How to Apply Data Governance for IBM Db2
Introduction
Data governance is the practice of managing how information is accessed, protected, and used inside an organization. It ensures that data remains trustworthy, secure, and aligned with regulatory requirements.
For IBM Db2, governance goes beyond understanding principles — it’s about putting them into action. Applying governance means configuring controls, monitoring activity, reviewing privileges, and ensuring data is handled consistently across environments.
Preparing for Governance in Db2
Before making technical changes, administrators should prepare:
- Define the policies your organization must enforce. Include rules for who can access sensitive information, how long data must be retained, and what kind of audit evidence regulators expect.
- Identify sensitive data across schemas and applications. Db2 provides system catalog views such as
SYSCAT.COLUMNSandSYSCAT.TABLESthat help administrators map where personally identifiable information (PII) or financial data resides. Reviewing these tables early ensures governance measures target the right datasets. - Consider regulatory drivers such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, or SOX. Each introduces different obligations — GDPR emphasizes data minimization, HIPAA requires confidentiality of health records, PCI DSS focuses on cardholder protection, and SOX demands integrity in financial reporting. Db2’s auditing (
db2audit) and monitoring views (SYSIBMADM) align with these requirements to generate the right kind of evidence.
Involve compliance officers and business stakeholders early. Db2 administrators bring technical expertise, but governance succeeds only when technical rules match organizational policy.
Step 1 – Configure Access Controls
Db2 offers Row and Column Access Control (RCAC) and Label-Based Access Control (LBAC). These features let administrators enforce policies directly at the database level.
Example: restrict each doctor to their own patients’ records:
ALTER TABLE patients ACTIVATE ROW ACCESS CONTROL;
CREATE PERMISSION doctor_only
ON patients
FOR ROWS WHERE CURRENT USER = doctor_id
ENFORCED FOR ALL ACCESS
ENABLE;
This ensures users see only their authorized data, a cornerstone of governance.
Step 2 – Enable Activity Monitoring
Governance requires visibility into who is connected and what they are doing. Db2 provides monitoring views such as SYSIBMADM.MON_CONNECTION_SUMMARY.
SELECT
APPLICATION_NAME,
SESSION_AUTH_ID,
TOTAL_APP_COMMITS,
APP_RQSTS_COMPLETED_TOTAL
FROM SYSIBMADM.MON_CONNECTION_SUMMARY;
This query shows current connections, identifying which applications and accounts remain active.
Export session data regularly into a secure repository. Over time, this history reveals unusual access trends that may indicate policy violations.
Step 3 – Review Privileges
Governance also requires knowing who holds elevated roles. Db2 makes this possible with catalog views:
SELECT
GRANTEE,
DBADMAUTH,
SECURITYADMAUTH,
DATAACCESSAUTH
FROM SYSCAT.DBAUTH
WHERE GRANTEETYPE = 'U';
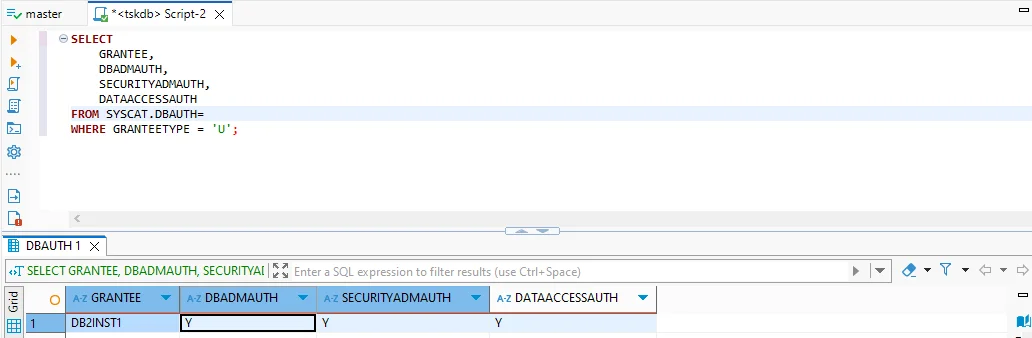
This helps administrators spot accounts with broad privileges and confirm whether they align with governance rules.
Step 4 – Track Data Inventory
Db2’s catalog helps administrators maintain an inventory of tables and row counts. This supports governance by ensuring sensitive data is not overlooked.
SELECT TABNAME, CARD
FROM SYSCAT.TABLES
WHERE TABSCHEMA = 'DB2INST1';
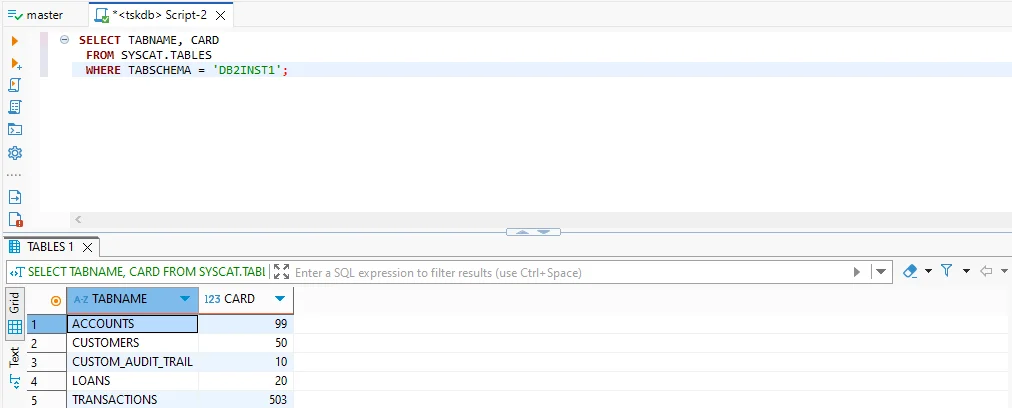
A table inventory makes it easier to track growth, detect anomalies, and verify that administrators properly control sensitive datasets.
What Happens If You Stop Here?
Relying on native features alone provides visibility and control, but governance gaps remain:
- Sensitive data stays fully visible to users with query rights — no dynamic masking.
- Identifying PII or PHI requires manual inspection of schemas.
db2auditlogs generate detail but remain cumbersome to parse at scale.- Each Db2 instance requires separate governance, leading to inconsistent enforcement.
These limitations create risks such as insider exposure, incomplete audits, and policy drift across environments.
Step 5 – Extend Governance with DataSunrise
DataSunrise is a database security and compliance platform that complements Db2 by addressing governance gaps that native tools cannot close. It integrates transparently without requiring application code changes and gives governance teams advanced tools for protecting and monitoring sensitive data.
Access and Visibility Enhancements
Stronger access control: Dynamic masking goes beyond Db2’s RCAC and LBAC. It hides sensitive fields such as credit card numbers or medical records in real time, tailoring the view according to user roles. This prevents analysts, developers, or support staff from viewing regulated data, reducing the risk of insider leaks.
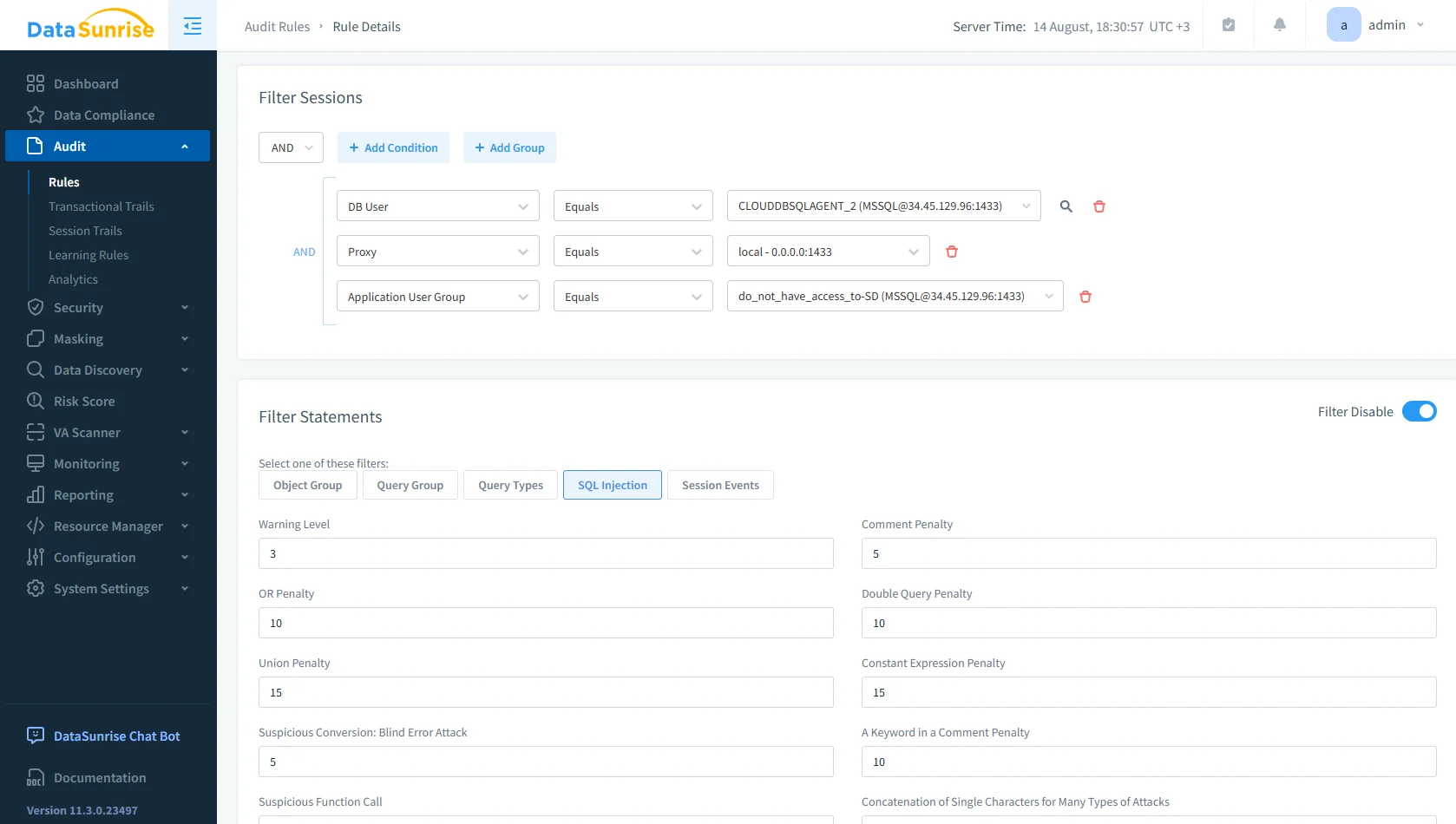
DataSunrise audit rules configuration screen for filtering sessions and statements, including SQL injection filters and penalty settings. Deeper visibility: The audit solution consolidates Db2 activity into dashboards and alerts. Instead of parsing raw
db2auditlogs, governance teams analyze structured, real-time views of logins, queries, schema changes, and data exports. This allows quicker responses to unusual behavior.
Discovery, Enforcement, and Reporting
Automated discovery: Data discovery tools scan Db2 schemas to identify where PII and PHI reside. Administrators cannot protect data they cannot locate. Automated discovery ensures no sensitive dataset remains hidden during audits.
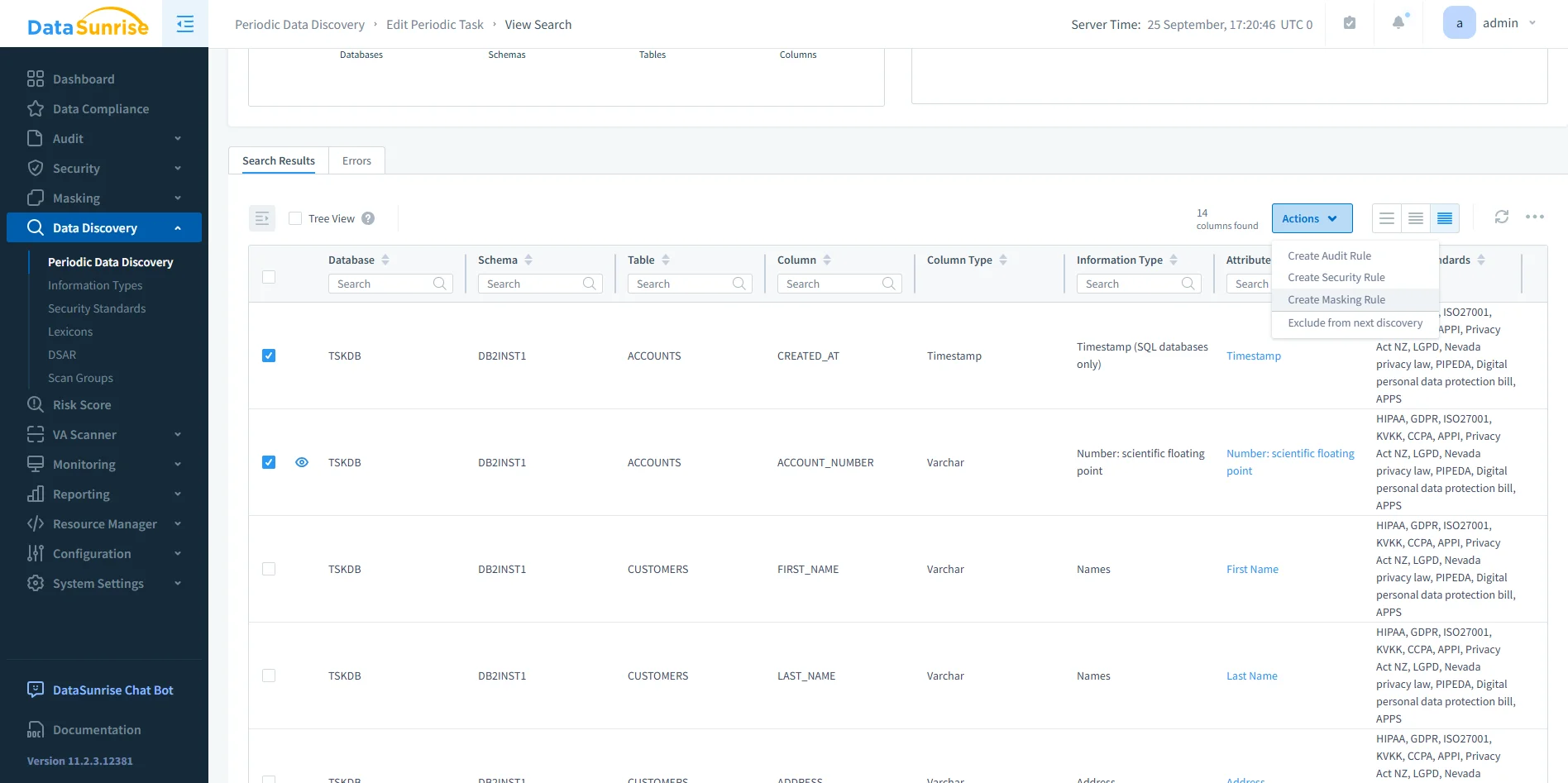
DataSunrise data discovery interface displaying periodic scan results, highlighting sensitive columns such as account numbers and personal names. Continuous enforcement: With Compliance Autopilot, governance policies for GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX apply consistently. As new users, roles, or objects appear in Db2, the system adjusts enforcement rules to prevent compliance drift.
DataSunrise security standards configuration window showing mappings to frameworks such as HIPAA, GDPR, PCI DSS, and SOX. Audit-ready evidence: Automated reporting produces clear PDF or HTML reports with one click. This removes the manual task of assembling evidence from multiple Db2 logs and helps organizations demonstrate accountability without delays.
By layering these capabilities on top of Db2’s native features, DataSunrise transforms governance from scattered manual checks into a comprehensive, proactive program. It strengthens security and streamlines oversight, ensuring data stays controlled and audit-ready at all times.
Applying Governance in Practice
The following table shows how governance tasks work in Db2 alone versus Db2 combined with DataSunrise.
| Governance Task | Db2 Native | Db2 with DataSunrise |
|---|---|---|
| Access Control | RCAC and LBAC restrict user access at row and column levels. | Dynamic masking hides sensitive values in real time, tailored to user roles. |
| Activity Monitoring | MON_CONNECTION_SUMMARY provides current session data; db2audit generates raw logs. | Unified audit trails with dashboards and alerts for clear oversight. |
| Privilege Review | SYSCAT.DBAUTH shows database-level roles but requires manual review. | Centralized view of privileges across Db2 and other databases. |
| Data Inventory | SYSCAT.TABLES reveals table names and row counts. | Automated discovery locates and classifies PII/PHI across all schemas. |
| Audit Reporting | No native reporting capabilities beyond raw logs. | One-click PDF/HTML compliance and governance reports. |
Conclusion
Applying data governance in Db2 means more than enabling a few features. Administrators must align access controls, monitor sessions, review privileges, and track data inventories. These steps create a governance foundation, but native Db2 capabilities fall short of addressing advanced needs.
DataSunrise extends this foundation with masking, automated discovery, unified auditing, and reporting. It transforms Db2 into a platform that sustains governance across hybrid and multi-database environments. By following a structured approach and augmenting Db2 with DataSunrise, organizations apply governance effectively and maintain it over the long term.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now