Data Obfuscation in MariaDB
MariaDB is widely used in transactional systems, customer-facing applications, analytics platforms, and internal business tools. In practice, the same database often serves developers, analysts, support engineers, and automated services at the same time. Because of this overlap, teams face a recurring challenge: how to provide access to real data structures without exposing sensitive values.
To address this issue, data obfuscation transforms sensitive data into a non-readable or non-usable form while preserving schema integrity and application behavior. Instead of protecting data only at rest, obfuscation actively controls data exposure, complementing broader data security and database security practices. As a result, organizations significantly reduce the risk of data leakage across operational workflows, non-production environments, and analytical use cases.
In this article, we explain how teams can implement data obfuscation in MariaDB using native mechanisms described in the official MariaDB documentation. Additionally, we show how centralized platforms such as DataSunrise extend obfuscation into a policy-driven, auditable, and compliance-aligned process that integrates with data masking and compliance workflows.
What Is Data Obfuscation?
Data obfuscation deliberately alters sensitive data so unauthorized users cannot interpret or misuse it. While the database still stores original values, users only see or export transformed output.
In practice, organizations commonly apply obfuscation to the following data types:
- Personally identifiable information (PII)
- Financial and payment data
- Authentication credentials
- Internal identifiers and reference values
Unlike encryption, obfuscation does not rely on decryption keys at query time. Instead, it enforces visibility rules that determine who can see real values and who receives transformed output based on context. Consequently, this approach aligns closely with modern data masking strategies.
Native Data Obfuscation Options in MariaDB
MariaDB does not provide a dedicated, built-in data obfuscation framework. However, administrators can approximate obfuscation behavior using SQL-level constructs and database design patterns. These approaches rely on views, functions, and privilege separation to limit exposure of sensitive values.
View-Based Obfuscation
One of the most common native approaches is to expose obfuscated values through database views. Instead of granting users access to base tables, access is restricted to views that return transformed output.
Sensitive columns can be masked using string functions, hashing, or conditional expressions.
Example: Partial Masking with a View
Assume a table containing customer data:
/*CREATE TABLE customers (
id INT PRIMARY KEY,
full_name VARCHAR(100),
email VARCHAR(255),
credit_card VARCHAR(20)
);/*
A view can be created to mask sensitive fields:
/*CREATE VIEW customers_masked AS
SELECT
id,
full_name,
CONCAT(
LEFT(email, 2),
'****@****',
SUBSTRING_INDEX(email, '@', -1)
) AS email,
CONCAT('**** **** **** ', RIGHT(credit_card, 4)) AS credit_card
FROM customers;/*
Privileges are then granted on the view rather than the table:
/*GRANT SELECT ON customers_masked TO 'reporting_user'@'%';
REVOKE ALL PRIVILEGES ON customers FROM 'reporting_user'@'%';/*
In this model, users never see raw values, even though the underlying data remains unchanged.
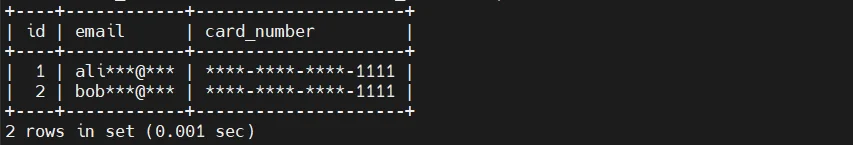
Conditional Obfuscation Using Views
Views can also implement conditional logic based on the connected database user.
/*CREATE VIEW customers_contextual AS
SELECT
id,
full_name,
CASE
WHEN CURRENT_USER() = 'admin@%' THEN email
ELSE 'hidden'
END AS email
FROM customers;/*
This allows limited role-based differentiation but quickly becomes hard to manage as roles and conditions increase.
Function-Based Transformations
MariaDB supports both built-in and user-defined functions that can transform values at query time. These functions can be embedded directly into queries or views.
Example: Hashing Sensitive Values
/*SELECT
id,
full_name,
SHA2(email, 256) AS email_hash
FROM customers;/*
This approach is commonly used for irreversible obfuscation, such as anonymizing identifiers or credentials.
User-Defined Functions for Reusable Logic
Reusable obfuscation logic can be wrapped in a function:
/*DELIMITER //
CREATE FUNCTION mask_email(email VARCHAR(255))
RETURNS VARCHAR(255)
DETERMINISTIC
BEGIN
RETURN CONCAT(
LEFT(email, 2),
'****@****',
SUBSTRING_INDEX(email, '@', -1)
);
END//
DELIMITER ;/*
The function can then be used consistently across queries or views:
/*SELECT
id,
full_name,
mask_email(email) AS email
FROM customers;/*
Session-Aware Transformations
MariaDB allows transformations based on session variables or connection context.
/*SET @masking_enabled = 1;
SELECT
id,
full_name,
IF(@masking_enabled = 1, '***', email) AS email
FROM customers;/*
This provides flexibility but relies entirely on correct session handling by applications.
Operational Considerations
Native obfuscation approaches in MariaDB are implemented entirely at the SQL layer. As a result, they depend on disciplined privilege management, consistent query usage, and careful coordination between database and application teams.
While effective for simple scenarios, these techniques require manual maintenance as schemas, roles, and access patterns evolve.
Centralized Data Obfuscation for MariaDB with DataSunrise
DataSunrise introduces an external security layer that enforces data obfuscation independently of database schemas and application logic. Obfuscation rules are applied transparently as queries are processed, without modifying MariaDB objects or rewriting SQL. This approach fits naturally into broader data security
and database security architectures.
This architecture allows obfuscation to function as a security control rather than a database design pattern. Protection logic is centralized, versioned, and enforced consistently across environments, alongside other controls such as dynamic data masking.
Dynamic Data Obfuscation
Dynamic obfuscation is applied in real time as queries are executed. The same column can appear obfuscated or unobfuscated depending on execution context.
Decisions can be based on factors such as database user, role, client IP address, application source, or session attributes. This enables controlled access scenarios where applications retrieve real values while analysts or support teams receive masked output, without altering SQL logic or database schemas.
Static Obfuscation Workflows
Static obfuscation is applied during controlled workflows such as database cloning, backup restoration, or test data provisioning.
In these scenarios, sensitive values are permanently transformed before data is shared or reused. This approach is commonly used for development, QA, analytics, and external data exchange, and aligns closely with structured static data masking processes.
Sensitive Data Discovery as the Foundation
Effective obfuscation starts with understanding what data requires protection.
DataSunrise automatically scans MariaDB schemas to identify sensitive data based on content and patterns rather than column names. Discovered fields are classified into sensitivity categories using automated data discovery techniques that remain effective as schemas evolve.
As new tables or columns are introduced, they are automatically included in protection policies without requiring manual rule updates.
Policy-Driven Obfuscation Rules
Instead of configuring rules per column or per table, DataSunrise allows obfuscation policies to be applied at the data category level.
Once defined, these policies automatically cover all matching fields across databases and schemas. This ensures consistent protection even as database structures change and reduces long-term maintenance overhead.
Typical transformations include partial masking of emails and phone numbers, format-preserving substitution for financial values, tokenization of identifiers, and irreversible hashing of credentials.
Auditable Obfuscation and Activity Visibility
Every obfuscated query is logged as part of a unified activity trail. Audit records capture which user accessed the data, which columns were involved, whether obfuscation was applied, and when and from where the access occurred.
This visibility directly connects data protection with database activity monitoring and supports forensic analysis, internal investigations, and compliance reporting.
Compliance Alignment
Data obfuscation plays a central role in meeting regulatory requirements that restrict exposure of sensitive data. Centralized obfuscation supports alignment with frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX by enforcing least-exposure principles and producing verifiable access records.
Automated reporting integrates obfuscation controls into broader regulatory compliance workflows, allowing teams to demonstrate protection coverage across MariaDB environments without relying on manual evidence collection.
Business Impact of Centralized Obfuscation
| Business Impact Area | Description |
|---|---|
| Reduced data exposure risk | Centralized obfuscation minimizes the likelihood of accidental disclosure of sensitive values by enforcing consistent protection across all access paths. |
| Safe non-production data usage | Production data can be reused in development, testing, and analytics environments without exposing real sensitive information. |
| Simplified compliance audits | Auditors can verify obfuscation policies and access controls through centralized logs and reports instead of reviewing scattered SQL logic. |
| Lower operational overhead | Obfuscation rules are defined once and applied consistently, eliminating the need to maintain masking logic across queries, views, and applications. |
| Clear separation of responsibilities | Security teams manage obfuscation policies independently, while application developers continue working with stable database schemas and queries. |
Conclusion
MariaDB environments often require flexible access to shared data without exposing sensitive values. While native SQL techniques can support basic obfuscation scenarios, centralized enforcement provides a more consistent and scalable approach.
By applying obfuscation transparently and independently of database schemas, DataSunrise turns data obfuscation into an auditable, policy-driven security control that integrates seamlessly with broader data protection strategies. This allows organizations to protect sensitive data while preserving operational flexibility and compliance readiness.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now