How to Apply Dynamic Masking in MariaDB
As MariaDB deployments grow, the same database increasingly serves multiple audiences at once, including application services, developers, analysts, support teams, and automation pipelines. As a result, organizations gain operational efficiency. However, this shared access model also introduces a persistent risk: sensitive data exposure through query results. The official MariaDB documentation describes this challenge in real-world database access models.
Dynamic data masking addresses this problem by transforming sensitive values at query time rather than altering stored data or database schemas. Instead of blocking access entirely, it enforces controlled visibility. Consequently, users see only the data they are authorized to view. This approach complements broader practices such as data security and database security, where teams protect data during access rather than only at rest.
In this article, we explain how teams can implement dynamic masking in MariaDB using native techniques. We also show how centralized platforms such as DataSunrise extend masking into a policy-driven, auditable, and compliance-aligned control layer. Therefore, the discussion closely connects to concepts like dynamic data masking and unified activity visibility.
What Is Dynamic Data Masking?
Dynamic data masking is a runtime protection technique that alters query results on the fly based on rules such as user identity, role, connection source, or access context. Unlike encryption or static masking, this technique does not change how the database stores data. Instead, it protects sensitive values precisely at access time, which makes it a core component of modern dynamic data masking strategies.
With dynamic masking, the same SQL query can return different results depending on who executes it. For example, authorized users receive full values, whereas restricted users see masked representations of the same fields. As a result, teams enable safe data access without duplicating datasets or modifying application logic.
In practice, organizations commonly use dynamic masking to protect:
- Personally identifiable information (PII)
- Contact details such as emails and phone numbers
- Financial data including card numbers and balances
- Internal identifiers and operational attributes
Native Approaches to Masking in MariaDB
MariaDB does not include built-in dynamic masking controls. However, administrators often attempt to approximate masking behavior using SQL constructs.
Views with Transformed Columns
The most common approach is to expose sensitive data through views that return transformed values instead of real ones.
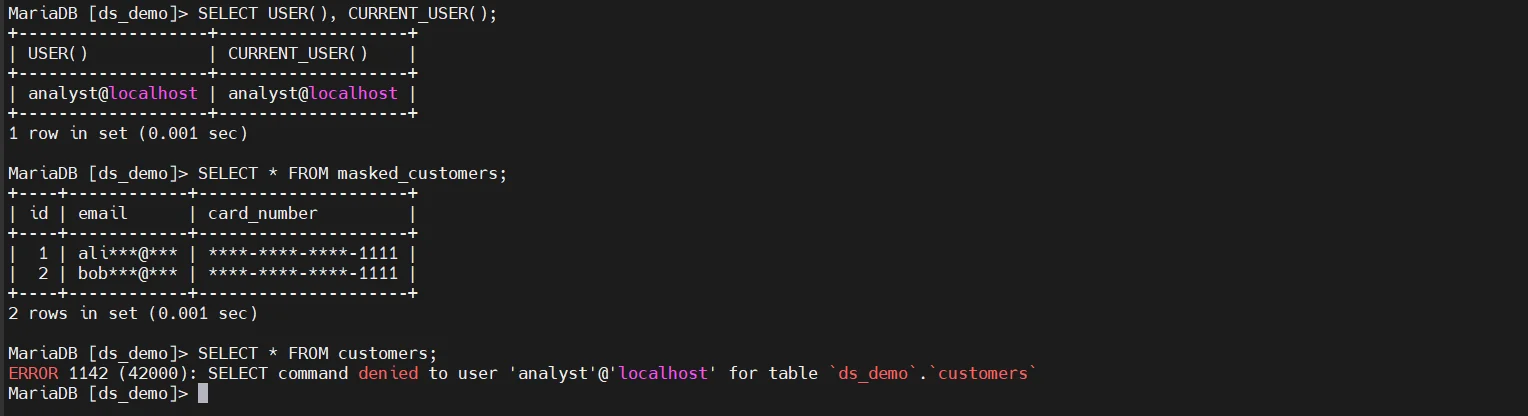
This approach relies entirely on enforcing access through the view. If users can query the base table directly, masking is bypassed.
Stored Functions with Conditional Logic
Another technique is to encapsulate masking logic inside stored functions that evaluate session attributes.
/*CREATE FUNCTION mask_email(email VARCHAR(255))
RETURNS VARCHAR(255)
RETURN
IF(USER() = 'admin@%', email, CONCAT(SUBSTRING(email,1,3),'***@***'));*/
Functions allow conditional masking but must be explicitly used in every query or view definition.
Separate Masked Copies of Data
Some environments maintain permanently masked copies of tables or schemas for non-production access.
This approach duplicates data and does not provide real-time protection. Masking is applied once and remains static until data is refreshed.
/*-- Create a masked copy of the original table
CREATE TABLE customers_masked AS
SELECT
id,
CONCAT(SUBSTRING(email, 1, 3), '***@***') AS email,
'****-****-****' AS card_number,
created_at
FROM customers;
-- Grant access only to the masked table
GRANT SELECT ON customers_masked TO analyst_user;*/
In this model, masking is performed during data copy. Any updates to the original table require the masked copy to be regenerated manually or via scheduled jobs, which makes this approach unsuitable for environments that require up-to-date data visibility or adaptive access control.
Approaches to Masking in DataSunrise
DataSunrise applies masking as an access-layer control rather than a database-side transformation. Instead of embedding masking logic into SQL objects, it evaluates queries in real time and applies masking rules transparently before results are returned to the client. This decouples data protection from database schemas and application logic.
Masking decisions are made dynamically for every query using execution context, ensuring consistent protection across applications, BI tools, administrative sessions, and automated processes. Different masking approaches are available depending on security, operational, and compliance requirements.
Masking Rules
Masking in DataSunrise is enforced through centralized rules that define when and how sensitive data is masked. These rules operate independently of database schemas and application logic and are evaluated in real time for every query, taking execution context into account. When rule conditions are met, masking is applied before results are returned to the client. This approach aligns with broader data security and database security practices, where protection is enforced at access time.
Multiple masking rules can coexist and be prioritized. This enables layered protection models, where default restrictions apply broadly while more specific rules selectively relax masking for trusted users, roles, or services. Masking rules integrate naturally with centralized dynamic data masking and policy-driven access controls.
- Centralized rule management across all protected databases
- Real-time evaluation for every query without SQL rewrites
- Priority-based rule execution for layered access control
Column-Level Dynamic Masking
Column-level masking applies transformation rules directly to selected columns when access conditions are met. This approach is well suited for clearly defined sensitive fields and is commonly used alongside structured data discovery processes.
Common use cases include partial masking of emails, full masking of card numbers, and redaction of identifiers. Rules can be scoped to individual tables, schemas, or entire databases, providing precise and predictable control over data exposure.
- Precise control over individual sensitive columns
- Consistent masking behavior across queries and tools
- Support for multiple masking formats per column
Role- and Context-Aware Masking
Role- and context-aware masking extends column-level masking by evaluating execution context instead of relying only on static permissions. This model complements role-based access control (RBAC) by adding runtime visibility controls.
Conditions may include database user or role, client IP address, application name, or authentication source. As a result, the same column can be masked or unmasked for different users executing identical queries.
- Adaptive data visibility based on user and connection context
- No need to duplicate roles or database objects
- Supports mixed-access environments with shared schemas
Policy-Based Masking by Data Type
Policy-based masking focuses on sensitive data categories rather than individual columns. Once data is classified, masking policies are automatically applied to all matching fields across schemas and tables, reducing manual effort and supporting compliance-driven workflows such as data compliance.
- Automatic protection of newly added sensitive columns
- Reduced operational overhead for large schemas
- Consistent masking aligned with classification results
Real-Time Enforcement Without Query Changes
All masking approaches operate without modifying SQL queries, views, stored procedures, or application logic. Applications continue issuing standard queries while masking is enforced transparently at runtime, integrating cleanly with unified database activity monitoring.
Because masking is applied outside the database engine, policies can be updated without redeploying applications or altering database objects.
- Zero changes to application code or SQL logic
- Immediate policy updates without service disruption
- Uniform enforcement across applications, BI tools, and admin access
Key Advantages of Masking with DataSunrise
| Capability | Description |
|---|---|
| Centralized masking policies | Teams define rules once and enforce them consistently across all access paths |
| Real-time enforcement | The platform protects sensitive data directly at query execution time |
| Context-aware masking | Data visibility adapts dynamically to user identity and connection context |
| Unified monitoring | The system logs masked access events and keeps them fully traceable |
| Compliance alignment | The solution supports regulatory and audit workflows out of the box |
Conclusion
MariaDB environments often require flexible access to shared data while still protecting sensitive values. Although SQL-based techniques can simulate masking behavior, they rely on manual enforcement and strict operational discipline.
By contrast, DataSunrise applies masking at the access layer and enforces protection in real time. As a result, teams secure sensitive MariaDB data through policy-driven controls that remain transparent, auditable, and aligned with security, compliance, and usability requirements.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now