Database Audit for Databricks SQL
Databricks SQL has emerged as a core analytical database layer for modern lakehouse architectures, enabling organizations to run business intelligence, reporting, and ad-hoc analytics directly on cloud data lakes. As adoption grows, organizations increasingly treat database audit for Databricks SQL as a foundational requirement for security, governance, and regulatory compliance.
Unlike traditional relational databases, Databricks SQL operates in a distributed and cloud-native environment. Queries execute across elastic compute resources, while identities rely on cloud IAM and SSO providers. Consequently, audit signals often scatter across services, which complicates end-to-end visibility.
This article explains how auditing in Databricks SQL works in practice, reviews native audit capabilities, outlines their limitations, and shows how centralized platforms such as DataSunrise deliver unified visibility, investigations, and compliance-ready audit trails.
Why Database Auditing Matters in Databricks SQL
Database auditing extends far beyond basic logging. In practice, an effective audit process must answer essential questions with precision: who accessed the database, which SQL statements ran, what objects were affected, and whether activity aligned with internal policies.
For environments processing regulated or sensitive data, these questions directly affect risk exposure. Therefore, regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX require organizations to demonstrate verifiable control over database activity.
For this reason, a structured database audit approach ensures that analytical flexibility never undermines accountability or traceability.
Database Audit Architecture for Databricks SQL
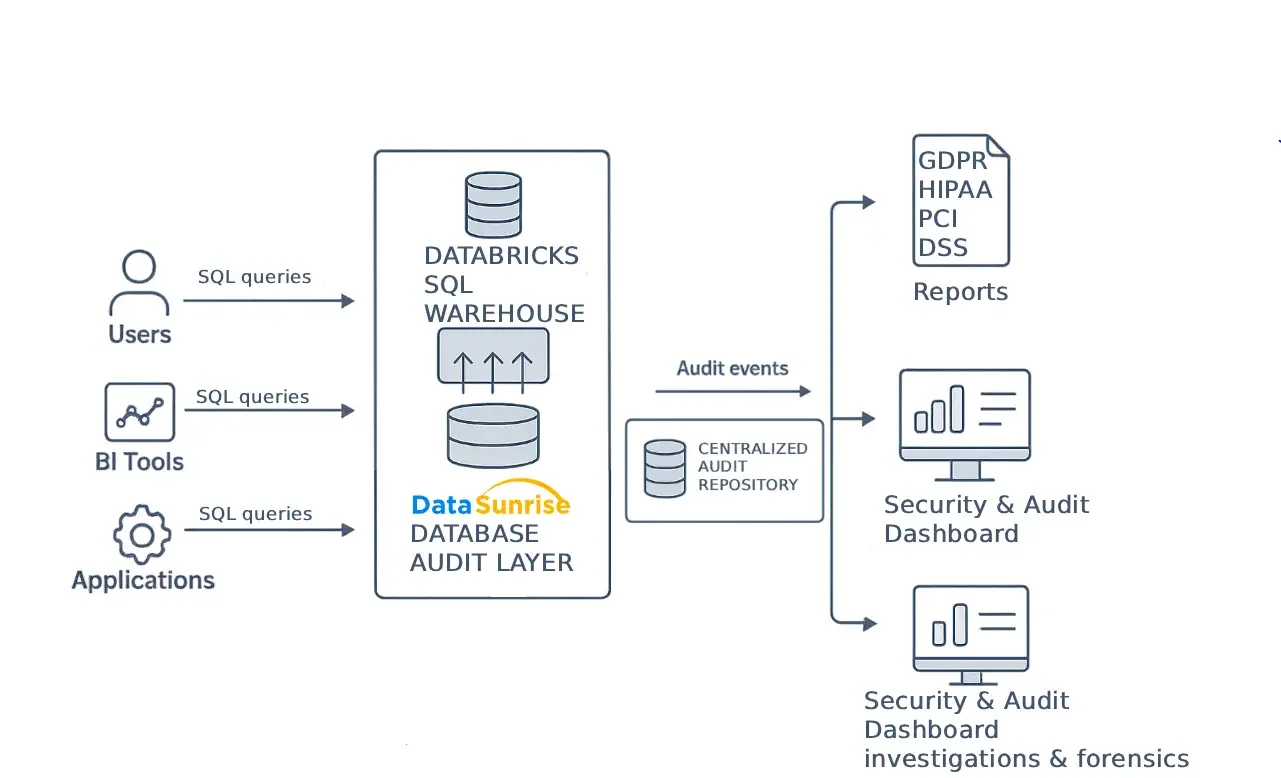
Database audit architecture for Databricks SQL illustrating centralized capture, storage, monitoring, and compliance reporting.
The architecture begins with multiple SQL query sources, including users, BI tools, and applications. These clients submit SQL queries to the Databricks SQL warehouse, where distributed compute resources process each request.
Alongside the execution layer, a dedicated DataSunrise audit layer operates transparently. Rather than relying solely on fragmented native logs, this layer captures SQL activity in real time and mirrors audit events without affecting performance.
After enrichment and correlation, the system forwards audit events to a centralized audit repository. From there, teams access dashboards for monitoring, workflows for investigations, and structured reports for regulatory reviews.
Native Audit Capabilities in Databricks SQL
Databricks provides native audit logs that record workspace-level and SQL-level activity. Typically, these logs include executed queries, timestamps, user identities, and operation types. Organizations often export native logs to external platforms such as Azure Log Analytics, Amazon CloudWatch, or Google Cloud Logging.
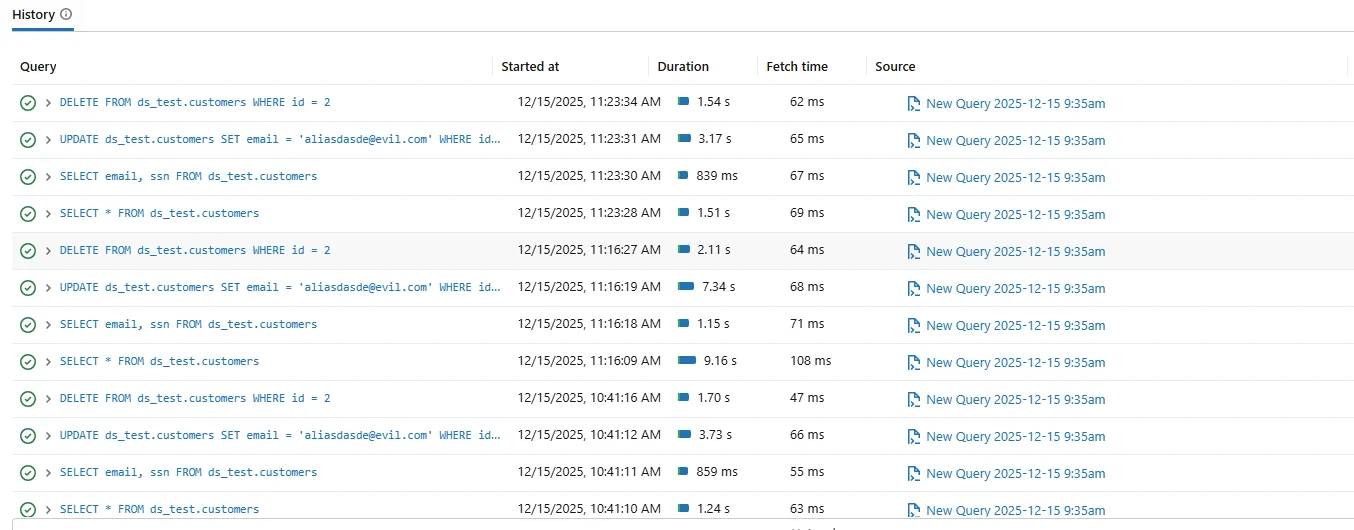
Native Databricks SQL audit history showing platform-level query execution events.
Although native logs provide baseline visibility, they introduce limitations. For example, correlation across users and sessions often requires manual effort. In addition, retention and reporting responsibilities fall outside the database platform itself.
As a result, native logging alone rarely satisfies enterprise-grade database auditing requirements.
Operational Risks of Relying Only on Native Logs
When organizations depend exclusively on native logs, operational risks increase. Security teams may overlook suspicious patterns because activity remains distributed. Meanwhile, compliance teams struggle to reconstruct historical events during audits.
As Databricks SQL environments scale across teams and workloads, database activity volumes grow rapidly. Without centralized auditing, visibility declines while investigation complexity rises.
Therefore, database activity monitoring and centralized audit trails become essential components of a mature governance strategy.
DataSunrise Database Audit for Databricks SQL
DataSunrise delivers a centralized database audit layer designed for distributed analytics platforms. In Databricks SQL environments, the platform captures SQL activity in real time and consolidates it into a unified audit trail.
Each database operation is recorded with enriched metadata, including user identity, query type, execution timing, and session context. Subsequently, DataSunrise stores normalized records in a centralized repository for monitoring, investigations, and compliance reporting.
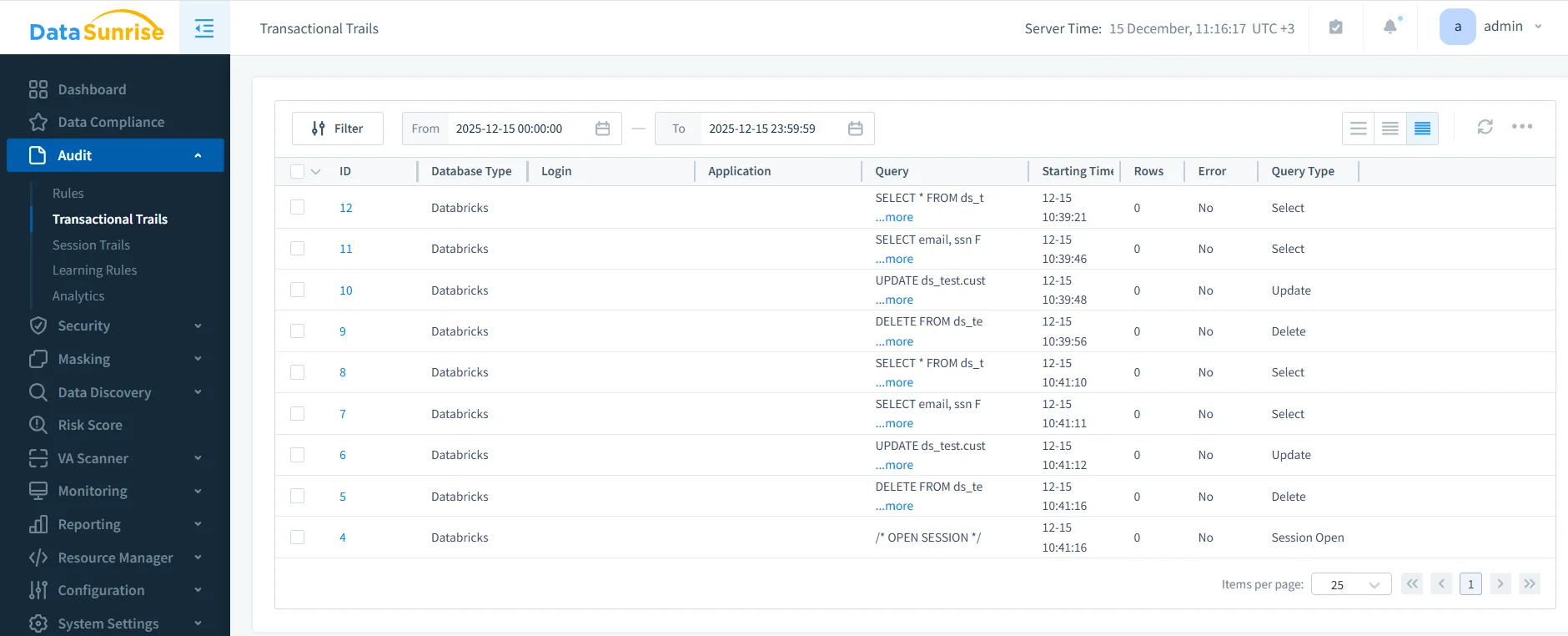
DataSunrise transactional trails providing a centralized and chronological view of Databricks SQL activity.
With this centralized approach, organizations gain:
- Centralized audit logs across analytical environments
- Detailed audit trails for investigations and forensics
- Continuous database activity monitoring
- Automated compliance evidence generation
Native Audit vs Centralized Database Audit
| Capability | Native Databricks SQL Audit | Centralized Audit with DataSunrise |
|---|---|---|
| Audit scope | Platform-level logs | Full database activity context |
| Correlation | Manual analysis | Automatic cross-session correlation |
| Retention | External log systems | Centralized audit repository |
| Investigations | Log reconstruction | Structured forensic workflows |
| Compliance reporting | Custom scripts | Automated regulatory reports |
Compliance and Governance Benefits
Database auditing in Databricks SQL plays a foundational role in regulatory compliance. Auditors expect organizations to demonstrate that controls operate consistently and produce verifiable evidence.
By integrating auditing with Data Compliance and Regulatory Compliance frameworks, organizations reduce audit friction and improve governance maturity.
As a result, centralized database auditing supports long-term retention, structured reporting, and faster responses to audit requests.
Conclusion: Building Reliable Database Auditing in Databricks SQL
Databricks SQL delivers scalable analytics; however, enterprise adoption requires strong governance. Although native audit logs provide a starting point, they lack the depth required for comprehensive database auditing.
A reliable auditing strategy for Databricks SQL requires centralized visibility, enriched context, and compliance-ready reporting. Platforms such as DataSunrise transform raw SQL activity into structured audit intelligence that supports monitoring, investigations, and regulatory alignment.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now