How to Apply Dynamic Masking in Percona Server
Protecting sensitive data at query time has become a baseline requirement for modern database environments. As a result, organizations using Percona Server for MySQL often need to expose real schemas to developers, analysts, and support teams while still preventing the disclosure of personal or financial values. In practice, this challenge sits at the intersection of modern data security and everyday database operations.
Dynamic data masking addresses this challenge by transforming sensitive fields in real time without modifying stored data. Unlike static masking, it preserves data integrity and actively controls visibility based on execution context. Consequently, dynamic masking serves as a core mechanism in advanced database security architectures.
In this article, we explain how teams can apply dynamic masking in Percona Server for MySQL. First, we examine the limitations of native MySQL techniques. Then, we show how centralized dynamic masking with DataSunrise delivers policy-driven, auditable, and compliance-ready protection.
Why Dynamic Masking Matters in Percona Server for MySQL
Percona Server for MySQL is commonly deployed in environments where a single database serves multiple roles simultaneously. As a result, this standard operational model introduces a fundamental data exposure challenge that directly affects both data security and overall operational stability.
In practice, organizations typically support several roles at the same time:
- Application services executing production queries
- Analysts running read-only reports
- Developers troubleshooting live issues
- Support teams accessing customer records
All of these roles interact with the same tables and columns. However, they require very different levels of data visibility. When teams provide unrestricted access in such scenarios, they significantly increase the risk of accidental exposure and complicate compliance with modern regulatory requirements.
Traditional MySQL access controls operate strictly at the table or column level. Once administrators grant access, users immediately see full, unmasked values. Consequently, this model fails when users need schema and relational context but must not see actual sensitive data, especially when working with personally identifiable information.
Dynamic data masking directly addresses this architectural limitation.
Instead of restricting access entirely, organizations apply masking at query execution time. This approach aligns with centralized dynamic data masking strategies used in modern database security architectures and enables teams to:
- Mask sensitive values at query execution time
- Preserve original data in storage
- Apply different visibility levels to the same column
Because the underlying data remains unchanged and the platform enforces masking rules consistently, protection stays effective across users, applications, and environments.
As a result, sensitive data remains protected even when organizations cannot fully restrict access, which turns dynamic masking into a foundational security control rather than a fragile workaround.
Native MySQL Masking Techniques: What Percona Inherits
Percona Server for MySQL inherits MySQL’s native capabilities. However, MySQL does not provide built-in dynamic data masking. Any masking logic must be implemented manually, which immediately limits flexibility and consistency.
View-Based Masking
The most common workaround relies on SQL views that return pre-masked values instead of raw data:
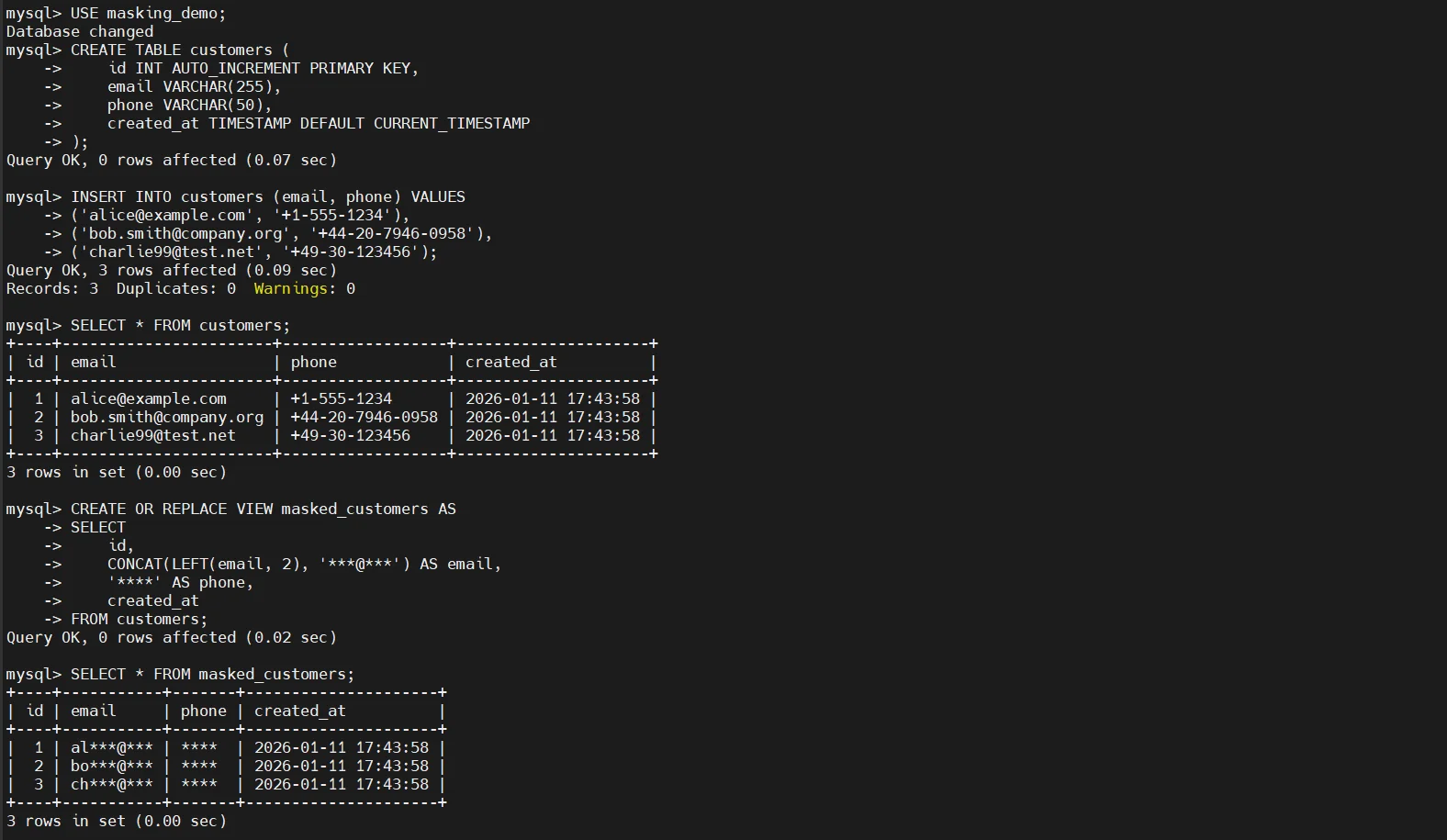
This approach works only if all access is strictly forced through the view, which is rarely realistic in production. As soon as a user, tool, or application bypasses the view and queries the base table, masking is completely defeated.
Application-Side Masking
Another common pattern is masking data inside application code after it is retrieved from the database:
SELECT
id,
email,
phone,
credit_card
FROM customers
WHERE customer_id = ?;
def mask_email(email):
return email[:2] + "***@***"
def mask_phone(phone):
return phone[:3] + "****" + phone[-2:]
response = {
"email": mask_email(row["email"]),
"phone": mask_phone(row["phone"]),
"credit_card": "****-****-****-****"
}
While this may appear flexible, it introduces serious architectural problems:
- Inconsistent enforcement across services and APIs
- Duplicate masking logic spread across multiple codebases
- No database-level audit visibility into how data was accessed
- No centralized policy control
As a result, masking becomes an application concern rather than a database security control, making it fragile, unprovable, and difficult to govern.
Dynamic Masking Architecture with DataSunrise
DataSunrise introduces an external security layer that enforces dynamic data masking without modifying Percona schemas or application logic. Masking rules are evaluated in real time as queries pass through the DataSunrise control plane, before results are returned to the client. Because masking is enforced externally, it operates independently of database structure and application code, aligning with modern data security principles.
Non-Intrusive Enforcement Model
Dynamic masking is applied transparently and does not require changes to database schemas, SQL queries, or application logic. Existing Percona Server deployments remain intact, while masking policies are enforced externally. This non-intrusive model follows the same architectural principles used for centralized database activity monitoring and data audit trails, enabling masking to integrate naturally into broader security workflows.
Data-Driven Sensitive Data Discovery
Dynamic masking policies are driven by automated sensitive data discovery rather than static schema assumptions. DataSunrise analyzes database content to identify sensitive columns using pattern matching, statistical profiling, and semantic classification, reflecting advanced data discovery capabilities. As a result, the platform maintains a continuously updated inventory of sensitive data. Masking rules follow the data itself, remaining effective even as schemas change over time.
Context-Aware Masking Policies
Masking decisions are evaluated at runtime using execution context such as database user or role, client IP address or network segment, application identity, and query type or execution environment. This approach is consistent with centralized dynamic data masking strategies used in enterprise environments. As a result, the same column can appear fully visible, partially masked, or fully masked depending on who accesses it.
Unlike view-based approaches, the same SQL query can return different results based on execution context, without requiring separate database objects or query rewrites.
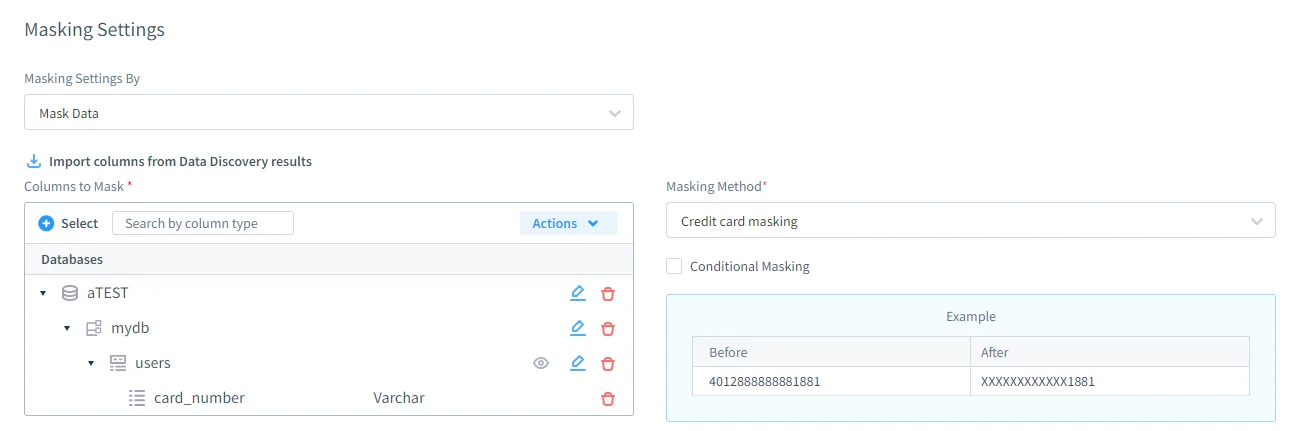
Runtime Masking and Data Integrity
Dynamic masking is applied only to query results. Data stored in Percona Server remains unchanged at all times, preserving transactional integrity, indexing behavior, backups, and replication processes. This design complements broader database security architectures by protecting data exposure without interfering with core database operations.
Because transformations occur at runtime, masking behavior can be validated safely in production-like environments without risking data corruption or operational disruption.
Auditable Dynamic Masking Operations
Every masking decision is logged. Audit records capture the executed query text, the applied masking rule, user and session metadata, and the timestamp of execution. This creates a verifiable audit trail that supports regulatory and internal oversight, reinforcing centralized audit logging and compliance processes.
As a result, masking becomes an explicit, reviewable security control rather than an implicit SQL convention.
Compliance Impact
Dynamic masking enforces data minimization and controlled data exposure, directly supporting regulatory requirements. By limiting sensitive data visibility at query time, organizations reduce compliance risk while preserving operational access.
Because masking policies and enforcement actions are centralized and logged, compliance evidence can be generated directly from audit records without manual reconstruction across applications or databases.
Comparison: Native MySQL Masking vs Dynamic Masking with DataSunrise
| Aspect | Native MySQL Masking | Dynamic Masking with DataSunrise |
|---|---|---|
| Masking at query time | No | Yes |
| Schema or SQL changes | Required | Not required |
| Context-aware masking | No | Yes |
| Same query, different output | No | Yes |
| Centralized policy control | No | Yes |
| Audit visibility | No | Yes |
| Compliance readiness | Limited | High |
Conclusion
Percona Server for MySQL provides a robust database foundation, but it does not include native dynamic data masking capabilities, as confirmed in the official Percona Server for MySQL documentation. SQL-level workarounds such as views and application-side masking are fragile, inconsistent, and difficult to audit.
By introducing a centralized dynamic masking layer, DataSunrise extends Percona Server with context-aware, policy-driven protection enforced at query time. Sensitive data remains usable, controlled, and auditable across users and environments.
Dynamic masking stops being a workaround and becomes a core component of secure database operations.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now