Data Masking Tools for Percona Server
As organizations expand their use of Percona Server for MySQL across production, analytics, and non-production environments, sensitive data protection becomes a structural requirement. Databases often store customer records, credentials, financial attributes, and personal identifiers in the same datasets. Developers, analysts, and automated services access this data daily.
Encryption protects data at rest and in transit. Data masking controls what users see during query execution. It allows teams to work with realistic data structures without exposing confidential values. This article explains how native masking techniques work in Percona Server for MySQL and how centralized platforms such as DataSunrise extend them with policy-driven enforcement and regulatory compliance alignment.
Importance of Data Masking Tools and Techniques
In real-world Percona Server for MySQL deployments, databases rarely serve a single purpose. Production applications, analytics jobs, developers, support teams, and automation pipelines often access the same data. While access controls define who can connect to the database, they do not control which values users can see. This gap frequently leads to data exposure incidents and weakens overall data security.
This is where data masking tools become critical. Masking adds a visibility layer that operates independently of application logic. It allows teams to preserve table structures, relationships, and data formats while hiding sensitive values. Common examples include emails, phone numbers, payment details, and personally identifiable information (PII).
Native masking techniques offer basic protection, but they rely on static SQL constructs. These constructs become difficult to manage as schemas grow and access patterns change. Manual masking logic often breaks consistency and increases operational risk. Centralized masking tools solve this problem by enforcing policies from a single control point and integrating masking into broader database security workflows.
From a compliance standpoint, masking is no longer optional. Regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS require strict limits on sensitive data exposure. Masking helps organizations meet these requirements by preventing unnecessary disclosure, even when teams share databases or copy data into non-production environments. These controls directly support structured data compliance strategies.
Effective masking reduces operational friction. Teams no longer need to lock down databases completely. Instead, they can provide realistic datasets for development, analytics, and testing. When combined with centralized enforcement and monitoring, masking becomes part of a broader database activity monitoring and risk-reduction framework.
In practice, data masking tools move protection away from isolated SQL objects. They establish an architectural control that scales with the environment and supports both security and usability.
Native Data Masking Techniques in Percona Server for MySQL
Percona Server for MySQL is fully compatible with MySQL masking techniques and inherits its flexibility. However, native masking is not a single built-in feature. Instead, it is implemented through SQL design patterns and access-layer controls.
Masking with Views
One of the most common native approaches is using SQL views to expose masked representations of sensitive columns.
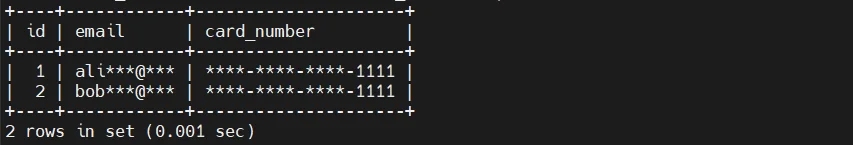
Applications or users are granted access to the view instead of the base table. This method preserves schema relationships while hiding original values.
Masking with Generated Columns
Percona Server for MySQL supports generated columns, which can store or compute masked values derived from original data.
ALTER TABLE customers
ADD COLUMN masked_email VARCHAR(255)
GENERATED ALWAYS AS (
CONCAT(
LEFT(email, 2),
'***@***'
)
) STORED;
This approach embeds masked data directly into the table structure.
Role-Based Access Controls
Native MySQL privileges can restrict access to sensitive columns while allowing access to non-sensitive fields.
GRANT SELECT (
id,
created_at
)
ON customers
TO analyst_user;
While effective for strict separation, this technique does not mask data — it hides it entirely. As a result, it is often insufficient for development, testing, or support workflows where partial visibility is required.
Centralized Data Masking for Percona Server for MySQL with DataSunrise
DataSunrise introduces an external security layer that enforces masking independently of database schemas and application logic. Masking rules are applied in real time as queries are processed, ensuring consistent protection across all access paths.
Dynamic Data Masking
Dynamic masking modifies query results at execution time, without altering the underlying data. The same column can be rendered differently depending on the execution context, allowing sensitive values to remain protected while preserving database structure and application behavior.
Masking decisions are evaluated dynamically based on factors such as the database user, the client application issuing the request, the access method used to connect, the time of access, and the structure of the executed query. This approach allows teams to maintain a single authoritative dataset while enforcing fine-grained visibility rules that adapt to real usage patterns rather than static permissions.
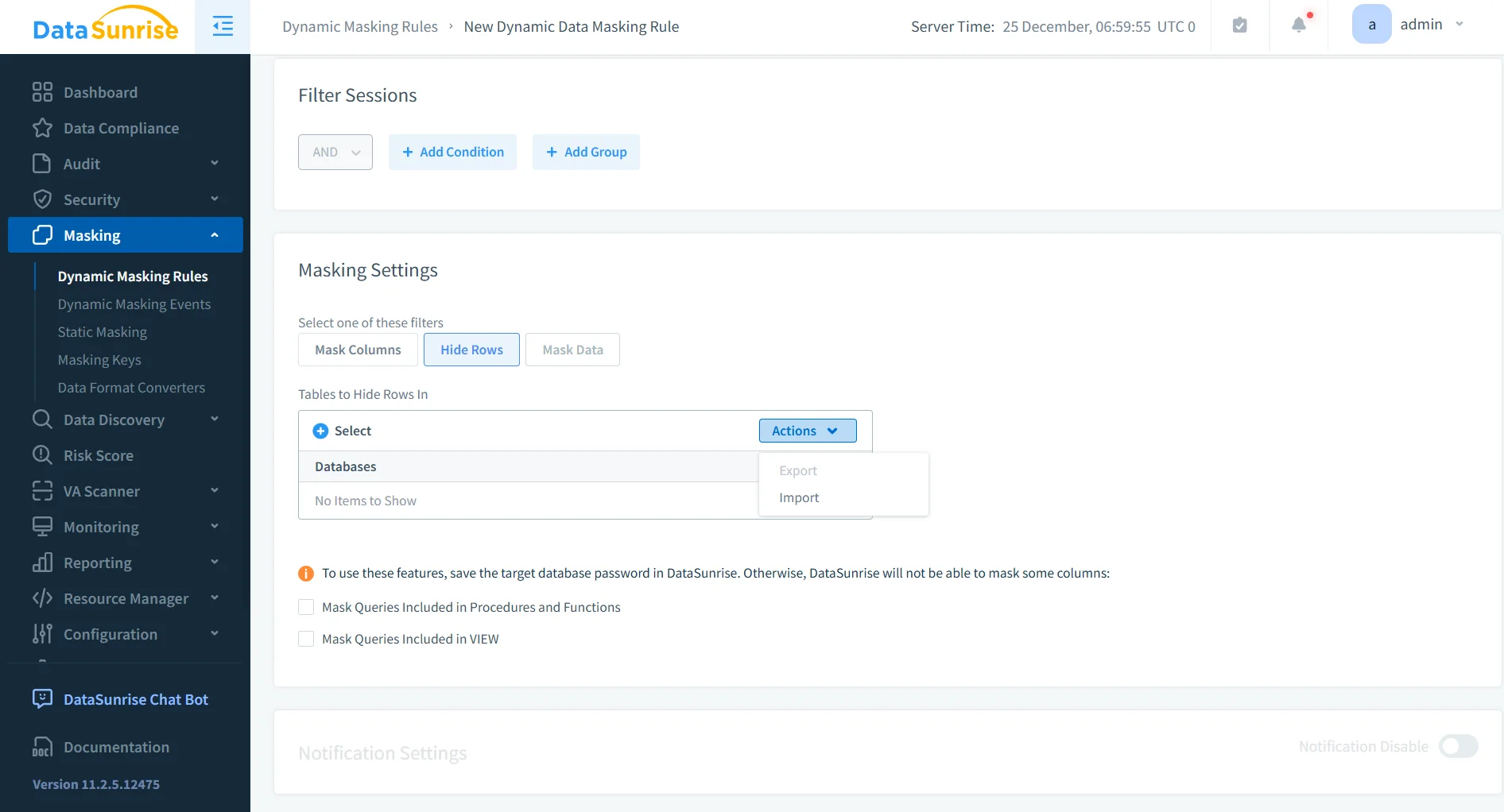
Static and In-Place Masking
For non-production environments, DataSunrise supports irreversible data transformation techniques designed to eliminate exposure risks entirely. Static masking generates a separate masked copy of the original dataset, making it suitable for development, testing, and analytics workflows that require realistic data structures without access to real values.
In-place masking applies irreversible transformations directly to the source tables. This method is commonly used when original data must be permanently removed or anonymized, such as during data offloading, third-party data sharing, or regulatory remediation processes. In both cases, masked values cannot be restored, ensuring that sensitive information is no longer present in the environment.
- Static masking preserves table structures, relationships, indexes, and data formats while replacing sensitive values with masked equivalents.
- In-place masking permanently transforms sensitive data inside existing tables, eliminating the original values at the source level.
- Both approaches prevent data re-identification by design, making them suitable for strict compliance and data-sharing scenarios.
- Masking operations can be executed selectively on specific schemas, tables, or columns to align with operational and regulatory requirements.
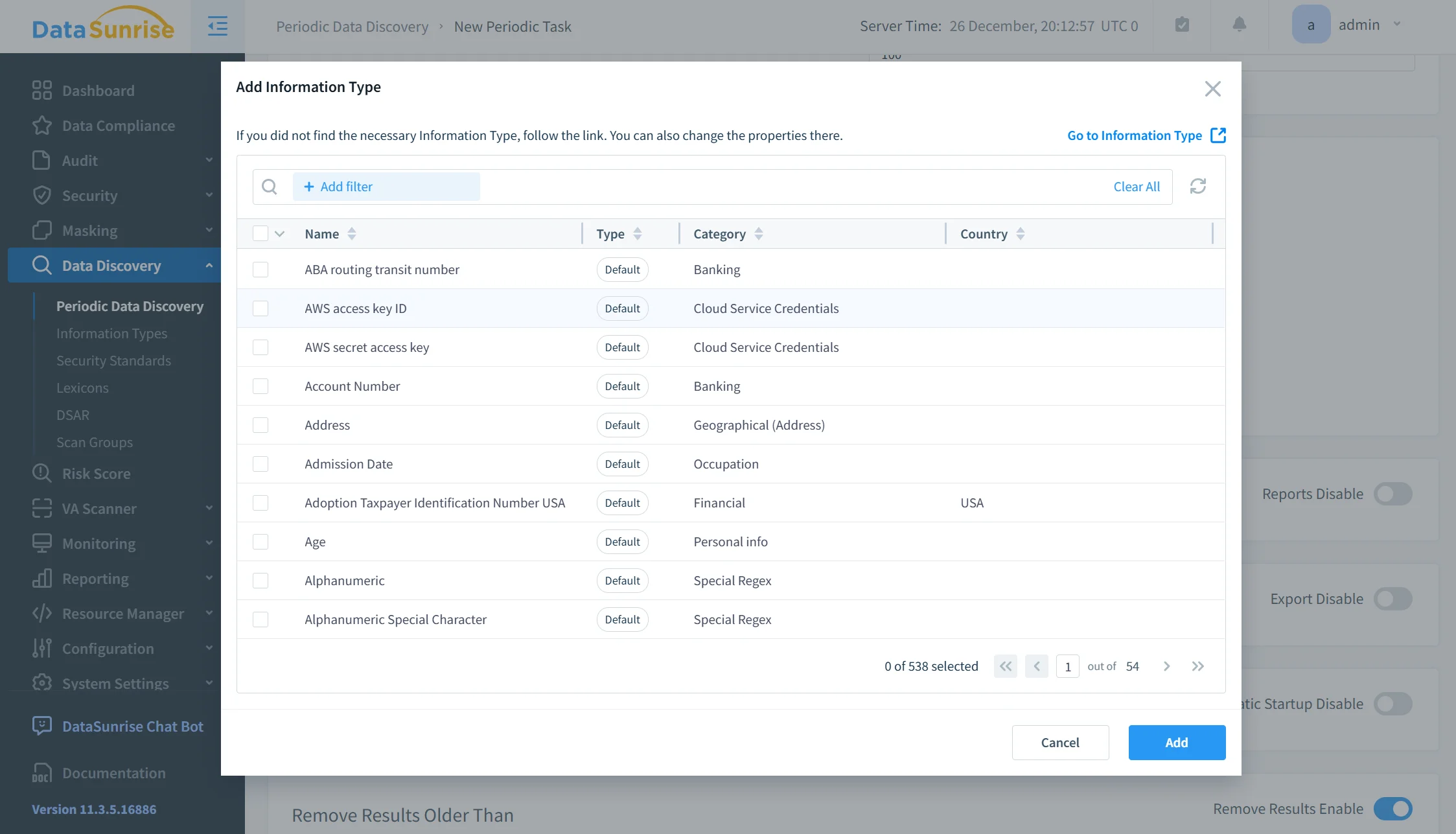
Sensitive Data Discovery
Before applying masking rules, DataSunrise can automatically discover sensitive data across database schemas. Discovery is based on content inspection rather than object names or schema conventions, which allows detection of personal data, financial attributes, credentials, and other sensitive elements even in poorly documented or inconsistently structured databases.
Once discovered, sensitive data elements can be directly mapped to masking policies. This significantly reduces manual configuration effort and helps ensure consistent protection coverage across large and evolving Percona Server for MySQL environments.
Business Impact of Centralized Masking
| Business Area | Operational Impact |
|---|---|
| Data Exposure Risk | Centralized masking significantly reduces the risk of sensitive data exposure in shared, non-production, and cross-team environments by enforcing consistent visibility controls. |
| Dataset Provisioning | Masked datasets can be generated and delivered faster, eliminating delays caused by manual sanitization and approval workflows. |
| Policy Consistency | Masking rules are enforced uniformly across teams, applications, and access methods, preventing configuration drift and ad-hoc exceptions. |
| Audit and Compliance | Masking simplifies audit preparation by ensuring sensitive data is protected by default, reducing the scope of compliance validation and evidence collection. |
| Operational Complexity | Centralized masking reduces reliance on custom SQL logic, database-specific workarounds, and application-level masking implementations. |
Conclusion
Percona Server for MySQL allows teams to implement data masking through native SQL techniques such as views, generated columns, and access controls. These methods work well in small, controlled environments where teams can enforce masking rules manually. However, their effectiveness drops when multiple teams and workflows reuse the same databases.
Organizations that need scalable governance, dynamic protection, and audit-ready workflows rely on centralized platforms such as DataSunrise. By combining dynamic data masking with automated sensitive data discovery, teams can enforce masking policies consistently across environments. This approach avoids embedding masking logic into database schemas or application code.
Centralized masking fits naturally into broader database security strategies and supports continuous adherence to data compliance requirements. When teams integrate masking with database activity monitoring, it becomes part of a unified control framework rather than an isolated safeguard.
As a result, sensitive data protection shifts from an afterthought to a core architectural element of secure Percona Server for MySQL deployments.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now