Apache Cassandra Compliance Management
Understanding the Compliance Landscape
Apache Cassandra has become the backbone of mission-critical systems in finance, telecommunications, e-commerce, and healthcare. Its masterless architecture and ability to handle petabyte-scale workloads make it the database of choice for organizations that cannot afford downtime. But this very scalability and distribution also create unique compliance challenges.
When businesses operate across multiple jurisdictions, they must satisfy overlapping regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX. These frameworks demand precise control over personal and financial data, enforceable audit trails, and proof that sensitive data remains secure at all times. Meeting those demands with Cassandra’s out-of-the-box features requires significant manual effort.
Why Compliance Management in Apache Cassandra is Harder
Cassandra’s strength — distributed, decentralized data — is also what complicates compliance:
- Replication and deletion: Data is stored on multiple nodes. Ensuring a GDPR “right to be forgotten” request propagates everywhere is not trivial.
- Audit fragmentation: Logs are stored locally on each node, leaving security teams with dozens or hundreds of files to reconcile.
- Operational complexity: Enabling authentication, encryption, or logging almost always requires editing
cassandra.yamland restarting nodes. - Eventual consistency: Regulators often expect strong guarantees, but Cassandra's model means data visibility can lag.
What Compliance Configuration Actually Looks Like
To illustrate the complexity, here's what enabling just basic compliance requires:
# cassandra.yaml - Must edit on EVERY node
authenticator: PasswordAuthenticator # Default: AllowAllAuthenticator
authorizer: CassandraAuthorizer # Default: AllowAllAuthorizer
audit_logging_options:
enabled: true # Default: false
logger:
- class_name: BinAuditLogger
audit_logs_dir: /var/log/audit # Required but often undocumented
After cluster restart, you still need CQL scripts:
-- Create compliance role with limited access
CREATE ROLE auditor WITH LOGIN = true AND PASSWORD = 'Complex$Pass2025';
GRANT SELECT ON KEYSPACE sensitive_data TO auditor;
-- Note: No way to grant time-limited access or conditional permissions
And custom log aggregation since each node logs independently:
# Must run on each node to collect distributed logs
for node in node1 node2 node3; do
scp cassandra@$node:/var/log/audit/*.log central-logger:/audit/$node/
done
Native Compliance Features in Cassandra
Although not enabled by default, Cassandra provides several technical features that form the foundation of a compliance strategy:
| Capability | Native Option | Limitation |
|---|---|---|
| Authentication & Authorization | Internal authentication with role-based access control | Effective at enforcing basic access boundaries, but requires manual user/role management and lacks contextual rules (time, location, device) |
| Audit Logging | BinAuditLogger or Full Query Logger | Records DDL, DML, and login attempts but stores logs per node; no cluster-wide aggregation; performance overhead can reach 15% |
| Encryption | SSL/TLS for client–server traffic; disk-level encryption handled externally | Provides strong protection in transit, but integration with enterprise key management is manual |
| Dynamic Data Masking | Available only in Cassandra 5.0+ with schema changes | Requires cluster restart; forces MASKED WITH syntax; existing tables must be recreated to apply masks |
These features demonstrate that Cassandra can participate in compliance programs — but they stop short of offering the automation and centralized visibility that enterprises need.
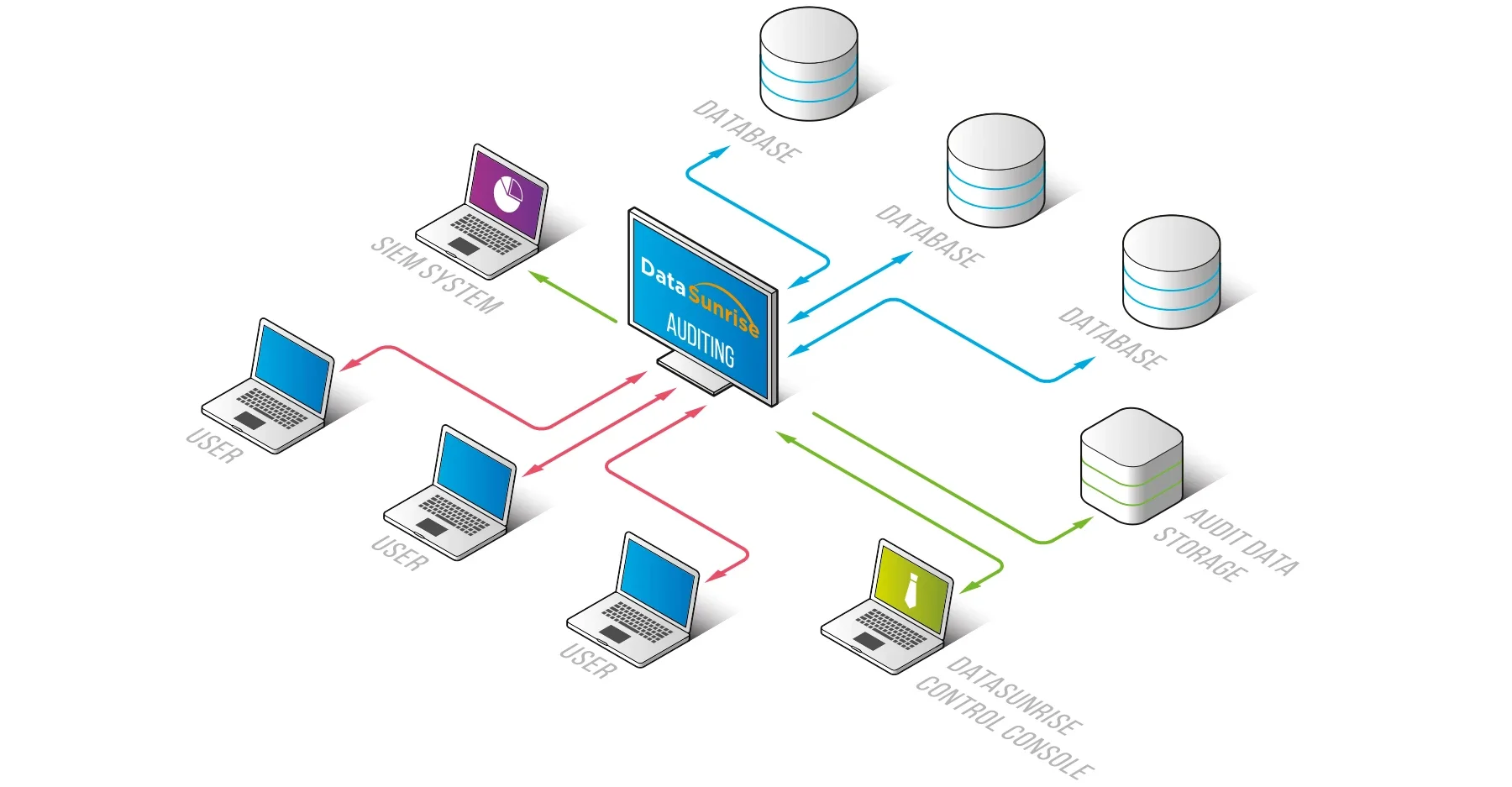
How DataSunrise Simplifies Compliance
DataSunrise addresses Cassandra’s compliance gaps by acting as a transparent proxy that sits in front of the cluster. Instead of configuring each node individually, administrators apply compliance rules centrally. The result is a platform that transforms Cassandra into an environment regulators can trust.
Automated Sensitive Data Discovery
Manual data classification is both expensive and error-prone. DataSunrise performs automated discovery across Cassandra keyspaces, finding:
- Credit card numbers, passport numbers, and national identifiers
- Protected Health Information (PHI) required under HIPAA
- Personally Identifiable Information (PII) under GDPR and CCPA
- Custom patterns defined by the organization
This creates a classification map that becomes the anchor for subsequent controls. Knowing exactly where sensitive attributes reside enables teams to prove compliance coverage rather than relying on guesswork.
Database Firewall and Policy Enforcement
Beyond visibility, DataSunrise acts as a database firewall. Administrators can create rules to block risky queries, enforce least-privilege access, or prevent large-scale exports of sensitive tables. This moves compliance from a passive documentation exercise into an active enforcement layer that reduces real-world risk.
Dynamic and Static Masking
While Cassandra 5.0 introduced experimental masking, its utility is limited. DataSunrise offers enterprise-grade dynamic masking that applies instantly to query results without altering schemas. Masking can adapt to user context — for instance, doctors may see full patient data, nurses partial, and clerks none at all.
For non-production environments, static masking anonymizes data while preserving relationships. This enables safe use of production-like datasets for testing and analytics, satisfying PCI DSS and GDPR requirements around data minimization.
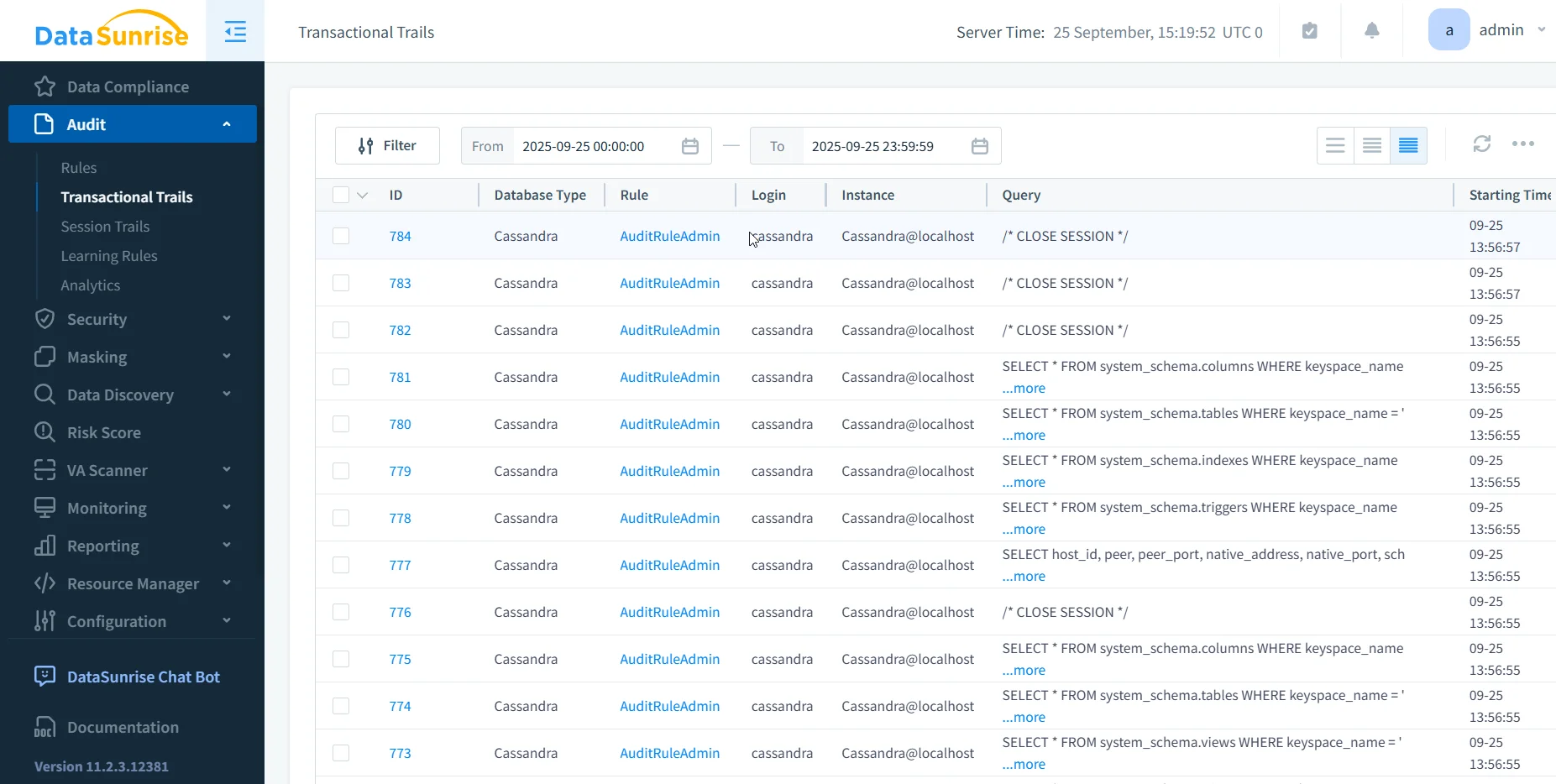
Centralized Auditing and Monitoring
One of the largest pain points with Cassandra is its fragmented audit trail. DataSunrise consolidates all activity into a central audit repository. Unlike native logs, this includes failed authentication attempts, a requirement under both HIPAA and PCI DSS.
| Feature | Native Cassandra | With DataSunrise |
|---|---|---|
| Log Location | Per node | Centralized |
| Failed Auth Tracking | No | Yes |
| Format | Binary | Human-readable, searchable |
| Correlation | Manual | Automatic across distributed transactions |
| Alerts | Not available | Real-time notifications |
This centralization dramatically reduces audit preparation time and gives security teams immediate visibility into suspicious behavior.
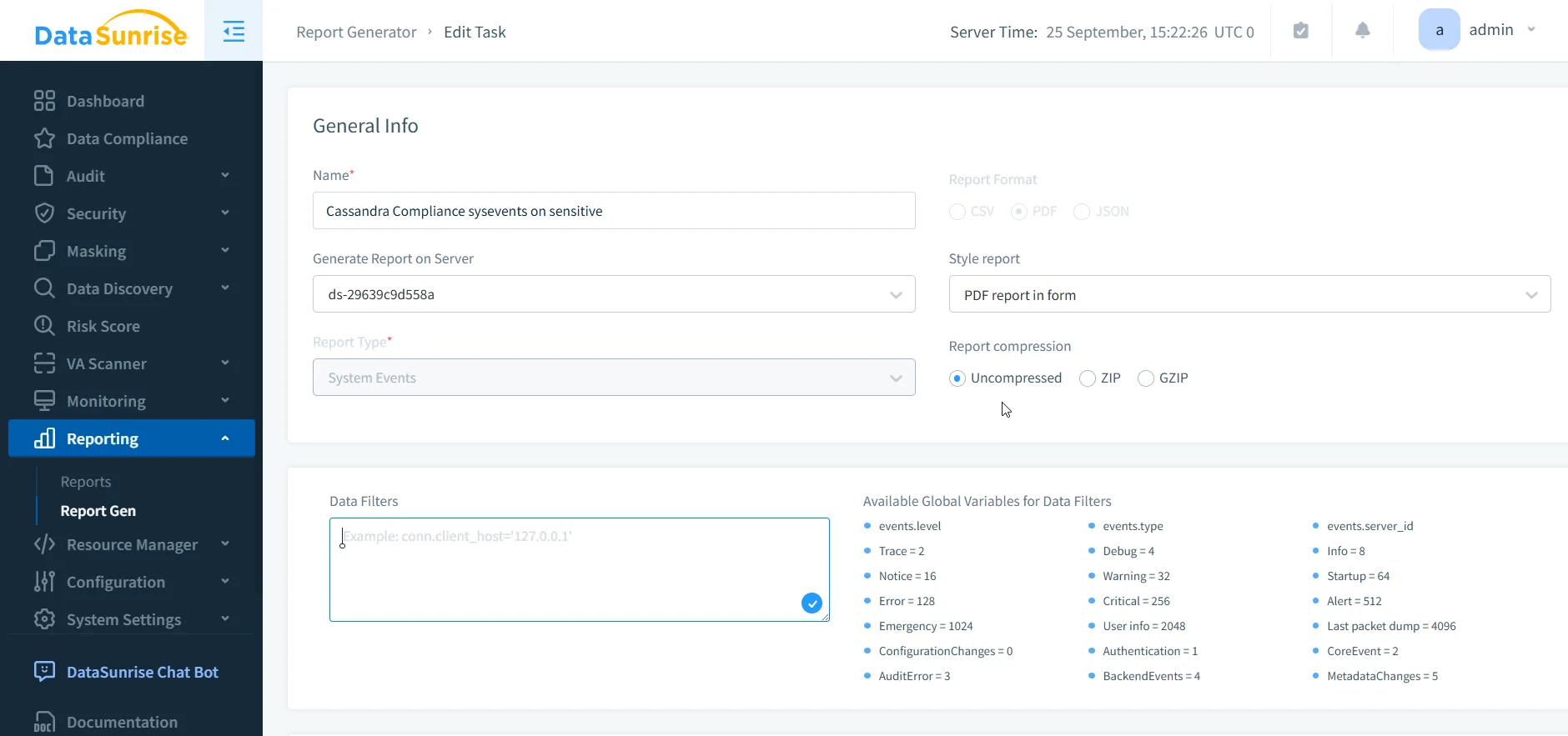
Compliance Reporting
Preparing evidence for auditors is traditionally one of the most time-consuming aspects of compliance. DataSunrise streamlines this with prebuilt report templates for GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX. Reports can be generated on demand or scheduled, ensuring that organizations are always ready to demonstrate compliance posture.
Conclusion
Compliance management for Apache Cassandra cannot be achieved through configuration tweaks alone. Native features such as RBAC, audit logging, and TLS provide a foundation, but they are siloed, manual, and limited in scope. As deployments grow, these shortcomings translate into regulatory risk and operational overhead.
DataSunrise eliminates this complexity by delivering automated discovery, centralized auditing, dynamic masking, and compliance reporting in one platform. For enterprises, the benefits are both strategic and practical: reduced risk exposure, faster audit cycles, and sustainable compliance at scale.
With DataSunrise, compliance management shifts from being a drain on resources to becoming a source of trust and competitive advantage for organizations running Apache Cassandra.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now