Managing Data Compliance for Amazon DynamoDB
Managing data compliance for Amazon DynamoDB requires a fundamentally different approach than traditional relational databases. Unlike SQL platforms, DynamoDB operates as a fully managed, schema-flexible NoSQL service and does not expose query-level logs, system tables, or native audit trails. Instead, AWS enforces compliance through identity controls, encryption mechanisms, infrastructure telemetry, and centralized monitoring at the service layer. As a result, DynamoDB compliance becomes part of a broader data security strategy rather than a database-native function.
For organizations that process regulated, sensitive, or business-critical data, this architecture creates both advantages and constraints. On the one hand, AWS delivers strong baseline security. On the other hand, organizations still share responsibility for compliance outcomes. Therefore, teams must design governance controls that align with established data compliance regulations. In practice, this means answering key regulatory questions about who accessed data, under which permissions, how systems protected that data, and how teams detect and investigate violations.
In this article, we explain how to manage data compliance for Amazon DynamoDB using native AWS capabilities, clarify where those controls reach their limits, and outline a structured compliance model aligned with modern regulatory requirements. Additionally, the article builds on core principles of database activity monitoring and consistent access controls, which together support auditability and long-term governance as DynamoDB environments scale.
What Data Compliance Means in DynamoDB Environments
In DynamoDB, organizations do not implement data compliance inside the database engine itself. Instead, they achieve compliance by coordinating multiple AWS services that collectively enforce access control, data protection, visibility, and accountability. As a result, DynamoDB compliance becomes part of a broader data management strategy rather than a database-native function.
In practice, teams usually focus on several core compliance objectives:
- Enforcing least-privilege access to tables and indexes through consistent access controls
- Protecting sensitive data through encryption and infrastructure safeguards that align with database encryption best practices
- Maintaining verifiable records of access and administrative actions to support effective database activity monitoring
- Supporting regulatory audits and internal investigations without relying on application-level instrumentation
- Preventing compliance drift as DynamoDB environments expand across AWS regions and accounts
Because DynamoDB does not generate SQL-style audit logs or query histories, organizations must derive compliance evidence from AWS-level controls rather than database internals. Therefore, effective compliance depends on how well teams configure, correlate, and govern those external control layers.
Core AWS Controls for DynamoDB Compliance Enforcement
At the infrastructure level, DynamoDB compliance is enforced through a set of foundational AWS services rather than database-native mechanisms. These controls operate outside the data plane, governing how requests are authorized, how data is protected at rest and in transit, and how operational actions are recorded for accountability.
Together, these AWS-native controls form the baseline compliance layer for DynamoDB. They establish who can access resources, under what conditions encryption is applied, and which actions are visible to auditors and security teams. However, because these controls function independently and at different layers of the AWS stack, compliance effectiveness depends on how consistently they are configured, monitored, and governed across accounts, regions, and environments.
The following sections examine the core AWS services that underpin DynamoDB compliance and explain both their strengths and their inherent limitations.
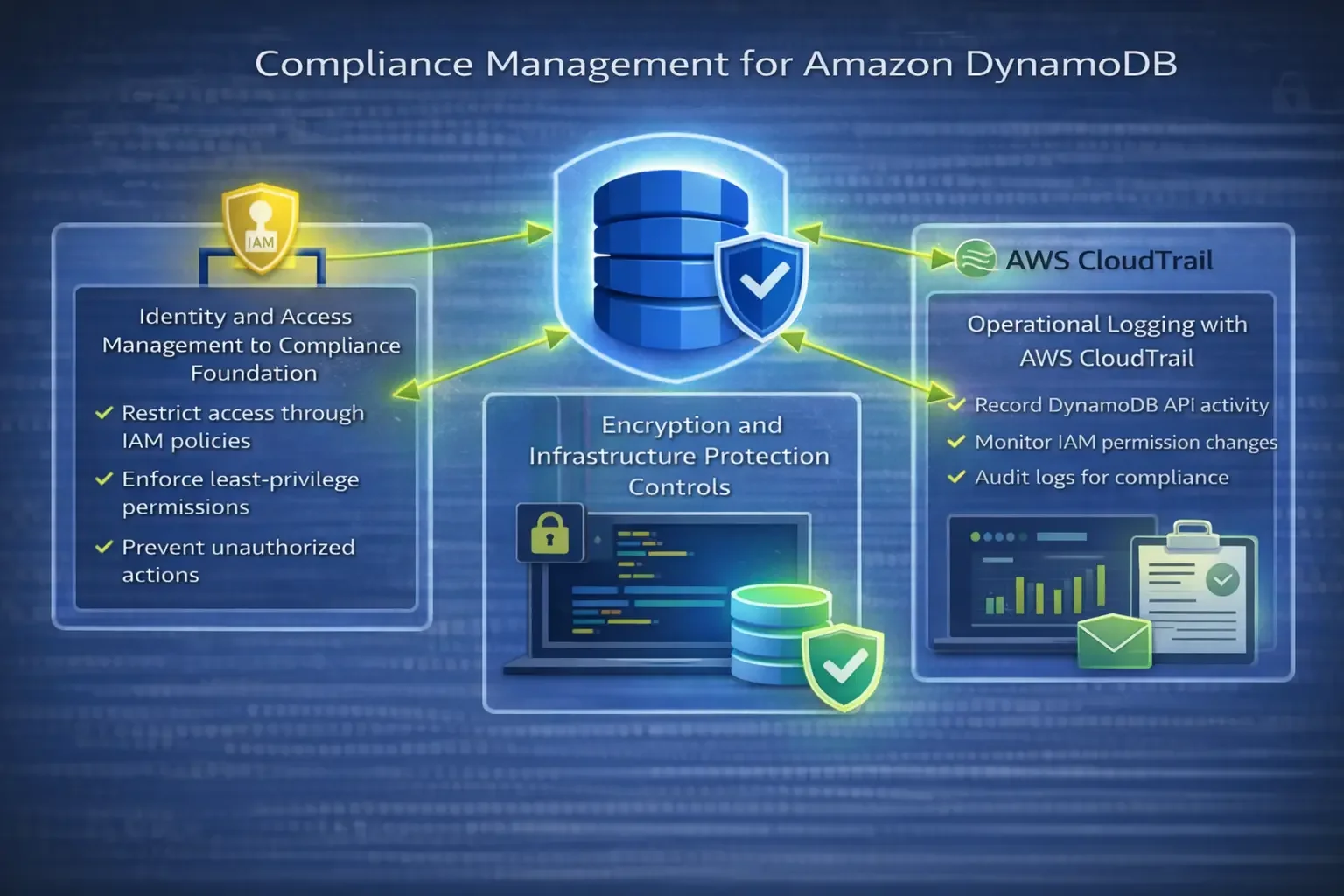
Identity and Access Management as the Compliance Foundation
Identity and access control form the core of DynamoDB compliance.
Every request to DynamoDB is evaluated by AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) before execution. IAM policies define which principals can perform actions such as GetItem, PutItem, Query, or Scan on specific resources.
Example: least-privilege IAM policy scoped to one table
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "OrdersReadOnly",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"dynamodb:GetItem",
"dynamodb:Query",
"dynamodb:Scan"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:dynamodb:us-east-1:123456789012:table/Orders"
}
]
}
From a compliance perspective, IAM enables:
- Fine-grained authorization at the table and index level
- Separation of duties through role-based access controls
- Centralized permission reviews and change tracking
- Enforcement of least-privilege principles
Example: separation of duties by denying destructive admin actions
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "DenyDangerousAdminActions",
"Effect": "Deny",
"Action": [
"dynamodb:DeleteTable",
"dynamodb:UpdateTable",
"dynamodb:UpdateContinuousBackups",
"dynamodb:UpdateTimeToLive"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
However, IAM answers only who is allowed to access DynamoDB. It does not explain what data was actually accessed or what values were returned, which is often required for audit and compliance investigations.
Encryption and Infrastructure Protection Controls
DynamoDB encrypts all data at rest by default using AWS-managed keys. For regulated environments, organizations commonly adopt customer-managed AWS KMS keys to maintain control over key rotation, revocation, and auditability.
Infrastructure-level compliance controls include:
- Encryption at rest using AWS KMS
- Encryption in transit via TLS
- Key ownership and lifecycle management
- Integration with centralized key policies
Example: create a DynamoDB table with SSE-KMS using a customer-managed key
aws dynamodb create-table \
--table-name Orders \
--attribute-definitions AttributeName=OrderId,AttributeType=S \
--key-schema AttributeName=OrderId,KeyType=HASH \
--billing-mode PAY_PER_REQUEST \
--sse-specification Enabled=true,SSEType=KMS,KMSMasterKeyId=arn:aws:kms:us-east-1:123456789012:key/abcd-1234
Example: KMS key policy that allows usage via DynamoDB service path
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "AllowKeyUseViaDynamoDBOnly",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"AWS": "arn:aws:iam::123456789012:root"
},
"Action": [
"kms:Encrypt",
"kms:Decrypt",
"kms:GenerateDataKey"
],
"Resource": "*",
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"kms:ViaService": "dynamodb.us-east-1.amazonaws.com"
}
}
}
]
}
These mechanisms protect data confidentiality and integrity, but they do not provide visibility into how encrypted data is accessed or used once permissions are granted.
Operational Logging with AWS CloudTrail
Because DynamoDB does not emit native query logs, AWS CloudTrail becomes the primary source of operational compliance evidence.
CloudTrail records API-level events such as:
- Table creation and deletion
- Permission changes
- Read and write API calls
- Administrative actions
Example: lookup DynamoDB API activity for an incident window
aws cloudtrail lookup-events \
--lookup-attributes AttributeKey=EventSource,AttributeValue=dynamodb.amazonaws.com \
--start-time 2026-01-27T00:00:00Z \
--end-time 2026-01-28T00:00:00Z \
--max-results 50
Example: CloudTrail event shape used for compliance evidence (who + what + where)
{
"eventSource": "dynamodb.amazonaws.com",
"eventName": "UpdateItem",
"awsRegion": "us-east-1",
"userIdentity": {
"type": "AssumedRole",
"arn": "arn:aws:sts::123456789012:assumed-role/app-role/session-1"
},
"requestParameters": {
"tableName": "Orders"
}
}
This data is essential for compliance audits, incident response, and governance reporting. However, CloudTrail logs are control-plane and data-plane metadata, not data content. They confirm that an operation occurred, but not what data was returned or modified at the item level.
As a result, CloudTrail alone may be insufficient for regulations that require detailed access traceability or sensitive data usage verification.
Data Compliance for Amazon DynamoDB with DataSunrise
Native AWS controls provide a necessary baseline for DynamoDB compliance, but they operate at the infrastructure and API level. They focus on authorization, encryption, and event logging rather than on data context. As a result, organizations often struggle to answer compliance questions related to sensitive data usage, access intent, and policy consistency across environments.
DataSunrise extends DynamoDB compliance by introducing a centralized compliance layer that complements AWS-native services. Instead of replacing IAM, KMS, or CloudTrail, DataSunrise builds on top of them, adding visibility, policy logic, and compliance awareness that are not available natively in DynamoDB.
From a compliance perspective, DataSunrise enables organizations to move from infrastructure-centric controls to data-centric governance.
Centralized Visibility Across DynamoDB Environments
DynamoDB environments often span multiple AWS accounts, regions, and application stacks. DataSunrise provides a unified control plane for compliance monitoring, allowing security and compliance teams to manage policies and review activity consistently, regardless of deployment topology.
This centralized approach reduces governance fragmentation and helps prevent compliance drift as DynamoDB usage scales.
Sensitive Data Awareness and Classification
Unlike native DynamoDB controls, which are blind to data semantics, DataSunrise introduces sensitive data discovery and classification capabilities. By identifying regulated data such as personal identifiers, financial records, or health-related attributes, compliance policies can be aligned with actual data risk rather than abstract resource permissions.
This allows organizations to apply differentiated controls based on data sensitivity instead of relying solely on table-level access rules.
Policy-Driven Compliance Enforcement
DataSunrise enables compliance enforcement through centrally managed, policy-driven rules. These policies define how sensitive data can be accessed, monitored, or masked, ensuring consistent compliance behavior across development, staging, and production environments.
Because policies are managed outside application code, compliance logic remains stable even as DynamoDB schemas, services, or workloads evolve.
Audit-Ready Evidence and Reporting
For regulatory audits, DataSunrise transforms raw operational telemetry into structured, compliance-ready evidence. Instead of relying exclusively on CloudTrail event logs, organizations gain contextual audit records that correlate identity, action, and data scope.
This significantly simplifies audit preparation and reduces the manual effort required to interpret AWS-native logs.
Reducing Compliance Risk in DynamoDB-Centric Architectures
By combining AWS-native security primitives with centralized compliance intelligence, DataSunrise helps organizations close the gap between infrastructure security and regulatory accountability. Compliance becomes proactive and measurable rather than reactive and log-driven.
In DynamoDB-centric architectures, this layered approach enables stronger regulatory alignment without disrupting application performance or AWS-managed service guarantees.
Business Impact of Proper DynamoDB Compliance Management
| Business Area | Measurable Impact |
|---|---|
| Regulatory & Legal Risk | Reduced exposure to regulatory penalties and compliance violations through consistent enforcement of access and protection controls |
| Audit Readiness | Faster and more predictable audit preparation with centralized evidence and repeatable compliance workflows |
| Visibility & Oversight | Improved insight into access patterns, administrative actions, and operational usage across DynamoDB environments |
| Trust & Reputation | Stronger confidence from customers, partners, and regulators due to demonstrable compliance posture |
| Operational Efficiency | Lower operational overhead for compliance and security teams by reducing manual reviews and ad-hoc investigations |
Compliance, when engineered correctly, becomes a stabilizing force rather than a blocking constraint.
Conclusion
Managing data compliance for Amazon DynamoDB requires abandoning assumptions rooted in relational databases. DynamoDB compliance is enforced through identity, encryption, telemetry, and governance coordination rather than native query logs or system tables, forming part of a broader data compliance strategy.
Organizations that treat compliance as an architectural responsibility — integrating IAM controls, encryption policies, operational logging, and centralized oversight — achieve stronger security, clearer regulatory alignment, and sustainable scalability. This approach aligns closely with modern data security principles and reduces reliance on fragmented, reactive controls.
When compliance is built into the DynamoDB operating model rather than bolted on afterward, it becomes an enabler of secure growth instead of a source of friction. In practice, this requires continuous database activity monitoring and disciplined access controls to maintain long-term governance integrity.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now