
Data Scrambling

Introduction
In today’s data-driven world, protecting sensitive information is of utmost importance. Data breaches and unauthorized access to confidential data can lead to severe consequences for individuals and organizations alike. This is where data scrambling comes into play.
Data scrambling is a technique used to obfuscate sensitive data while preserving its original format, structure, and usability. This article explains data scrambling basics, various techniques, and tips for implementing it in your organization.
What is Data Scrambling?
Data scrambling, also known as data masking, replaces sensitive information with fake data to protect privacy. The goal is to protect the original data while maintaining its utility for testing, development, or analytics purposes. Scrambled data resembles the original data and is usable in non-production environments.
For instance, imagine a database with customer details. You can employ data scrambling techniques instead of using real names, addresses, and credit card numbers in development or QA environments.
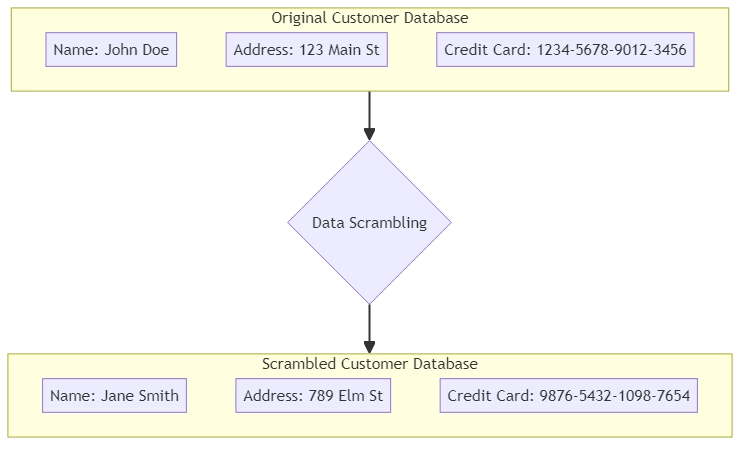
These methods replace the sensitive data with randomly generated values that mimic the original information.
Data Scrambling vs Data Masking
While often used interchangeably, data scrambling and data masking have important distinctions. Data scrambling primarily focuses on randomizing or rearranging data while maintaining format. It typically involves irreversible transformations and is commonly used for test data preparation where exact values are less important than maintaining statistical properties.
In contrast, data masking emphasizes replacing sensitive data with functional, realistic-looking substitute values that “preserve the look and feel of the data while hiding sensitive information.” Unlike scrambling, masking can be partially or fully reversible for authorized users and is often employed in production environments where maintaining data structure and referential integrity is crucial.
Both techniques are recognized in compliance frameworks like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. Many organizations implement both as part of a comprehensive data security framework, applying the appropriate method based on the specific context and sensitivity of the data being protected.
Why is Data Scrambling Important?
Data scrambling plays a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive information and ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations. Here are some key reasons why data scrambling is essential:
- Protecting sensitive data: By replacing sensitive data with fictitious values, data scrambling helps prevent unauthorized access to confidential information. Even if the scrambled data falls into the wrong hands, it does not reveal any real sensitive details.
- Compliance with regulations: Many industries are subject to strict data privacy regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS. Data scrambling helps organizations comply with these regulations by de-identifying sensitive data before using it for testing, development, or analytics purposes.
- Enabling realistic testing and development: Scrambled data resembles the original data. Developers and testers can use it to work with data that is similar to production data. This ensures that testing is more accurate and reduces the risk of issues when deploying the application to production.
- Reducing breach impact during data leaks: In the event of a data leak, scrambled data reduces the likelihood of exposing real, sensitive information, mitigating potential damage.
- Facilitating data sharing: Data scrambling allows organizations to share data with outside parties, like partners or vendors, without risking the privacy of sensitive information. Users can use the scrambled data for collaboration or analyzing while maintaining the confidentiality of the original data.
Real-World Use Cases of Data Scrambling
Data scrambling is widely adopted across various industries to protect sensitive information while enabling operational needs. Here are some examples of how organizations use data scrambling in practice:
- Healthcare: Patient records containing personal health information (PHI) are scrambled to enable safe testing and development of medical software without exposing real patient data.
- Financial Services: Banks and payment processors scramble credit card numbers and transaction details to protect customer data during application testing and analytics, helping maintain compliance with PCI-DSS standards.
- Retail: Retailers scramble customer names, addresses, and purchase histories to share data securely with third-party vendors or marketing partners without risking privacy breaches.
- Government Agencies: Sensitive citizen data is scrambled to facilitate internal data analysis and research while complying with data protection regulations.
These real-world applications demonstrate how data scrambling helps organizations balance data privacy with operational requirements, enabling secure and effective use of sensitive information.
Scrambler Techniques
Various techniques use data scrambling, each with its own strengths and use cases. Let’s explore some common scrambler techniques:
1. Substitution
In substitution, we replace sensitive data with random values from a set or pattern. For example, you can change names to made-up names from a list. You can also replace credit card numbers with syntactically valid numbers that pass format checks (like the Luhn algorithm) but do not correspond to real accounts.
Example:
Original data: John Doe, 1234-5678-9012-3456 Scrambled data: Jane Smith, 9876-5432-1098-7654
2. Shuffling
Shuffling involves rearranging the order of data values within a column or across multiple columns. This technique maintains the original data distribution but breaks the relationship between different columns. Shuffling is useful when preserving the statistical distribution is important, but the individual value-to-record associations are not.
Example: Original data:
Name Age Salary John Doe 35 50000 Jane Doe 28 60000
Scrambled data (Age and Salary columns shuffled):
Name Age Salary John Doe 28 60000 Jane Doe 35 50000
3. Encryption
Encryption involves converting sensitive data into an unreadable format using an encryption algorithm and a secret key. You can only decrypt the scrambled data back to its original form using the corresponding decryption key. Encryption provides a high level of security but may impact performance, and unlike scrambling, it requires real-time key management for encryption/decryption processes.
Example:
Original data: John Doe Scrambled data: a2VsZmF0aG9uIGRvb3IgZ
4. Tokenization
Tokenization replaces sensitive data with a randomly generated token or identifier. The system securely stores the sensitive data in a separate database or vault. The user then uses the token to retrieve the original information when needed. Companies commonly use tokenization to protect credit card numbers and other sensitive financial data. Tokenization is especially valuable in industries handling payment data, such as finance and retail, and is often used in compliance with PCI-DSS standards.
Example:
Original data: 1234-5678-9012-3456 Scrambled data: TOKEN-1234
5. Masking
Three common masking techniques include character masking, partial masking, and regular expression masking. Character masking involves replacing characters with a symbol. Partial masking shows only part of the data. Regular expression masking replaces data based on a pattern.
Example:
Original data: 1234-5678-9012-3456 Masked data: XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-3456
Data Scrambling Best Practice
To effectively implement data scrambling in your organization, consider the following best practices:
- Identify sensitive data: Perform a comprehensive examination of your data environment to pinpoint sensitive data components that necessitate obfuscation. Consider legal and regulatory requirements, as well as your organization’s internal data classification policies.
- Choose appropriate scrambler techniques: Select the most suitable scrambling or encryption method depending on the type of data and its intended use. Consider factors such as data format, complexity, and the level of security required.
- Maintain data consistency: Ensure that the scrambled data maintains referential integrity and consistency across related tables and systems. Use consistent scrambling techniques, seed values, and rules to ensure reproducibility where necessary.
- Protect scrambling algorithms and keys: Safeguard the algorithms, rules, and encryption keys used for data scrambling. Store them securely and restrict access to authorized personnel only.
- Test and validate scrambled data: Carefully examine the jumbled data to ensure it adheres to the required format, quality, and uniformity standards. Ensure that the scrambled data does not include any confidential information and is suitable for its intended use.
- Establish access controls: Use strict controls and monitoring to stop unauthorized access to sensitive data and scrambled data. Regularly review and update access permissions.
- Document and maintain scrambling processes: Document the process of data integration, including the volume of data involved and any specific configurations or guidelines. Maintain version control and keep the documentation up to date.
- Audit and monitor scrambling usage: Periodically audit the use of data scrambling to ensure compliance, detect misuse, and verify that the techniques remain effective against emerging data threats.
Conclusion
Data scrambling is an effective technique for protecting sensitive information while still enabling its use in testing, development, and analytics. By substituting real data with realistic yet fictitious values, organizations can safeguard confidential details, ensure compliance with data privacy laws, and enable secure data sharing.
When implementing data scrambling, it is crucial to select methods that correspond to the data’s sensitivity, structure, and intended purpose. Adhering to best practices—such as maintaining data consistency, securing algorithms and encryption keys, and enforcing strict access controls—will help keep your data safe.
Incorporating data scrambling into your overall data protection strategy allows you to strike the right balance between data utility and privacy, fostering trust among your customers and stakeholders while making effective use of your data.
