Data Audit for Databricks SQL
Databricks SQL has become a core analytical layer for modern data platforms, powering BI dashboards, ad-hoc analytics, and large-scale reporting on top of data lakes. Its strength lies in distributed execution, elastic compute, and tight integration with cloud storage. Data Audit for Databricks SQL is essential in this context because that same flexibility creates serious audit challenges when regulated or sensitive data is involved.
As organizations increasingly rely on Databricks SQL to query personal, financial, and operational datasets, effective data audit for Databricks SQL environments stops being optional. Regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX require clear answers to basic questions: who accessed the data, what queries were executed, when changes occurred, and whether controls were enforced consistently.
This article explains how data audit for Databricks SQL works using native capabilities, where those mechanisms fall short, and how centralized platforms like DataSunrise extend audit coverage with real-time visibility, correlation, and compliance-ready evidence.
Why Data Audit for Databricks SQL Is Not Straightforward
Databricks SQL does not behave like a traditional single-node database. Queries are executed across clusters, logs are distributed, and identities are often federated through cloud IAM, SSO providers, or workspace-level permissions. As a result, audit data is fragmented by design, which complicates consistent Databricks SQL auditing.
From a compliance perspective, this fragmentation creates risk. Native logs may show that a query ran, but not always the business context, the sensitivity of accessed columns, or the broader session behavior. Security teams end up stitching together events from multiple sources just to reconstruct a single incident.
Native Data Audit Capabilities in Databricks SQL
Databricks provides native audit logs that capture key workspace and SQL activity. These logs typically include query execution events, user identities, timestamps, and high-level operation types such as SELECT, UPDATE, or DELETE. They are usually exported to cloud storage or log analytics services for further analysis.
In practice, Databricks SQL audit events are often forwarded to external observability platforms such as Azure Log Analytics, Amazon CloudWatch, or Google Cloud Logging. While these tools help with retention and search, they are not designed specifically for compliance-driven data audit workflows.
This native audit layer is useful for baseline visibility and troubleshooting. It confirms that queries ran and shows which users or service principals executed them. However, it has important limitations when used as the sole audit mechanism.
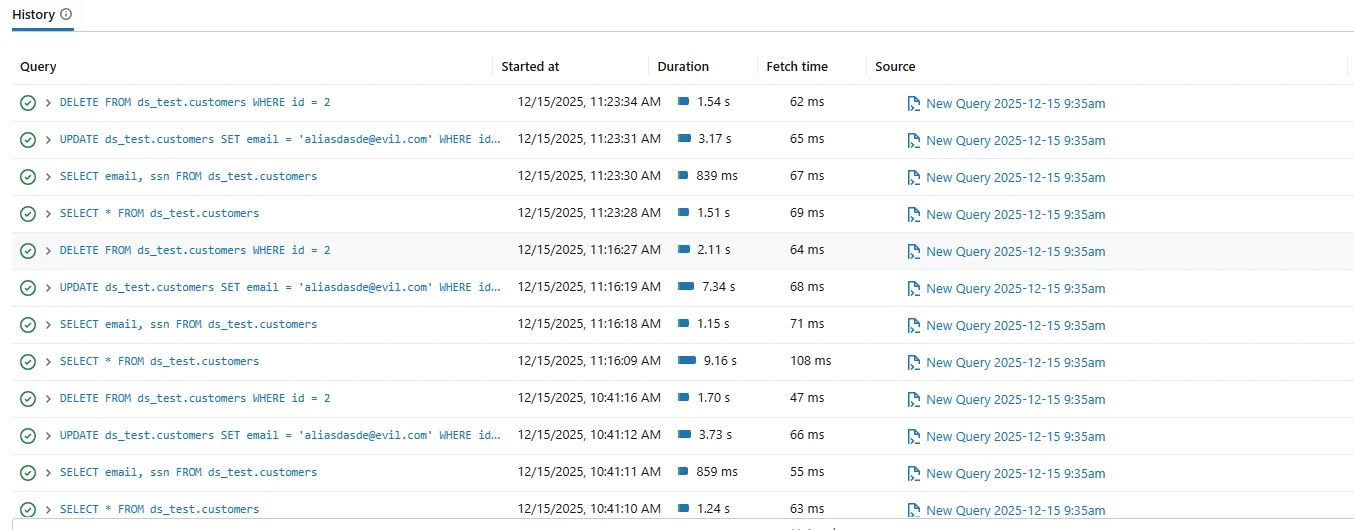
Native Databricks SQL auditing generally lacks:
- Column-level context for sensitive data access
- Correlation across sessions and repeated queries
- Centralized audit views across multiple workspaces
- Compliance-oriented reporting aligned to regulatory controls
For organizations subject to external audits, these gaps often translate into manual log analysis and custom scripts — fragile solutions that break as environments evolve and scale.
Operational Risks of Relying Only on Native Logs
When audit data is incomplete or scattered, security and compliance teams lose time and confidence. Investigations become reactive exercises instead of structured workflows. Even worse, some incidents remain undetected because no one is actively correlating low-level signals into meaningful risk indicators.
This is where database activity monitoring and centralized audit trails become critical. A proper data audit solution for Databricks SQL must not only collect events, but also normalize them, enrich them with context, and retain them in a form that auditors can actually consume.
This approach aligns with the broader principles of Database Activity Monitoring, Data Activity History, and guidance from frameworks such as NIST, which emphasize traceability, accountability, and evidence-based security controls.
DataSunrise Audit for Databricks SQL
DataSunrise introduces a centralized audit layer purpose-built for data audit for Databricks SQL. Instead of relying solely on scattered native logs, DataSunrise captures SQL activity in real time, correlates events across sessions, and stores them in a unified audit repository.
This model provides consistent visibility regardless of how many clusters, users, or workspaces are involved. Every query is recorded with rich metadata, including user identity, query type, timing, execution context, and policy evaluation results.
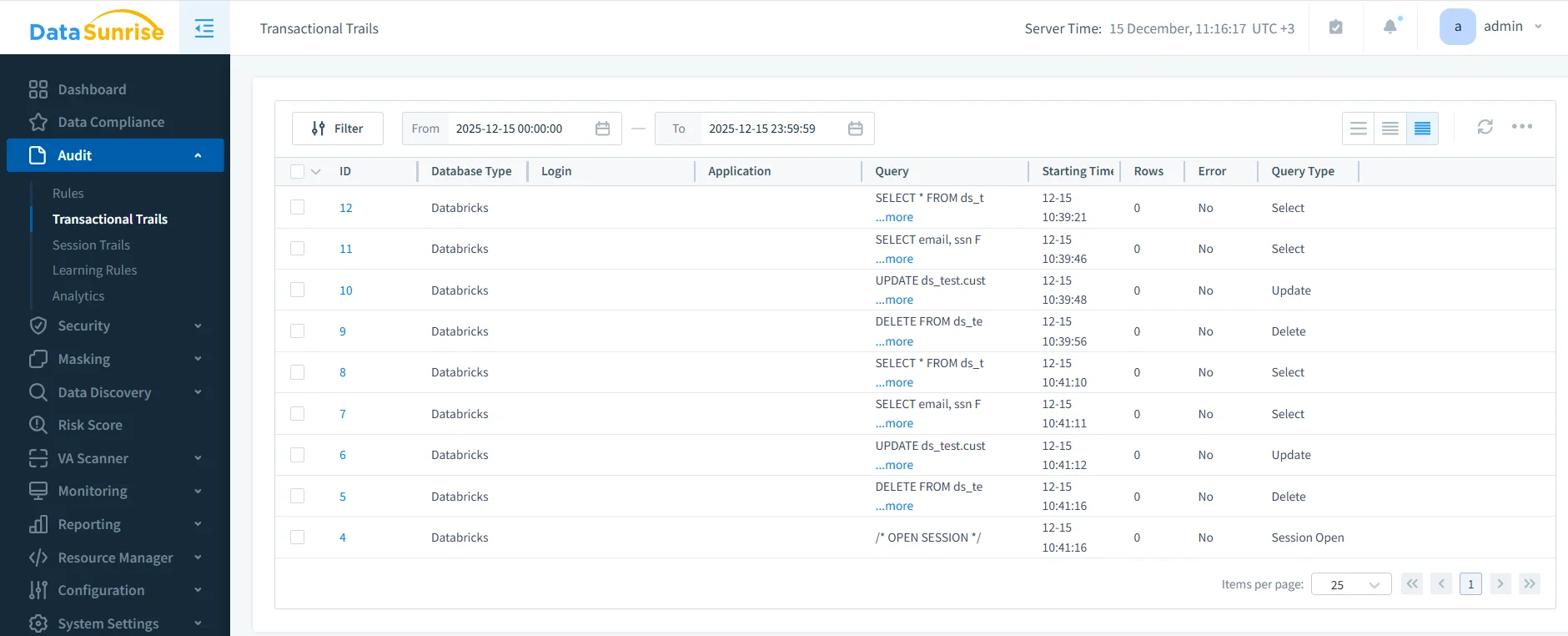
Because DataSunrise operates as a unified auditing and security layer, it supports advanced use cases such as:
- Centralized audit logs across environments
- Detailed audit trails for investigations
- Policy-driven database security enforcement
- Automated evidence generation for compliance reviews
Native Audit vs Centralized Audit: Key Differences
| Capability | Native Databricks SQL Audit | DataSunrise Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Query visibility | Basic query events | Full query context and correlation |
| Centralized view | Multiple log sources | Single unified audit trail |
| Compliance reporting | Manual processing | Automated compliance reports |
| Real-time monitoring | Limited | Real-time audit and alerts |
| Regulatory alignment | Indirect | Direct mapping to GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, SOX |
Compliance and Governance Benefits
Auditing Databricks SQL is not just about visibility — it is about defensible governance. Regulators expect organizations to demonstrate that controls exist, are enforced, and can be proven with reliable evidence.
By combining data audit for Databricks SQL with Data Compliance and Regulatory Compliance frameworks, DataSunrise helps organizations move from reactive log collection to proactive compliance management.
This includes support for structured reporting, long-term retention, and consistent audit policies across analytical and operational data platforms.
Conclusion: Making Databricks SQL Auditable by Design
Databricks SQL delivers speed and scale, but those benefits must be balanced with accountability. Native audit logs provide a starting point, yet they are rarely sufficient for enterprise-grade compliance or security investigations.
A centralized audit approach transforms Databricks SQL from a powerful analytics engine into an auditable, governable platform. With unified trails, real-time monitoring, and compliance-ready reporting, organizations can confidently answer the questions auditors always ask — without scrambling for logs.
When implemented correctly, data audit for Databricks SQL becomes a foundational control for modern analytics governance. Platforms like DataSunrise make this possible by turning raw SQL activity into structured, actionable audit intelligence that scales with modern data architectures.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now