Databricks SQL Audit Tools
Databricks SQL is widely used as an analytical query engine in lakehouse architectures, supporting dashboards, exploratory analytics, and automated workloads. As more teams and applications rely on shared Databricks SQL warehouses, organizations must ensure that database activity is visible, traceable, and auditable. This need has driven growing interest in Databricks SQL audit tools.
Audit tools provide the mechanisms required to observe database activity, capture execution details, and retain records for security investigations and compliance audits. In Databricks SQL environments, these tools range from native logging capabilities to external platforms that provide centralized auditing, correlation, and reporting.
This article reviews the available audit tools for Databricks SQL, explains what each approach can and cannot do, and shows how DataSunrise extends native auditing with enterprise-grade audit tooling.
What Are Audit Tools in Databricks SQL?
Audit tools are systems and mechanisms used to record and analyze database activity. In the context of Databricks SQL, audit tools capture executed SQL statements along with metadata such as user identity, execution time, query type, and execution outcome.
Unlike basic query history views, audit tools are designed to support long-term retention, correlation, and structured analysis. They help answer questions such as who accessed specific data, when changes occurred, and whether access aligned with security and compliance policies.
Audit tools play a critical role in meeting regulatory requirements under frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX.
Native Databricks SQL Audit Tools
Databricks SQL includes native capabilities for reviewing query execution. The platform exposes a query history that displays executed statements, start time, duration, execution status, and the user who initiated each query.
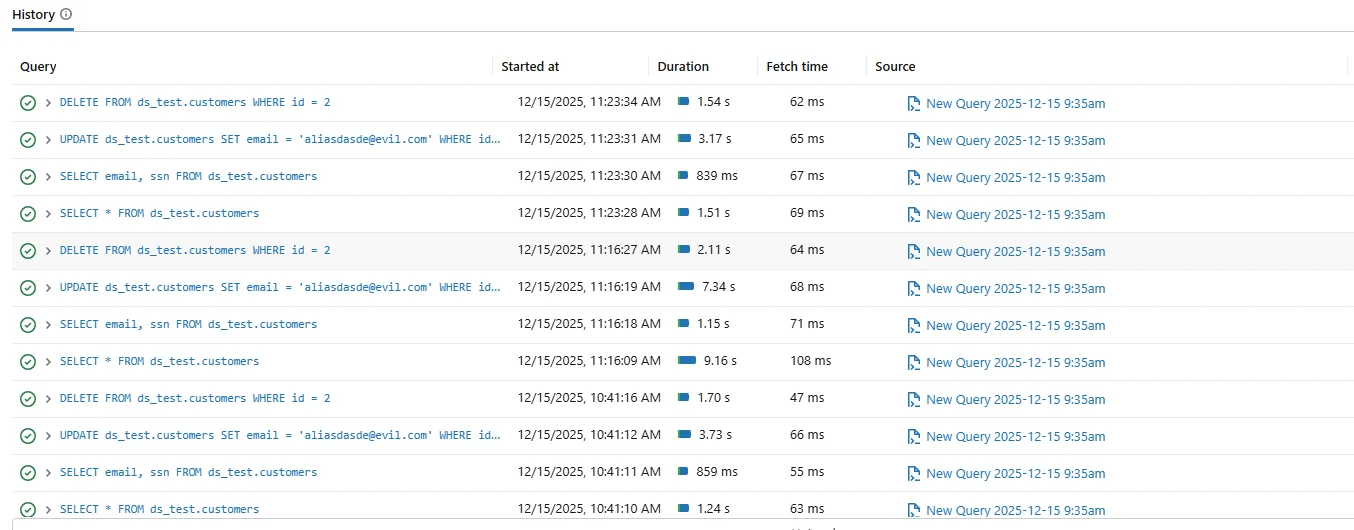
Native Databricks SQL query history used as a basic audit tool for reviewing executed SQL statements.
These native audit tools are useful for short-term troubleshooting and operational review. Administrators can quickly inspect recent activity to identify failed queries or performance issues.
However, native tools are limited in scope. Retention is typically short, correlation across sessions is minimal, and logs are not optimized for long-term audit evidence. As a result, organizations often export native logs to external platforms such as Azure Log Analytics or Amazon CloudWatch.
Limitations of Native Audit Tools
While native Databricks SQL audit tools provide basic visibility, they are not designed for enterprise auditing. They focus on individual query execution rather than structured audit workflows.
Native tools typically lack centralized storage, immutable records, and built-in reporting aligned with compliance requirements. In addition, reconstructing multi-step workflows or user sessions often requires manual analysis.
For organizations operating in regulated environments, these limitations increase audit effort and operational risk.
Centralized Audit Tools for Databricks SQL
Centralized audit tools extend Databricks SQL auditing by collecting SQL activity in real time and storing it in a unified repository. These tools capture events as they occur and enrich them with additional context.
DataSunrise acts as a centralized audit tool for Databricks SQL by capturing SQL activity across users and applications and normalizing it into structured audit records.
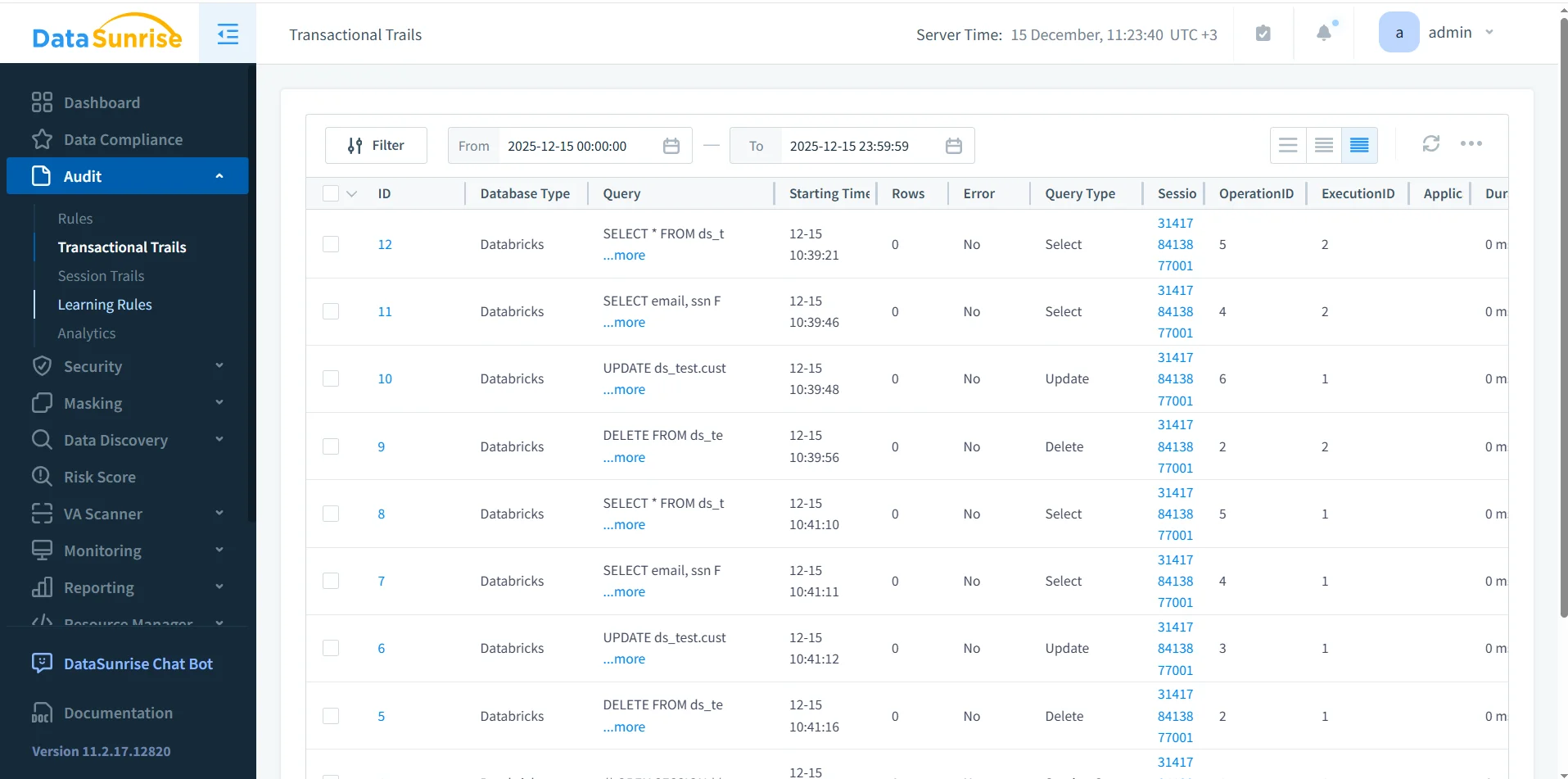
Centralized Databricks SQL audit tools in DataSunrise showing correlated and searchable audit records.
Each audit record includes query text, execution timing, query category, session identifier, user identity, and execution result. This enriched data allows teams to perform investigations and compliance reviews without manually stitching logs together.
Comparison of Databricks SQL Audit Tools
| Capability | Native Databricks Tools | Centralized Audit Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Query visibility | Recent execution only | Real-time and historical |
| Retention | Limited | Configurable long-term storage |
| Session correlation | Manual | Automatic |
| Compliance reporting | Not available | Built-in and automated |
| Investigation readiness | Low | High |
Operational Use Cases for Audit Tools
Databricks SQL audit tools support a range of operational scenarios. Security teams use them to investigate suspicious access and validate access controls. Database administrators rely on audit tools to analyze query behavior and detect misuse.
Audit tools also help organizations improve governance by enforcing the principle of least privilege and supporting continuous database activity monitoring.
Audit Tools and Compliance Alignment
| Regulation | Audit Requirement | Audit Tool Support |
|---|---|---|
| GDPR | Tracking access to personal data | User-attributed audit records |
| HIPAA | Monitoring access to sensitive records | Query-level audit logs |
| PCI DSS | Auditing database interactions | Centralized and retained logs |
| SOX | Auditability of data changes | Immutable audit history |
Choosing the Right Audit Tools
Selecting audit tools for Databricks SQL depends on organizational requirements. Native tools may be sufficient for small teams or short-term troubleshooting. However, enterprises with compliance obligations typically require centralized audit tools.
Centralized audit tools reduce manual effort, improve visibility, and provide consistent audit evidence across environments.
Conclusion: Using Databricks SQL Audit Tools Effectively
Databricks SQL audit tools provide essential visibility into database activity. Native tools offer a basic starting point, while centralized audit tools deliver the depth required for investigations and compliance.
By combining Databricks SQL with centralized auditing platforms such as DataSunrise, organizations gain structured, searchable, and compliance-ready audit records.
Effective use of Databricks SQL audit tools enables secure operation, transparent governance, and confident regulatory alignment.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now