcement.
Centralized Amazon Redshift Audit Logging with DataSunrise
To build a structured audit trail on top of native Redshift logging, organizations often deploy centralized audit platforms that aggregate, normalize, and enrich Redshift audit data.
DataSunrise extends Amazon Redshift audit logging by operating as a centralized audit and activity history engine. It collects events generated by Redshift and transforms them into structured, searchable audit records suitable for operational analysis and compliance workflows.
Unified Audit Log Collection
DataSunrise consolidates Redshift audit signals from multiple sources into a single audit stream. This includes query activity, authentication events, schema changes, and access to sensitive objects. By normalizing this data, it creates a consistent audit format across sessions, users, and clusters, aligning with best practices for centralized database activity monitoring.
- DataSunrise aggregates Amazon Redshift audit signals from system tables, exported logs, and access metadata into a unified audit stream.
- Query execution, authentication events, schema changes, and sensitive object access are normalized into a consistent structure.
- Unified collection eliminates fragmentation across sessions, users, and clusters, enabling centralized audit visibility.
Context-Aware Audit Trails
Each audit event is enriched with contextual metadata that clarifies how and why an action occurred. This context allows audit records to move beyond raw execution details and become usable for investigations and compliance workflows, similar to the objectives of a well-defined database audit trail.
- Each audit event is enriched with user identity, role, and session context for clear attribution.
- Source application, client type, and execution timestamps are added to provide operational context.
- Accessed objects, data categories, and compliance relevance are attached to each event.
- Enriched audit records are suitable for forensic analysis and regulatory reporting.
Granular Audit Rules
Instead of capturing every event indiscriminately, DataSunrise enables granular audit policies that focus on high-value and high-risk activity. This selective approach mirrors modern guidance on designing effective audit rules for complex database environments.
- DataSunrise supports fine-grained audit policies rather than blanket event capture.
- Audit rules can target specific schemas, tables, and sensitive data categories.
- Privileged users, service accounts, and high-risk operations such as DDL or bulk exports can be audited selectively.
- Focused audit rules reduce noise while ensuring critical activity is fully captured.
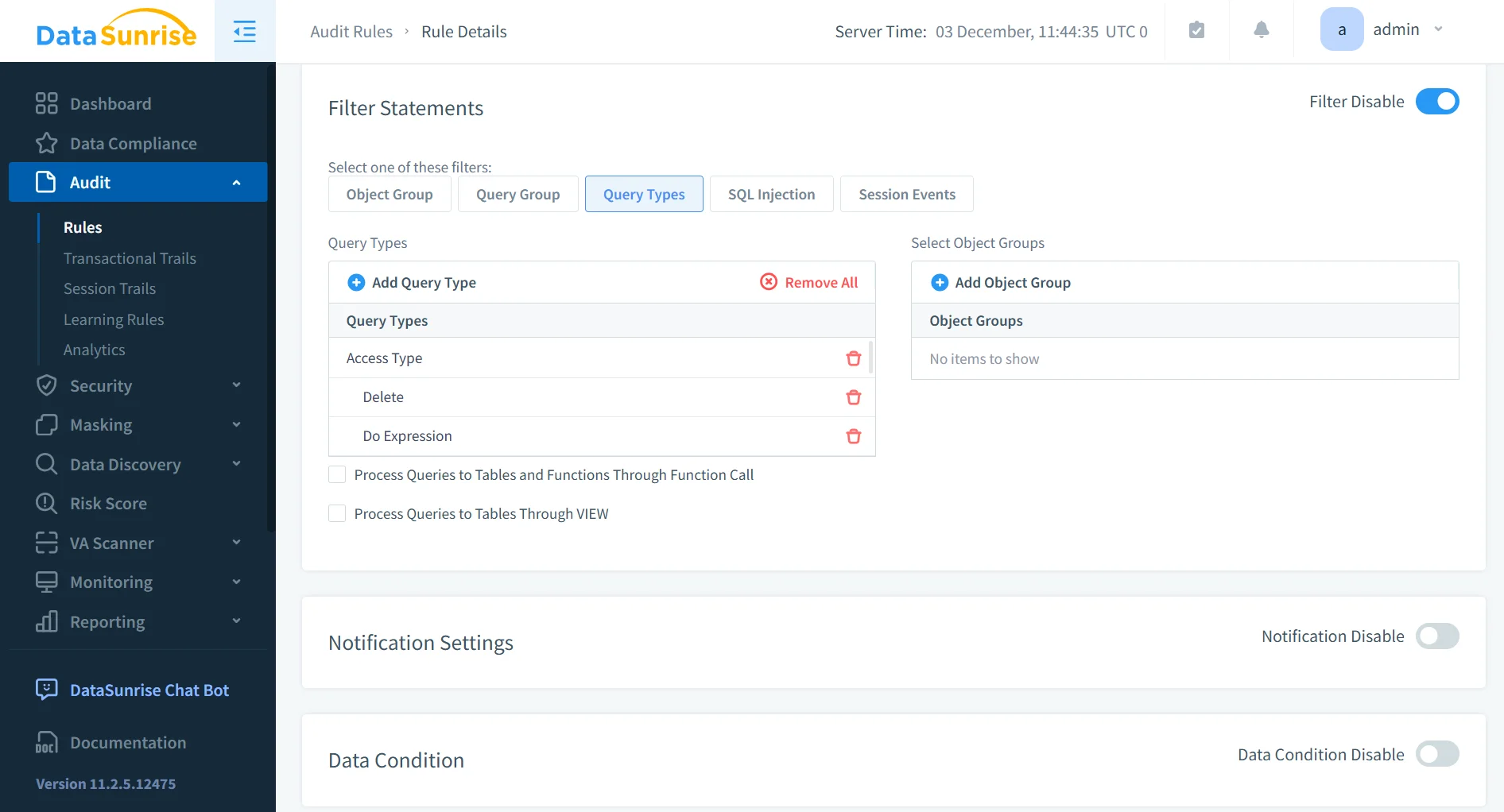
Centralized Activity History
All audit data collected and enriched by DataSunrise is stored in a centralized activity history. This repository provides a continuous, time-ordered view of database activity across Redshift environments, supporting long-term data activity history analysis.
- All audit events are stored in a centralized activity history repository.
- The activity history provides a continuous timeline across clusters and environments.
- Centralization simplifies investigations and accelerates root-cause analysis.
- A unified view improves operational visibility in distributed analytical environments.
Compliance and Regulatory Alignment
Amazon Redshift is frequently deployed in environments subject to strict regulatory requirements. A structured audit log strategy is essential for demonstrating control over data access and processing and for aligning with recognized data compliance regulations.
- Amazon Redshift environments are commonly governed by GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX.
- A structured audit log strategy ensures consistent, reviewable records of database activity.
- Centralized audit platforms support evidence generation for audits and compliance assessments.
- Automated audit data management reduces manual effort and compliance overhead.
Key Advantages of DataSunrise
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Unified Audit Log Collection | Consolidates Amazon Redshift audit signals from system tables, exported logs, and access metadata into a single, normalized audit stream, eliminating fragmentation across sessions, users, and clusters. |
| Context-Aware Audit Trails | Enriches each audit event with user identity, role, source application, accessed objects, execution timestamps, and compliance context to support investigations and reporting. |
| Granular Audit Rules | Enables fine-grained audit policies focused on specific schemas, tables, sensitive data categories, privileged users, and high-risk operations such as DDL or bulk exports. |
| Centralized Activity History | Stores all audit events in a unified, time-ordered activity history, providing continuous visibility across Redshift environments and simplifying forensic analysis. |
| Compliance and Regulatory Alignment | Supports compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX by maintaining consistent, reviewable audit records and enabling evidence generation for audits and assessments. |
| Reduced Operational Overhead | Minimizes manual log correlation and analysis by centralizing, normalizing, and structuring audit data for efficient review and long-term retention. |
Conclusion
Amazon Redshift provides native audit logging through system tables and exported log files, forming the foundation for activity tracking and operational visibility. However, producing a structured, end-to-end audit record in distributed environments requires centralized collection and enrichment.
By extending Redshift audit logs into a unified, searchable audit history, DataSunrise enables organizations to achieve consistent visibility, compliance alignment, and operational clarity across their analytical infrastructure.
For teams running Amazon Redshift in regulated or security-sensitive environments, a structured audit log strategy built on centralized data audit capabilities is a critical component of responsible data operations.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now