Data Anonymization in Percona Server for MySQL
Data anonymization in Percona Server for MySQL is not a cosmetic security feature. It is a structural control used when real production data must be shared outside its original trust boundary without exposing identities, credentials, or regulated attributes. In practice, anonymization reduces long-term exposure risks and directly supports broader data security strategies.
Unlike auditing or activity tracking, anonymization changes the data itself. The goal is to permanently remove the ability to identify individuals while preserving enough structure for testing, analytics, and development workflows. This approach is especially important when handling personally identifiable information (PII) and other regulated data categories.
This article explains how anonymization works in Percona Server for MySQL using native SQL techniques, where those approaches break down, and how centralized platforms extend anonymization into a governed, repeatable process aligned with data compliance regulations and security requirements.
What Data Anonymization Means in MySQL Context
Data anonymization is the irreversible transformation of sensitive values so that data subjects cannot be re-identified, even by administrators. Once applied, anonymized data typically falls outside the scope of data compliance regulations and significantly reduces long-term data security risks.
In MySQL-based systems, anonymization is used when production data is reused for testing, analytics, or storage outside controlled environments. It is commonly applied to personal identifiers, financial attributes, and behavioral or location-related data, especially in non-production workflows and test data management scenarios.
Unlike database activity monitoring or access controls based on the principle of least privilege, anonymization protects data at rest by replacing sensitive values entirely. Once anonymized, data can be exported, replicated, or archived without additional runtime controls.
Native Data Anonymization Techniques in Percona Server for MySQL
Percona Server for MySQL does not provide a native anonymization engine, policy model, or lifecycle controls for anonymized data. There are no built-in mechanisms for identifying sensitive columns, enforcing anonymization scope, or validating results. As a result, anonymization is implemented by combining standard SQL primitives such as UPDATE, functions, joins, and helper tables.
These approaches can achieve irreversible transformations, but they rely entirely on manual logic and operational discipline.
Deterministic Replacement with UPDATE Statements
The most direct anonymization technique is overwriting sensitive columns with generated or synthetic values. This method is commonly used when preparing copies of production databases for testing or development.
UPDATE customers
SET
email = CONCAT('user_', id, '@example.com'),
phone = NULL,
full_name = CONCAT('Customer_', id),
address = 'REDACTED',
birth_date = NULL;
This approach preserves primary keys and row counts, which helps maintain basic referential stability. Downstream systems that depend on identifiers such as id continue to function, while real personal data is removed.
However, this method scales poorly. Every table requires its own anonymization logic, and every sensitive column must be explicitly handled. If a new column is added later, it will remain unanonymized unless the script is updated. Referential consistency across related tables must be maintained manually, and execution order becomes critical in schemas with shared identifiers. There is no built-in validation to confirm that anonymization is complete, and once executed, rollback is impossible without restoring from backups. The original data is permanently destroyed.
Hash-Based Anonymization
Hashing replaces sensitive values with fixed-length digests, removing readability while preserving uniqueness. This is sometimes used when correlation or deduplication is required without exposing original values.
UPDATE users
SET
national_id = SHA2(CONCAT(national_id, 'static_salt_123'), 256),
email = SHA2(CONCAT(email, 'static_salt_123'), 256);
Hash-based anonymization is irreversible, but it introduces subtle risks. Predictable or reused salts weaken protection and make hashes vulnerable to inference. Because identical inputs always produce identical hashes, relationships across tables and datasets remain visible.
UPDATE payments
SET
payer_id = SHA2(CONCAT(payer_id, 'static_salt_123'), 256);
Maintaining cross-table consistency now depends on using the exact same hashing and salting logic everywhere. Any deviation breaks joins and correlations. In addition, hashed values may still be considered personal data under certain regulations, depending on context and re-identification risk. As datasets grow, managing salts and enforcing consistent hashing across environments becomes fragile and error-prone.
Token Substitution Tables
A more controlled technique uses lookup tables that map original values to synthetic tokens. This allows anonymized data to remain realistic while preventing direct identification.
CREATE TABLE token_emails (
original_email VARCHAR(255),
token_email VARCHAR(255)
);
INSERT INTO token_emails VALUES
('[email protected]', '[email protected]'),
('[email protected]', '[email protected]');
Anonymization is then applied through join-based replacement:
UPDATE orders o
JOIN token_emails t
ON o.email = t.original_email
SET
o.email = t.token_email;
This approach improves data quality for testing and analytics, but it significantly increases operational overhead. Token generation must avoid collisions, tokens must remain consistent across all related tables, and reuse must be carefully controlled to prevent inference. Over time, token tables themselves become sensitive assets that require protection, rotation, and access control. Without centralized governance, token lifecycle management quickly becomes difficult to maintain and audit.
Centralized Data Anonymization with DataSunrise
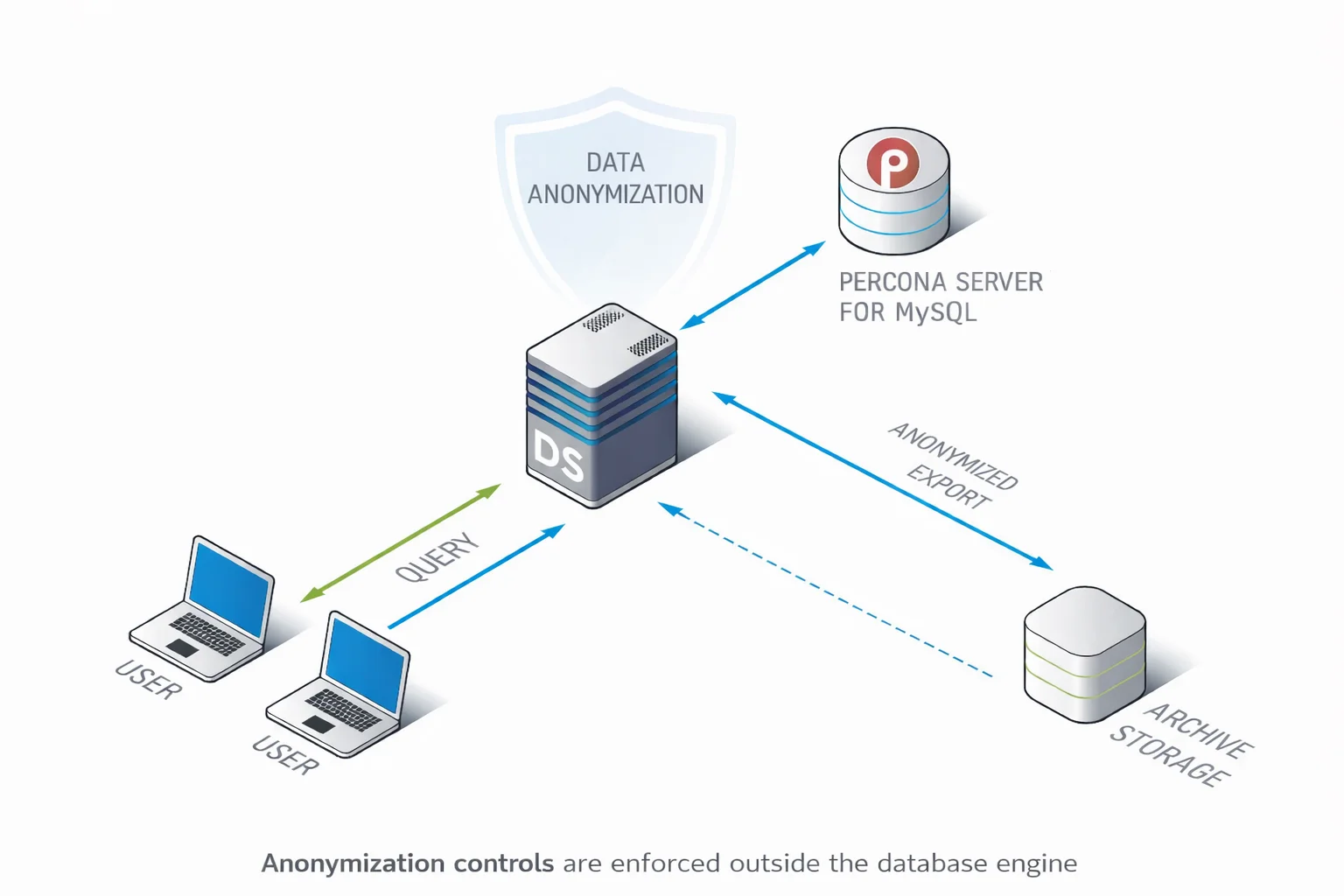
DataSunrise treats data anonymization as a governed security process rather than a destructive, one-off SQL operation. Instead of embedding irreversible logic into database schemas or maintaining fragile anonymization scripts, anonymization rules are defined centrally and enforced consistently across Percona Server for MySQL environments.
This approach separates anonymization logic from database structure. Databases remain intact, while anonymization is applied as a controlled transformation layer. As a result, the same policies can be reused across production replicas, test environments, exports, and archives without rewriting SQL or risking inconsistent outcomes.
Centralized anonymization also introduces visibility and control that native approaches lack. Administrators can see which data was anonymized, how it was transformed, and where those transformations were applied.
Sensitive Data Discovery
The process starts with automated sensitive data discovery. Instead of relying on manual schema reviews, DataSunrise scans databases to identify personal data, financial attributes, credentials, and other regulated fields. Discovery operates at the column level and accounts for both naming patterns and data content, reducing the risk of missing hidden identifiers.
This step establishes a verified scope for anonymization, ensuring that protection is applied to all relevant data rather than a best-guess subset.
Policy Definition
Once sensitive data is identified, anonymization policies are defined centrally. Policies specify how different categories of data should be transformed, such as replacement with synthetic values, tokenization, or irreversible anonymization.
Policies are reusable and versioned. The same anonymization logic can be applied consistently across multiple databases and environments, eliminating divergence caused by copy-pasted SQL scripts. Changes to policies propagate automatically without modifying database schemas or application code.
Execution Mode Selection
Anonymization is then applied based on execution context rather than hardcoded SQL. This allows organizations to control where and when anonymization occurs without duplicating logic.
Typical execution targets include test and development environments, data exports shared with third parties, database replicas used for analytics, and archived datasets retained for long-term storage. Each context can reuse the same policies while remaining operationally isolated.
This model ensures that production systems remain untouched while downstream data consumers receive safe, anonymized datasets.
Verification and Reporting
After execution, DataSunrise provides verification and reporting capabilities that native approaches lack. Administrators can confirm which datasets were anonymized, which policies were applied, and whether coverage was complete.
These reports serve as evidence for internal security reviews and external compliance audits. Instead of relying on trust in scripts, organizations gain documented proof that anonymization was applied consistently and correctly.
By turning anonymization into a managed workflow rather than a destructive SQL task, centralized anonymization eliminates guesswork, reduces operational risk, and scales across environments without increasing complexity.
Business Impact of Proper Data Anonymization
| Business Area | Impact |
|---|---|
| Security Risk | Reduced breach impact by removing usable sensitive data from non-production systems and shared datasets |
| Operational Efficiency | Faster provisioning of test, QA, and analytics environments without waiting for manual data cleanup |
| Compliance | Lower compliance audit scope by excluding anonymized datasets from regulatory oversight |
| Engineering Reliability | Elimination of human error associated with manual SQL anonymization scripts |
| Data Governance | Clear and enforceable separation between production and non-production data |
Proper anonymization shifts security left. Sensitive data is removed before it can spread into environments where access controls, monitoring, and operational discipline are weaker. Instead of trying to protect data everywhere, organizations prevent exposure at the source.
Conclusion
Percona Server for MySQL provides enough flexibility to implement basic data anonymization using native SQL techniques. For small datasets and one-time operations, this approach may be sufficient, especially when anonymization is tightly scoped and manually controlled. However, even in these cases, anonymization must be treated as part of broader data security practices rather than an isolated maintenance task.
As environments grow and data compliance regulations tighten, manual anonymization quickly becomes fragile, opaque, and difficult to validate. Scripts drift, sensitive columns are missed, and there is no reliable way to prove that anonymization was applied consistently across test, analytics, and archival datasets. This is especially problematic in large-scale test data management workflows where data is frequently copied and reused.
Centralized platforms such as DataSunrise transform anonymization into a controlled, auditable, and repeatable process. By combining automated sensitive data discovery, policy-driven transformations, and compliance-ready reporting, anonymization becomes part of the security architecture rather than a destructive afterthought. This centralized model also aligns naturally with other protection mechanisms, including dynamic data masking, without duplicating logic or increasing operational overhead.
When done correctly, anonymization is not just about hiding data. It is about removing risk at the source, before sensitive information spreads into environments where it no longer belongs.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now