
How to Manage Data Compliance for Apache Cassandra

Introduction
Managing data compliance for Apache Cassandra is not a one-time project but an ongoing operational discipline. Regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS require not only secure configuration at deployment but also continuous monitoring, auditing, and reporting in production.
This guide explains how to manage data compliance for Apache Cassandra on a daily, weekly, and long-term basis, while also showing how DataSunrise reduces operational overhead with automation.
Understanding the Compliance Management Lifecycle
Compliance management brings together several interconnected elements. For Apache Cassandra, it is not only about database settings but also about aligning technology with organizational and regulatory requirements. The core pillars of compliance management include:
- Compliance Regulations: Frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX define the obligations for data privacy, retention, and reporting.
- Security Practices: Day-to-day technical controls like authentication, encryption, access management, and activity monitoring that enforce those regulatory requirements.
- IT Infrastructure: The consistency of Cassandra nodes and clusters, replication across datacenters, and backup/restore strategies that support secure and compliant operations.
- Integration & Visibility: Centralized dashboards, log aggregation, and automated reporting that provide organizations with real-time insight into their compliance posture.
Together, these components create a governance cycle that ensures Cassandra environments remain both secure and audit-ready.
Managing Audit Logs at Scale
The Challenge
Cassandra generates logs locally on each node. A 50-node cluster can easily produce tens of gigabytes of audit data per day. Without centralization, correlating events across nodes is nearly impossible, leaving organizations exposed during audits.
Centralized Aggregation Example
Administrators often set up a shipping pipeline to compress, encrypt, and forward logs:
audit_logging_options:
enabled: true
logger: BinAuditLogger
audit_logs_dir: /var/log/cassandra/audit
included_categories: AUTH, DML, DDL
roll_cycle: HOURLY
archive_command: "/scripts/ship_to_central.sh %path"
# ship_to_central.sh
gzip -c "$1" | \
openssl enc -aes-256-cbc -pass pass:$COMPLY_KEY | \
ssh compliance@central-logger \
"cat > /audit/$(hostname)_$(date +%Y%m%d_%H%M%S).gz.enc"
Once ingested, logs can be indexed for search and alerting. This approach works, but it demands scripting effort and ongoing maintenance.
Data Classification and Governance
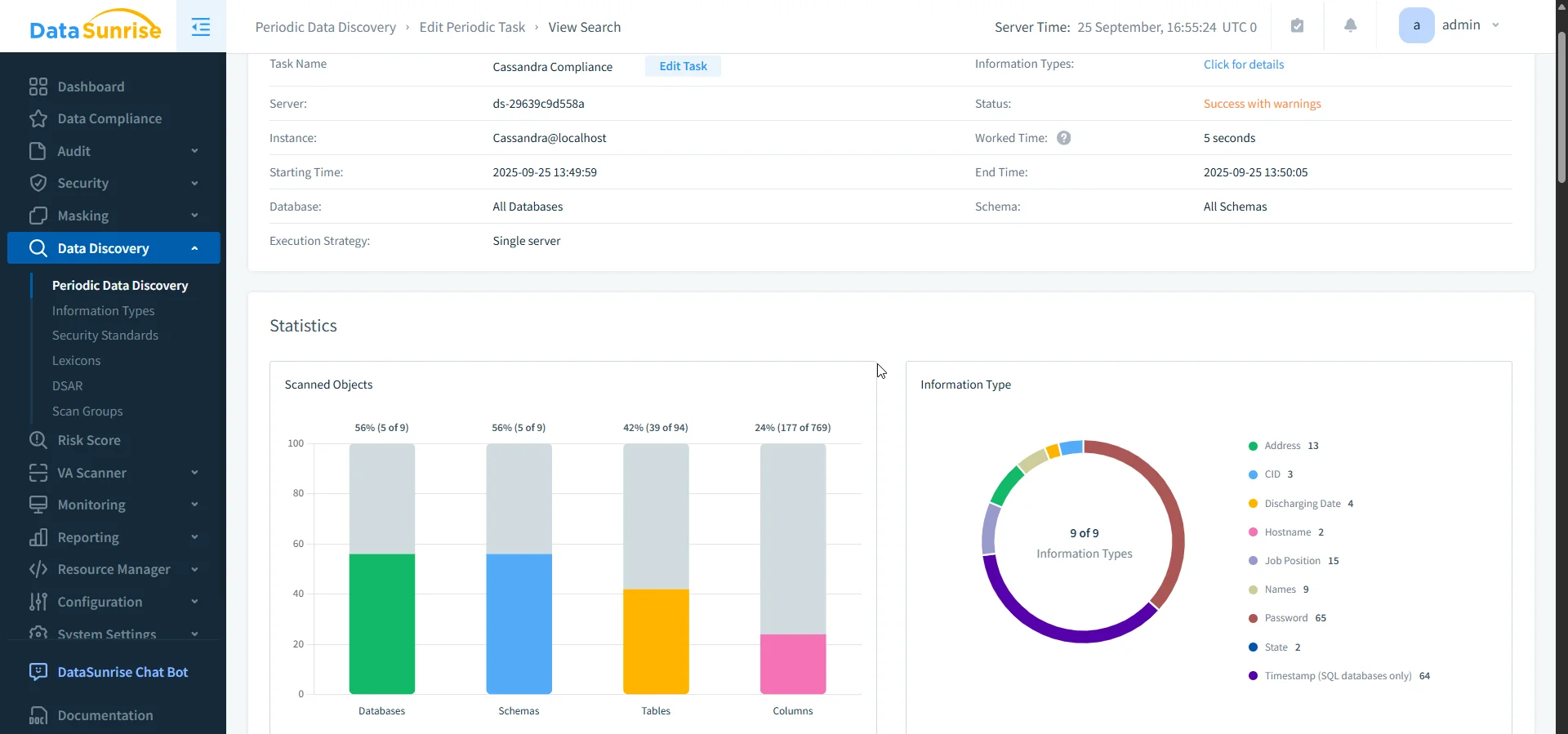
Continuous Discovery
Identifying sensitive data is central to GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. Cassandra does not provide automatic classification, so DBAs often write custom queries to locate potential PII columns:
SELECT keyspace_name, table_name, column_name
FROM system_schema.columns
WHERE column_name ~ '(ssn|passport|tax_id|email|phone)';
The output becomes the basis for policies on masking, encryption, or retention.
Enforcing Retention
Cassandra tables can accumulate years of data, creating compliance risk. Automated scripts can delete records older than a cutoff date, then trigger compaction to reclaim space. This satisfies regulatory retention limits but adds operational overhead if done manually.
Access Control Management
Dynamic Role Management
Cassandra supports role-based access control (RBAC). Ongoing compliance requires periodic reviews:
- Export current permissions.
- Compare against actual usage from audit logs.
- Revoke unused rights and apply least-privilege policies.
A simplified role segregation matrix looks like this:
| Role | Read | Write | Delete | Schema | Users | Audit Logs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Application Service | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ |
| Analyst | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ |
| DBA | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ |
| Security Admin | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Compliance Officer | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ |
This mapping demonstrates compliance with segregation-of-duties requirements.
Incident Response for Compliance Violations
Even with policies in place, incidents will occur. Examples include failed logins, large unauthorized exports, or after-hours access. A lightweight Python monitor can scan logs for patterns and trigger alerts.
High-severity incidents typically require immediate isolation of a node and revocation of credentials, while medium-severity incidents may only require permission adjustments and documentation. The important part is to have repeatable playbooks and proof of timely response.
Streamlining Compliance with DataSunrise
While native Cassandra can meet compliance obligations, it requires constant manual oversight. Administrators must configure nodes individually, ship logs manually, and prepare reports through ad hoc scripts. This approach consumes resources and often leaves gaps when auditors ask for proof.
DataSunrise changes this equation by providing a compliance management layer on top of Cassandra. Instead of treating each node as a separate unit, DataSunrise consolidates discovery, auditing, masking, and reporting into a single system that spans the entire cluster.
Automated Compliance Management
At the heart of DataSunrise is its centralized dashboard. Compliance officers and DBAs no longer need to sift through dozens of log files or custom scripts. Instead, they can:
- Track a real-time compliance score, showing how well Cassandra clusters align with GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX.
- Receive automated violation alerts whenever policies are breached, such as failed login storms or bulk unauthorized exports.
- Use predictive risk analytics to identify areas where compliance drift is likely to occur.
- Generate audit-ready reports instantly, eliminating days of manual preparation.
This single pane of glass brings visibility and assurance that native Cassandra cannot provide.
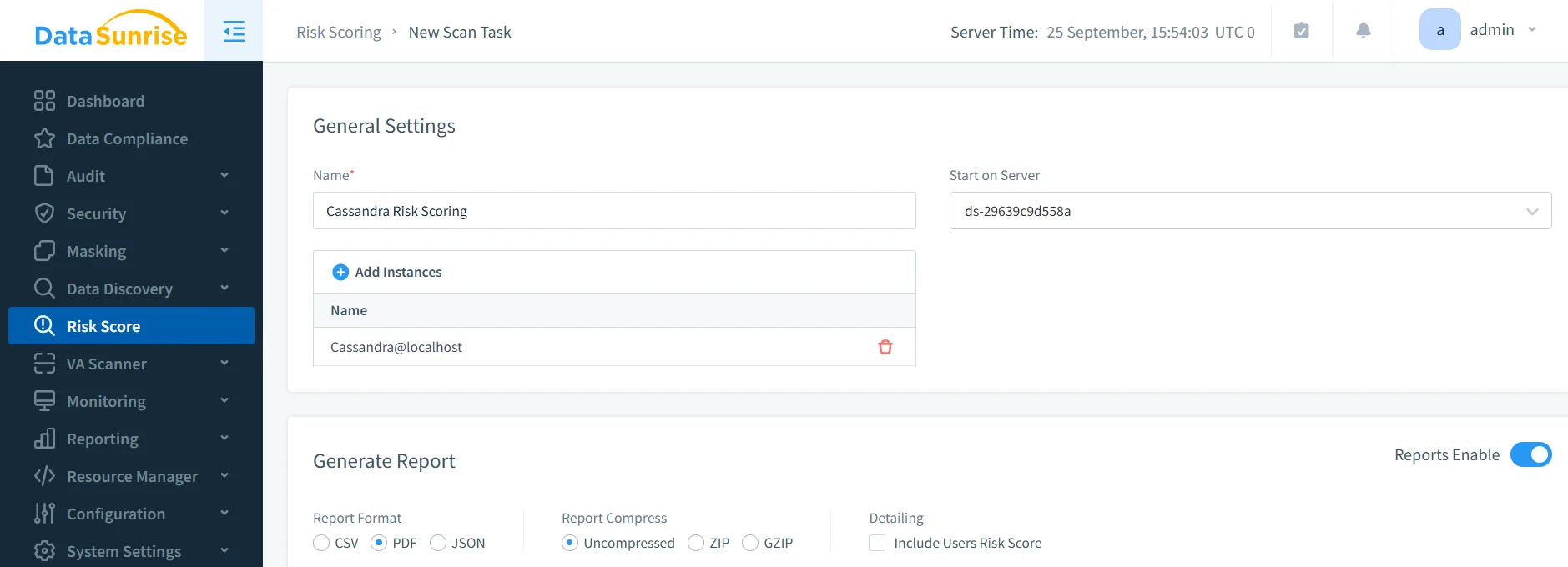
Automated Sensitive Data Discovery
DataSunrise includes built-in data discovery that scans Cassandra keyspaces for sensitive information such as PII, PHI, or PCI data. Instead of relying on manual SQL scripts to guess column names, the system uses NLP and pattern recognition to classify fields automatically.
This ensures that organizations know exactly where regulated data resides—a fundamental requirement for GDPR’s “data subject rights” and HIPAA’s patient privacy rules.
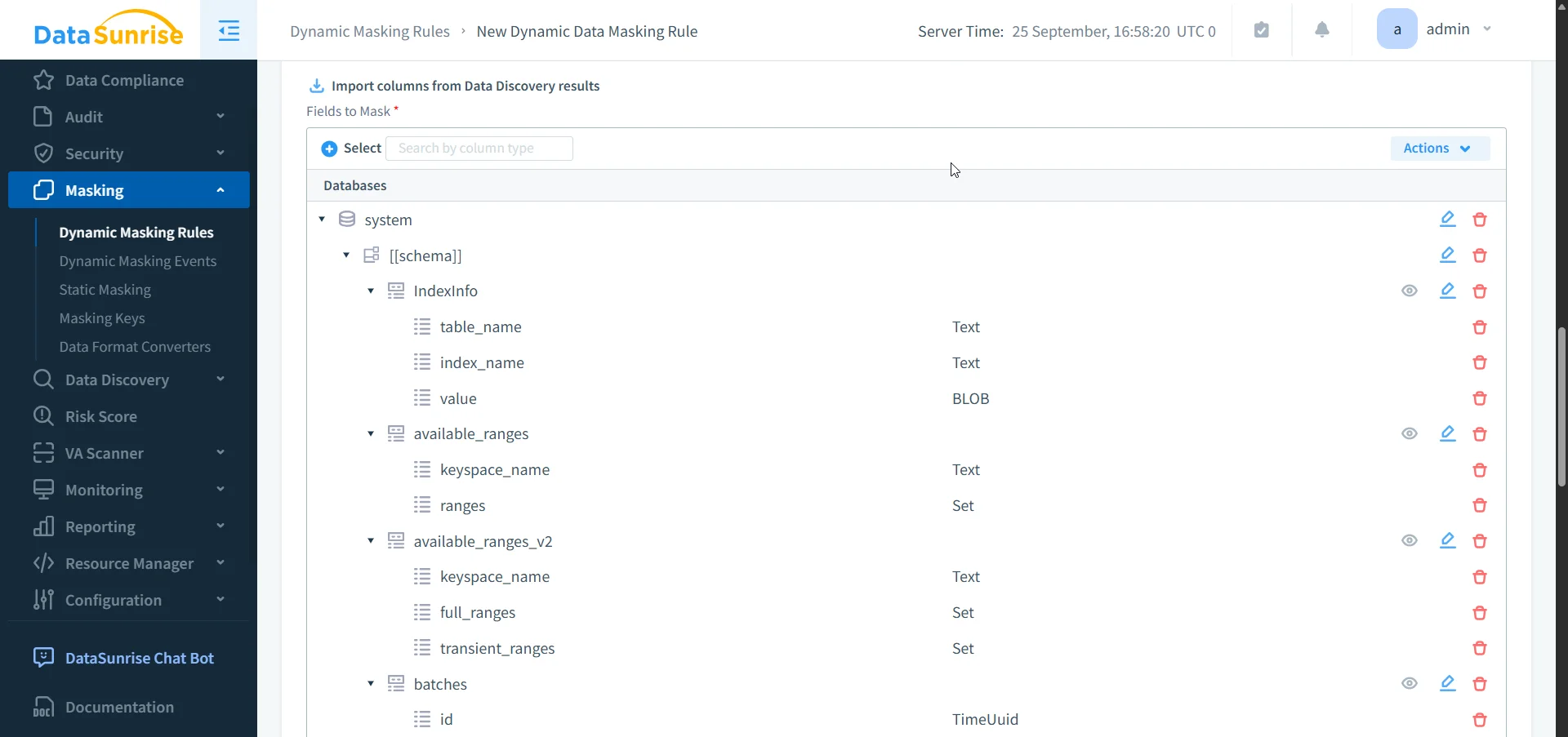
Dynamic and Static Data Masking
One of Cassandra’s limitations is that masking is only available in version 5.0 and requires schema changes. DataSunrise removes those barriers. It applies:
- Dynamic masking in real time, role-aware, without schema modification. Users see only what they are authorized to see.
- Static masking for test and development environments, ensuring production data can be anonymized while preserving integrity.
By applying masking at the proxy layer, DataSunrise makes compliance feasible across Cassandra versions 3.x, 4.x, and 5.x.
Centralized Auditing and Monitoring
With Cassandra alone, logs are fragmented by node and stored in binary formats. DataSunrise consolidates all audit activity into a cluster-wide repository, making searches, filtering, and correlation easy.
| Feature | Native Cassandra | With DataSunrise |
|---|---|---|
| Audit Logs | Node-local, binary | Centralized, human-readable |
| Failed Logins | Not captured | Tracked and alerted |
| Cross-Node Correlation | Manual effort | Automatic across cluster |
| Alerts | Not available | Real-time monitoring |
This makes regulatory audits faster and more reliable, since auditors can access consistent evidence instead of scattered files.
Automated Compliance Reporting
Another major benefit is report automation. With Cassandra alone, weekly or monthly compliance reports require custom exports, manual compilation, and spreadsheets. DataSunrise generates regulator-ready PDF or HTML reports instantly, aligned with GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX templates.
Effort Comparison
Managing compliance in Apache Cassandra manually quickly becomes a resource-heavy task. Every node must be checked individually, logs have to be aggregated, and reports often involve days of preparation. By contrast, DataSunrise centralizes these activities, reducing routine work from hours to minutes. The table below highlights how common compliance tasks compare between native Cassandra operations and a DataSunrise-enabled environment.
| Task | Native Cassandra | With DataSunrise |
|---|---|---|
| Daily Log Review | Hours across nodes | Minutes in one console |
| Access Audit | Manual SQL queries | Automated with drift alerts |
| Report Generation | Days of preparation | One-click PDF/HTML |
| Incident Response | Ad hoc scripts | Automated workflows |
Conclusion
Managing data compliance for Apache Cassandra is resource-intensive if done solely with native tools. Daily log reviews, weekly access audits, and retention enforcement quickly consume time and talent.
DataSunrise provides a way to cut compliance overhead by more than 80% while improving audit readiness. Its automated discovery, masking, auditing, and reporting features turn compliance from a burden into a sustainable practice.
Compliance management is not about perfection, but about continuous improvement supported by the right tools — and DataSunrise makes that improvement achievable for organizations running Cassandra at scale.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now