Sensitive Data Protection in Percona Server
Percona Server for MySQL runs in environments that demand performance, transparency, and strict operational control. In practice, these systems store personally identifiable information, financial records, credentials, and internal business data. As a result, teams must treat sensitive data protection as a core operational requirement rather than a secondary task tied only to traditional data security.
Unlike auditing, which tracks who did what, sensitive data protection answers a different question: who can see specific data and under which conditions. Therefore, organizations must implement database security controls that move beyond activity tracking and actively govern data visibility.
Consequently, teams focus on preventing accidental exposure, limiting insider access, and ensuring that regulated data never leaves approved contexts. Moreover, these requirements appear consistently in environments that follow modern data compliance regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS.
In this article, we explain how sensitive data protection works in Percona Server for MySQL using native mechanisms, where those mechanisms reach their limits, and how centralized platforms extend protection without altering application logic. Specifically, we examine how data masking and policy-driven access enforcement operate alongside continuous database activity monitoring.
What Counts as Sensitive Data
Sensitive data includes any information that creates security, legal, or operational risk when unauthorized users access it. Organizations define sensitivity not by storage location, but by the impact of disclosure and its role in overall data security.
For example, data that identifies an individual often requires protection. This category includes names, email addresses, phone numbers, and physical locations. In addition, credentials and access-related information demand strict control. Password hashes, API keys, authentication tokens, and session identifiers enable direct system access and can bypass standard access controls when exposed.
Financial information introduces another layer of risk. Payment card numbers, transaction records, billing details, and account balances typically fall under formal regulatory oversight. Therefore, organizations must handle this data in accordance with established data compliance regulations.
In practice, sensitive data rarely appears in isolation. Instead, it resides inside operational tables alongside non-sensitive fields and flows through normal application queries. Consequently, effective protection relies on fine-grained techniques such as contextual data masking rather than broad permissions applied at the database or table level.
Native Sensitive Data Protection Capabilities in Percona Server for MySQL
Percona Server for MySQL relies on native MySQL security mechanisms for sensitive data protection. These mechanisms provide foundational controls but operate primarily at the access level rather than at the data visibility level.
Privilege Management
Access to sensitive tables and columns is controlled using MySQL privilege grants. Administrators can restrict which users may read, insert, update, or delete specific objects.
GRANT SELECT (email, phone)
ON customer_db.customers
TO 'support_user'@'%';
GRANT SELECT, UPDATE
ON customer_db.orders
TO 'app_user'@'%';
This approach is effective for separating broad roles but does not control how data is presented. Once a user is granted SELECT access to a column, the database returns the full value without modification.
SELECT email, phone
FROM customer_db.customers;
If access is granted, the result always contains the original values, regardless of user role, context, or intent.
Encryption at Rest and in Transit
Percona Server supports encryption for InnoDB tablespaces and secure client connections using TLS. These controls protect data from storage-level theft and network interception.
Encryption at rest can be enabled at the table level:
CREATE TABLE payments (
id INT PRIMARY KEY,
card_number VARBINARY(255),
amount DECIMAL(10,2)
) ENCRYPTION='Y';
TLS is used to encrypt data in transit between client and server:
[mysqld]
require_secure_transport = ON
ssl_cert = server-cert.pem
ssl_key = server-key.pem
ssl_ca = ca.pem
However, encryption does not prevent exposure during legitimate queries. Once data is decrypted for a session, it is fully visible to the querying user.
SELECT card_number
FROM payments;
The database does not differentiate between users once decryption occurs.
Application-Level Masking
Some teams implement masking logic in application code or database views. A common workaround is to expose masked values through SQL views.
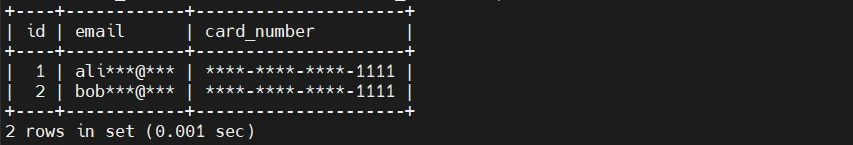
Applications are then instructed to query the view instead of the base table:
SELECT email, phone
FROM masked_customers;
While this can obscure values for specific use cases, it introduces operational complexity. Masking rules become scattered across applications and views, difficult to audit, and easy to bypass through direct table access or ad-hoc queries.
SELECT email, phone
FROM customers; -- bypasses masking entirely
Centralized Sensitive Data Protection with DataSunrise
To overcome the limitations of native database controls, organizations introduce an external security layer that enforces sensitive data protection independently of database privileges and application logic. This approach shifts protection from static configuration inside the database to centrally managed, policy-driven enforcement aligned with modern data security practices.
DataSunrise extends Percona Server for MySQL by operating as an intermediary control plane. It analyzes database traffic, identifies sensitive data, and applies protection rules in real time without modifying stored values, schemas, or application queries. As a result, protection remains consistent even as access patterns and environments change, complementing traditional database security controls.
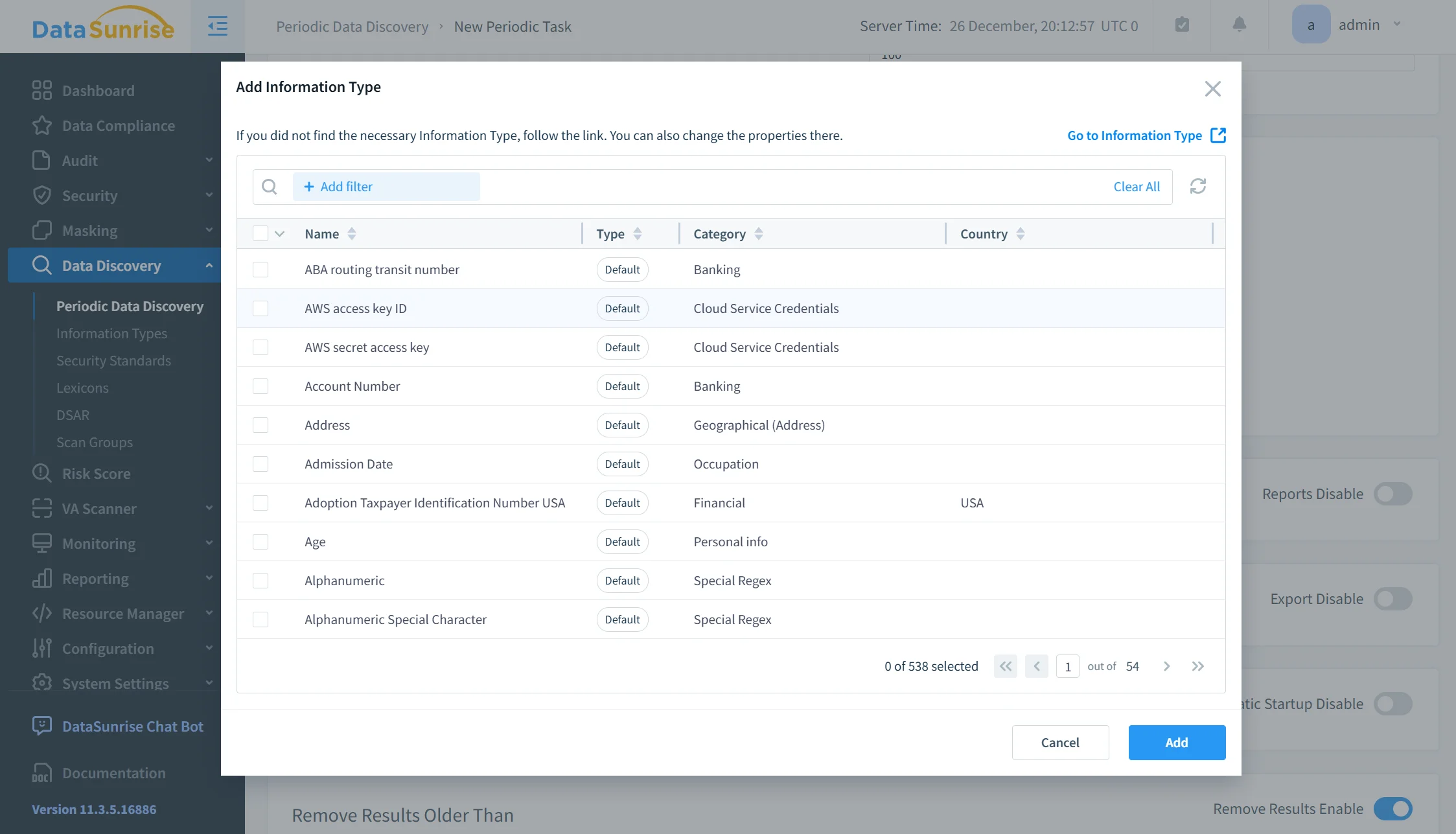
Sensitive Data Discovery
Before protection can be applied, sensitive data must be identified accurately. DataSunrise performs automated discovery by scanning database schemas and inspecting column content using pattern analysis, metadata evaluation, and classification rules supported by built-in data discovery capabilities.
This process detects personal identifiers, financial attributes, credentials, and other regulated data elements without requiring manual annotation. Discovery tasks can run continuously or on a schedule, allowing the system to detect newly created tables and columns as soon as they appear.
By automating discovery, organizations reduce the risk of unprotected data introduced through schema changes, migrations, or new application features.
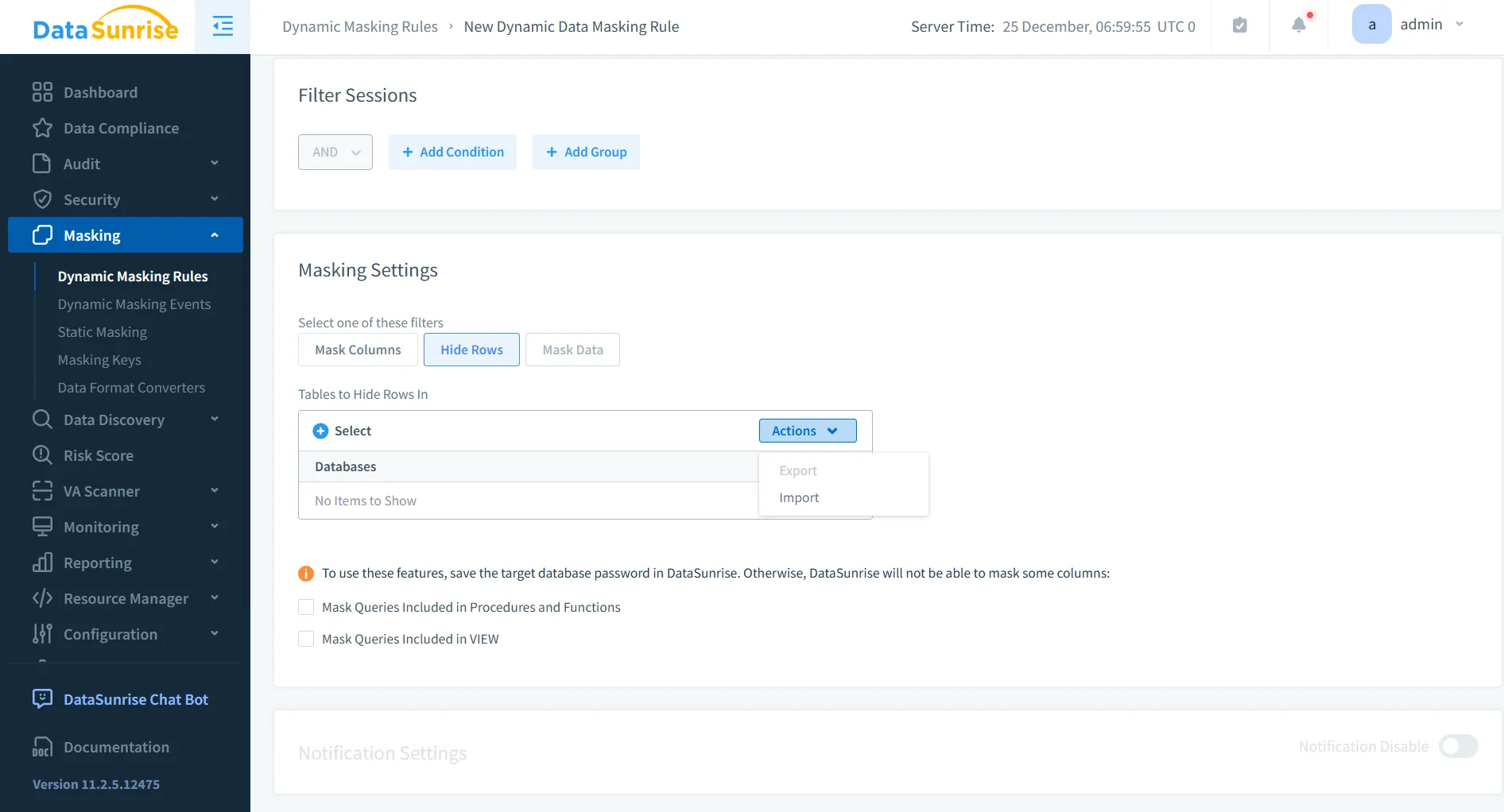
Dynamic Data Masking
Dynamic data masking applies transformations at query time rather than at rest. Sensitive values are never altered in storage. Instead, masking is applied only to query results based on policy conditions defined through dynamic data masking rules.
The same column can return different representations depending on who is querying it, from which application, and under which context. Production services can retrieve full values, while analysts, support teams, or external users see masked outputs that preserve format and usability without exposing real data.
Because masking happens transparently, applications do not need to be rewritten, and database schemas remain unchanged.
Policy-Based Enforcement
Protection rules in DataSunrise are defined centrally and enforced consistently across all connections. Policies can incorporate user identity, authentication method, client application, source network, time of access, query type, and data classification, aligning with structured access controls rather than hard-coded application logic.
This allows organizations to express protection logic in operational terms instead of relying solely on database privileges. Since enforcement occurs outside the database engine, policies remain effective even when users bypass application layers or connect using alternative tools.
Environment-Wide Coverage
DataSunrise applies identical protection policies across production, staging, and development environments. This is particularly important when production datasets are copied for testing, analytics, or troubleshooting.
By enforcing masking and visibility rules consistently, organizations prevent sensitive data from leaking into non-production systems where access controls are often weaker. This approach supports ongoing alignment with evolving data compliance regulations and reduces risk introduced by environment sprawl.
Business Impact of Structured Sensitive Data Protection
| Impact Area | Operational Effect | Practical Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Data Exposure Risk | Reduces accidental and insider-driven exposure of sensitive values | Sensitive fields remain protected even during legitimate access |
| Policy Consistency | Enforces the same protection rules across all teams and environments | Eliminates gaps between production, staging, and development systems |
| Regulatory Alignment | Accelerates compliance with GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX | Shorter audit cycles and fewer remediation findings |
| Operational Stability | Removes reliance on application-level masking and custom logic | Fewer failures caused by bypassed or inconsistent controls |
| Audit Readiness | Provides enforced and observable data visibility controls | Clear evidence of protection during audits and investigations |
Sensitive data protection shifts from a trust-based model to an enforced, observable control that scales with data access complexity rather than breaking under it.
Conclusion
Percona Server for MySQL provides strong foundational security through access control and encryption. However, these mechanisms alone do not prevent sensitive data exposure during legitimate use and should be viewed as part of a broader database security strategy.
Effective sensitive data protection requires controlling not only who can access data, but how that data is revealed in different contexts. Centralized platforms extend native capabilities by adding automated data discovery, dynamic masking, and policy-driven enforcement without disrupting applications or database design.
By treating sensitive data protection as a continuous control rather than a static configuration, organizations can reduce risk while preserving operational flexibility and maintaining alignment with evolving data compliance regulations in Percona Server for MySQL environments.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now