Data Obfuscation in Percona Server for MySQL
Data obfuscation in Percona Server for MySQL provides a practical way to reduce data exposure without redesigning schemas or rewriting applications. While encryption protects data at rest and auditing records access after execution, obfuscation directly limits what users see at query time. As a result, it prevents sensitive values from appearing in query results while preserving application behavior and query logic. This approach naturally complements broader data security practices.
In practice, teams apply this technique in environments where developers, analysts, support engineers, or external services reuse production data. However, strict access controls alone do not solve the problem. Once the database allows a query, it returns raw values by default. Obfuscation changes this behavior by transforming output data while maintaining structural integrity, data types, and relationships.
Therefore, alongside audit trails and data activity history, obfuscation plays a direct and active role in enforcing data security and compliance strategies.
What Data Obfuscation Means in MySQL Context
In Percona Server for MySQL, data obfuscation actively transforms sensitive values into non-meaningful representations while preserving formats, data types, and relational structure. Teams commonly use this technique to protect personally identifiable information and other high-risk data categories.
Obfuscated data follows several core principles:
- The transformation prevents reconstruction of the original value
- Queries continue to execute without modification
- Indexes, joins, and constraints remain intact
- Applications consume data without requiring changes
Because of this behavior, organizations rely on obfuscation to protect credentials, identifiers, and business-critical attributes that must remain hidden outside restricted roles defined by role-based access control policies.
Unlike data masking, which often exposes partial values for usability, obfuscation fully replaces sensitive data with deterministic or randomized substitutes. Consequently, it removes the possibility of inference or reverse reconstruction.
Native Obfuscation Techniques in Percona Server for MySQL
Percona Server for MySQL does not include a dedicated obfuscation engine. Instead, obfuscation is implemented using native SQL constructs. These methods are effective in controlled scenarios but require careful design, consistent privilege management, and ongoing maintenance.
Obfuscation with Views
Views are the most common native technique. Sensitive columns are transformed using SQL expressions while the underlying table remains unchanged.

This approach works well for read-only access and reporting use cases. However, it does not protect direct access to the base table and must be recreated or adjusted for each schema or role that requires obfuscated data.
Generated Columns for Persistent Obfuscation
Generated columns allow obfuscated values to be stored alongside original data while preserving deterministic behavior.
-- Add a generated column with an obfuscated value
ALTER TABLE customers
ADD obfuscated_email VARCHAR(64)
GENERATED ALWAYS AS (
SHA2(email, 256)
) STORED;
-- Query using the generated obfuscated column
SELECT
id,
obfuscated_email,
created_at
FROM customers;
This method enables applications or reports to reference obfuscated data directly without recalculating transformations at query time. However, the original column still exists and remains readable unless access is explicitly restricted.
Role-Based Exposure Control
Views and generated columns are typically combined with role-based privileges to limit exposure.
-- Create a role for analysts
CREATE ROLE analyst_role;
-- Grant access only to the obfuscated view
GRANT SELECT ON obfuscated_customers TO analyst_role;
-- Explicitly deny access to the base table
REVOKE SELECT ON customers FROM analyst_role;
-- Assign the role to a user
GRANT analyst_role TO 'analyst_user'@'%';
This model depends entirely on correct privilege configuration. Users with elevated privileges can still bypass obfuscation by querying base tables directly, making this approach fragile in environments with shared administrative access.
Centralized Data Obfuscation with DataSunrise
DataSunrise enforces data obfuscation externally, without modifying database schemas or application queries. Obfuscation rules are applied transparently as queries pass through the platform, ensuring sensitive values are transformed before results are returned to the client.
This approach follows the same architectural model used for centralized audit trails, database activity monitoring, and compliance enforcement.
Architectural Placement of Obfuscation Controls
DataSunrise operates as an intermediary layer between database clients and Percona Server for MySQL. Depending on deployment mode, it functions as a proxy, agent-based interceptor, or traffic inspection layer.
In all cases, obfuscation is enforced outside the database engine. Sensitive data never reaches unauthorized consumers, even if they are allowed to execute queries. The database itself remains unchanged.
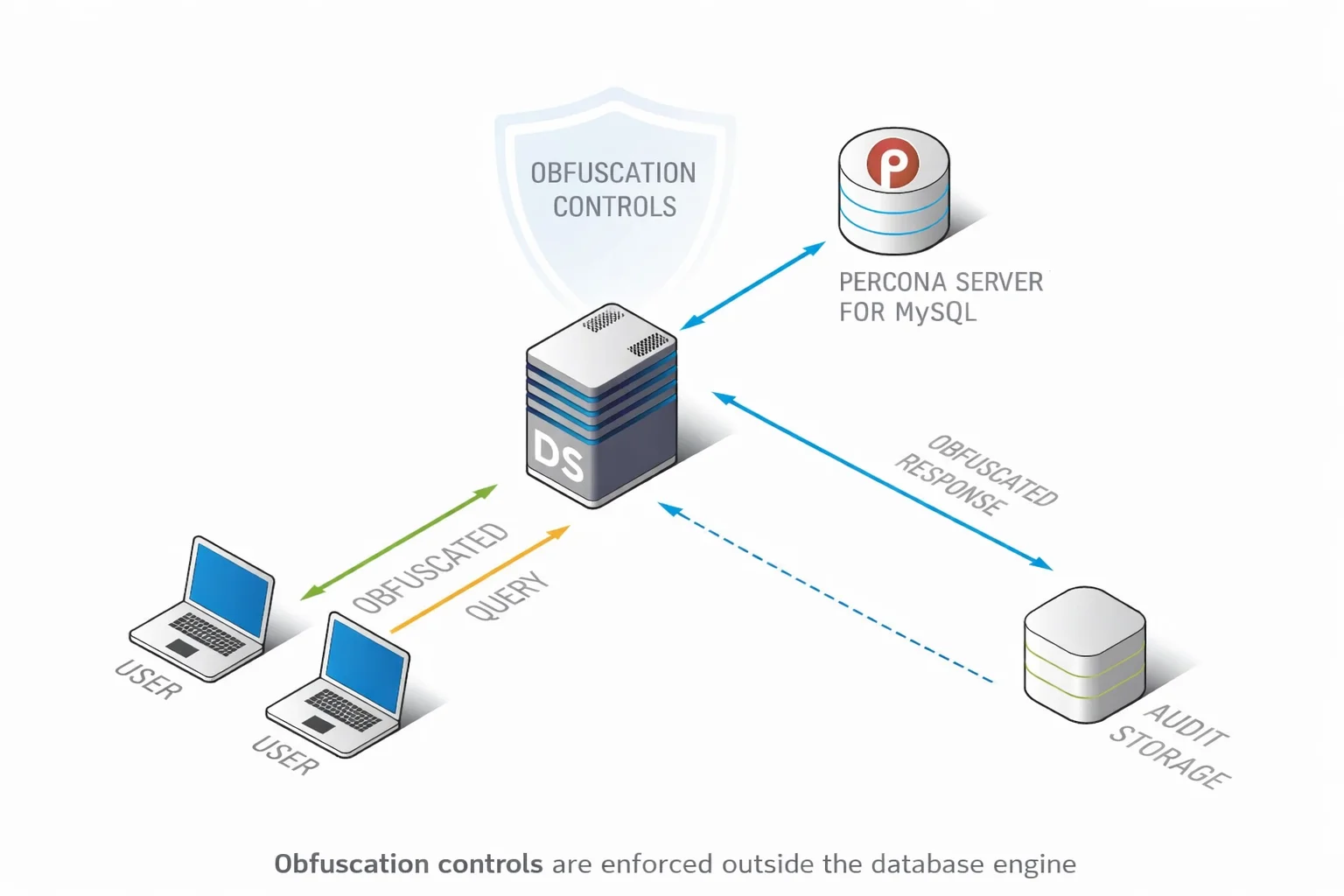
How Obfuscation Is Enforced at Runtime
Incoming queries are inspected in real time. Obfuscation rules are evaluated using contextual signals such as user identity, access privileges, request origin, query characteristics, and detected data sensitivity.
When a rule applies, DataSunrise dynamically transforms the result set while preserving data types and query structure. Clients receive usable but non-sensitive data. The database engine remains unaware that obfuscation has occurred.
Policy-Based and Context-Aware Enforcement
Obfuscation rules are defined centrally and managed independently from database schemas. Policies can target specific tables, columns, or classified data categories and can vary by user role or access scenario.
This enables different representations of the same data to be returned simultaneously to different users or services. Policy changes take effect immediately without redeploying SQL objects or modifying applications.
Visibility and Audit Alignment
All obfuscated access events are fully visible in DataSunrise audit logs and activity history views. Security teams can correlate data access with applied obfuscation rules, closing a common visibility gap found in native implementations.
Obfuscation becomes a first-class, auditable control rather than an opaque SQL transformation.
Advantages of Centralized Obfuscation
| Aspect | Native Obfuscation (SQL-Based) | Centralized Obfuscation |
|---|---|---|
| Enforcement location | Embedded in views and SQL logic | External enforcement layer |
| Policy management | Scattered across schemas | Centrally defined policies |
| Schema dependency | Requires views or generated columns | No schema or query changes |
| Context awareness | Static and object-bound | Context-aware and adaptive |
| Bypass risk | Can be bypassed by privileged users | Enforced regardless of DB privileges |
| Audit visibility | Limited and indirect | Fully visible in audit trails |
| Scalability | Hard to maintain at scale | Consistent across environments |
This approach removes the fragility of SQL-based obfuscation and allows protection to scale cleanly across development, staging, and production systems.
Conclusion
Data obfuscation in Percona Server for MySQL addresses a problem that neither encryption nor auditing solves alone. It controls what users actually see after access has been granted, complementing broader database security strategies.
Native SQL techniques can cover limited scenarios but are difficult to govern at scale. Centralized obfuscation moves enforcement out of database schemas and into a managed control plane aligned with auditing, database activity monitoring, and compliance workflows.
When combined with audit trails and data activity history, obfuscation closes the final visibility gap by ensuring sensitive data is never exposed, even to authorized users.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now