How to Apply Data Governance for Apache Cassandra
Introduction
Apache Cassandra is a distributed NoSQL database known for handling large-scale, mission-critical workloads across clusters and multiple datacenters. With its high availability and fault tolerance, Cassandra is often deployed in environments where sensitive information such as financial transactions, healthcare records, or customer profiles must be managed responsibly.
This raises the question: how to apply data governance for Apache Cassandra so that organizations stay compliant, secure, and efficient? Data governance in this context means defining, controlling, and monitoring how data is accessed, used, and protected across the system.
Before diving into governance frameworks, you may want to review general concepts of data compliance and regulatory obligations like GDPR or HIPAA.
What Cassandra Offers Out-of-the-Box for Data Governance
Cassandra provides basic governance features, but all are disabled by default and require significant manual configuration, which is mostly done via configuring the cassandra.yaml file. Let's explore what's actually available—and the reality of implementing it.
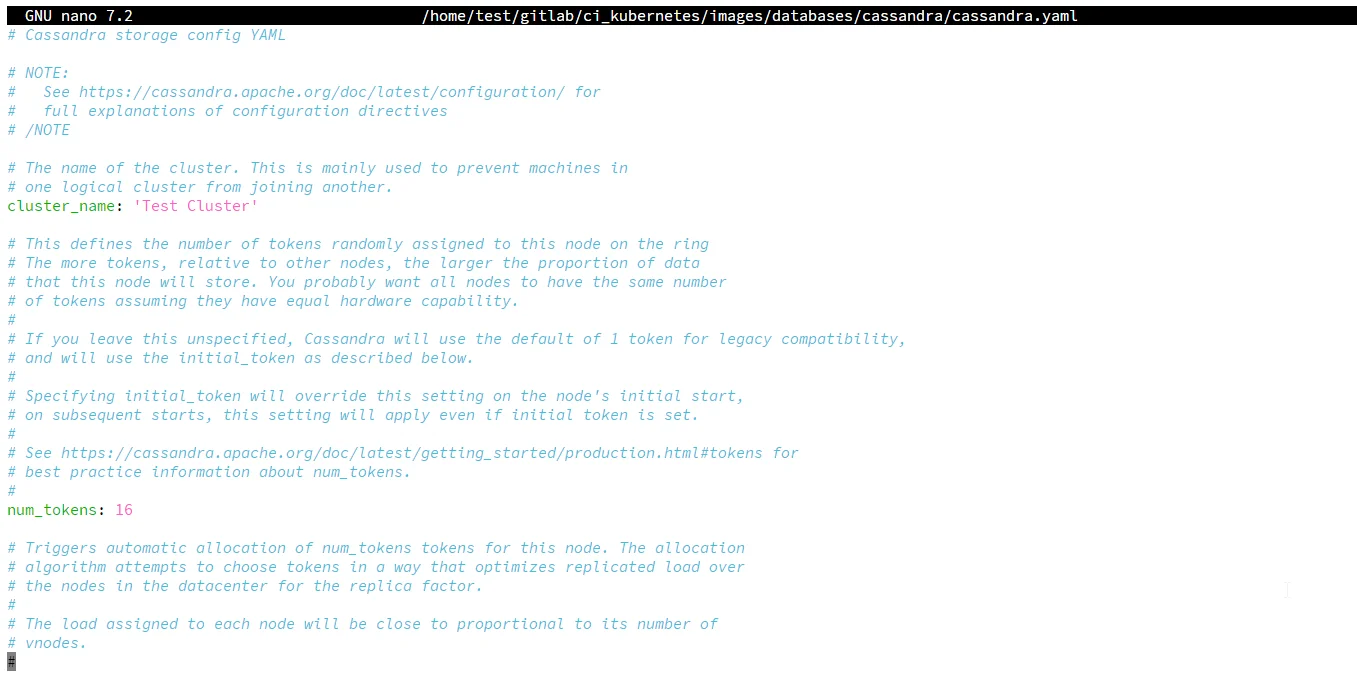
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Important Note: RBAC requires enabling authentication first. Without proper configuration in cassandra.yaml, you'll encounter "You have to be logged in and not anonymous" errors—even as a superuser.
Prerequisites (often undocumented):
# Must edit cassandra.yaml on EVERY node
authenticator: PasswordAuthenticator # Default: AllowAllAuthenticator
authorizer: CassandraAuthorizer # Default: AllowAllAuthorizer
role_manager: CassandraRoleManager
After cluster restart, you can create roles:
-- First, create keyspace (often forgotten in docs)
CREATE KEYSPACE IF NOT EXISTS customer_data
WITH replication = {'class': 'SimpleStrategy', 'replication_factor': 3};
-- Then create role
CREATE ROLE analyst WITH LOGIN = true AND PASSWORD = 'strongPassword';
GRANT SELECT ON KEYSPACE customer_data TO analyst;
Limitations:
- No role hierarchy or inheritance
- No time-based access controls
- No conditional permissions (e.g., "access only during business hours")
- Password changes require manual CQL commands on each node
Audit Logging: Complex and Node-Local
Intended Purpose: Track all database activity for compliance.
Implementation Considerations: Audit logging requires careful configuration and produces node-local binary logs that need aggregation:
audit_logging_options:
enabled: true # Default: false
logger:
- class_name: BinAuditLogger # Correct structure (not just "BinAuditLogger")
audit_logs_dir: /var/log/cassandra/audit # REQUIRED but often missing in examples
included_categories: DML, DDL, AUTH # Must specify what to audit
excluded_keyspaces: system, system_schema # Avoid logging system operations
roll_cycle: HOURLY
block: true # Critical: ensures no audit loss
max_log_size: 17179869184 # 16 GiB limit per file
Major Limitations:
- Logs scattered across every node in binary format
- No built-in log aggregation or centralization
- Doesn't capture failed authentication attempts
- Requires custom tooling to parse and analyze
- No real-time alerting capabilities
Data Masking: Version-Limited and Schema-Dependent
Only in Cassandra 5.0+, and disabled by default:
# Must enable in cassandra.yaml first
dynamic_data_masking_enabled: true # Default: false
After restart, you can create masked tables:
-- Requires keyspace first
CREATE KEYSPACE IF NOT EXISTS healthcare
WITH replication = {'class': 'SimpleStrategy', 'replication_factor': 1};
USE healthcare;
-- Then create masked table
CREATE TABLE patients (
id UUID PRIMARY KEY,
name TEXT MASKED WITH mask_inner(1, null),
birth DATE MASKED WITH mask_default()
);
Critical Limitations:
- Not available in Cassandra 3.x or 4.x (most production deployments)
- Cannot mask existing tables without dropping and recreating
- Masking rules are hardcoded in schema (not dynamic)
- No context-aware masking (same mask for all users)
- Performance impact not well documented
Implementation Challenges and Considerations
Key Considerations: After implementing all native features, organizations often encounter:
| Configuration Complexity | Operational Limitations | Compliance Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Features disabled by default | No unified governance dashboard | Manual retention and policy management |
| Manual YAML editing on every node | Audit logs need custom parsers/aggregation | Reliance on Cassandra-specific tools |
| Cluster restarts for each change | Role management only via CQL commands | Custom report generation required |
| No validation until runtime | Limited enterprise identity integration | Manual data classification and discovery |
For organizations managing multiple databases (MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB alongside Cassandra), maintaining separate governance systems for each becomes unsustainable.
How to Implement Complete Data Governance with DataSunrise
Unlike native Cassandra's fragmented approach, DataSunrise provides a unified governance platform. Here's how to achieve comprehensive governance in just a few steps:
Step 1: Deploy DataSunrise (15 Minutes Installation)
No YAML editing, no restarts, no downtime:
- Install DataSunrise between your applications and Cassandra
- Configure connection to your Cassandra cluster via web interface
- DataSunrise auto-discovers all keyspaces, tables, and columns
Zero Impact: DataSunrise acts as a transparent proxy. Applications continue using the same connection strings—they don't know DataSunrise exists.
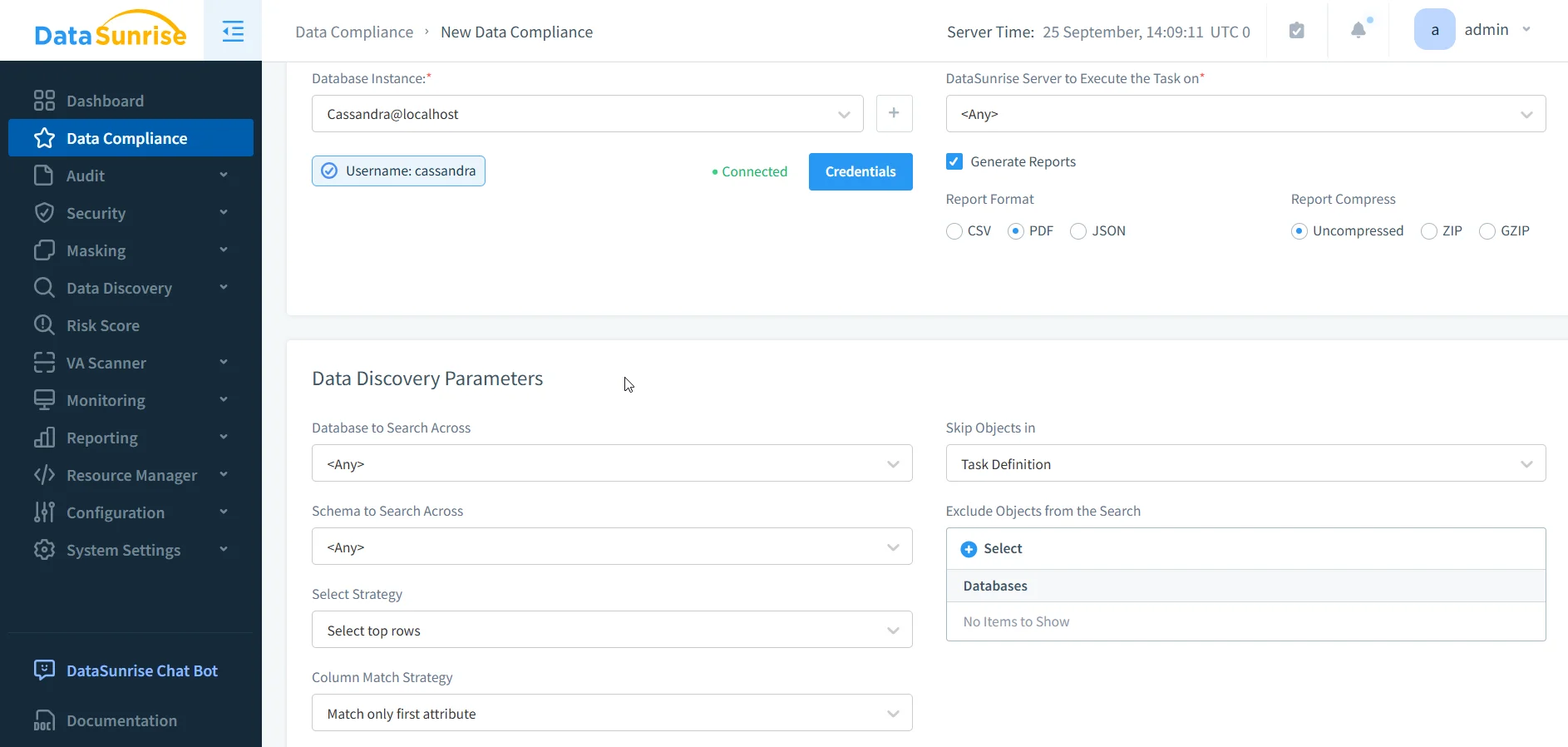
Step 2: Setup Automatic Data Compliance in DataSunrise (5 Minutes Setup)
Simply navigate to "Data Compliance" in the left-side menu, select your target database and the regulations you need to comply with (GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, SOX), and start Data Discovery.
DataSunrise will automatically:
- Detect sensitive data (PII, PHI, PCI, and custom patterns).
- Enable cluster-wide auditing with centralized storage and real-time search.
- Apply dynamic masking policies per role and context.
- Configure security/firewall controls against high-risk queries.
- Generate automated compliance reports, keeping you audit-ready at all times.
Step 3: Generate Compliance Reports (1 Click)
Navigate to Reporting → Report Generation:
- GDPR: Data processing activities, retention policies, access logs
- HIPAA: PHI access audit, encryption status, user activity
- PCI DSS: Cardholder data access, security controls verification
- SOX: Financial data access, change management, segregation of duties
Reports are audit-ready and include all required documentation.
Business Impact of Applying Data Governance
Applying structured data governance with Cassandra and DataSunrise brings measurable benefits:
| Governance Objective | Native Cassandra | With DataSunrise |
|---|---|---|
| Role-based access control | ✅ Basic RBAC | ✅ Advanced RBAC, centralized policies |
| Audit trail | ⚠ Limited detail | ✅ Detailed, exportable, SIEM integration |
| Data masking | ⚠ Partial (5.0+) | ✅ Dynamic, static, consistent |
| Compliance automation | ❌ Manual only | ✅ Pre-built templates & reports |
| Threat detection | ❌ Not available | ✅ Behavior analytics, alerts |
These improvements not only reduce compliance risks but also streamline internal operations and improve trust with customers and auditors.
Conclusion
When planning how to apply data governance for Apache Cassandra, organizations should consider both native features and external governance platforms. While Cassandra offers foundational controls like RBAC, audit logging, and masking, advanced requirements call for an integrated solution.
DataSunrise provides a unified governance framework with automated compliance, detailed auditing, and real-time protection. This combination helps businesses meet regulatory requirements while keeping Cassandra environments efficient, secure, and resilient.
If you’re ready to improve governance across your Cassandra deployment, schedule a demo to explore DataSunrise’s capabilities in action.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now