
Synthetic Data Generation

Synthetic data generation is rapidly becoming a foundational element of modern AI development, advanced analytics, and privacy-driven digital transformation. It enables organizations to create realistic, statistically accurate datasets that mirror real-world information—without exposing genuine customer or corporate data. This approach supports secure experimentation, machine learning training, and model validation while remaining compliant with established privacy regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA. According to a recent Gartner report, nearly half of global executives have increased their AI spending, underscoring the expanding need for responsible and secure data use. Additional guidance from the NIST AI Risk Management Framework highlights synthetic data’s role in reducing bias and supporting safer model development. Capabilities such as dynamic data masking further enhance an organization’s ability to safeguard sensitive information throughout the process.
DataSunrise positions synthetic data as a natural evolution of data protection—complementing existing methods including data masking, encryption, and database activity monitoring. This functionality empowers organizations to generate fully anonymized, production-quality datasets that retain real data’s structure, relationships, and statistical patterns. As a result, teams can conduct testing, analytics, and development in safe, controlled environments without violating privacy or regulatory requirements. Synthetic datasets support secure collaboration, accelerate innovation, and ensure compliance across every stage of the AI lifecycle.
When paired with automation and intelligent policy controls, synthetic data not only enhances data protection and regulatory compliance but also boosts scalability, operational agility, and continuity. It enables enterprises to adopt AI and analytics within secure, ethically governed ecosystems—unlocking innovation while maintaining trust and regulatory alignment.
What Is Synthetic Data?
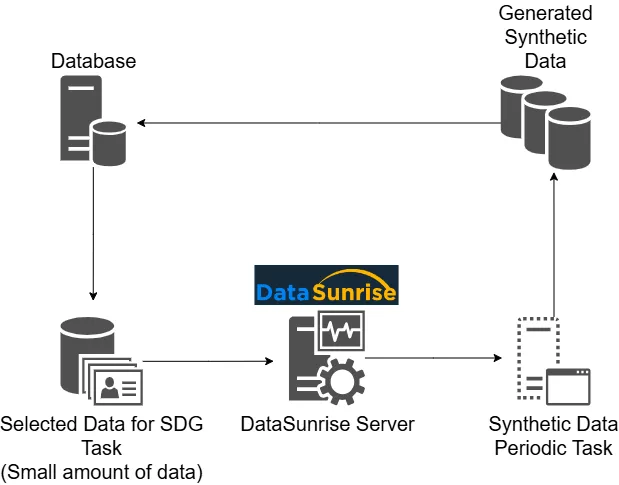
Synthetic data refers to artificially created information that reflects the structure and statistical behavior of real datasets without retaining actual values. It maintains formats, relationships, and distributions, allowing teams to develop, test, and analyze securely. Because no genuine records are used, synthetic datasets eliminate privacy risks while remaining highly effective for AI modeling, system validation, and compliance efforts.
When to Use Synthetic Data vs. Masking
Static or dynamic masking is great when you need to retain the structure and logic of production data—but still want a reference to real values. However, masking can’t be shared externally if the source schema or metadata creates re-identification risk.
Synthetic data is better when:
- You need to simulate large datasets with no connection to real individuals
- Compliance requires zero exposure to production values
- You’re working with unstructured logs or training LLMs
Scenario: Why Synthetic Beats Masking
Picture a data science team training an anomaly detection model. Masked production data preserves structure, but residual correlations can still risk re-identification. Synthetic datasets, by contrast, carry no linkage to real customers. The team gets statistically faithful data for AI pipelines, while compliance officers get peace of mind that nothing identifiable ever leaves production.
Synthetic data isn’t just a dev tool—it’s a compliance accelerator. By generating privacy-safe records, enterprises cut regulatory risk, accelerate AI adoption, and enable safe vendor collaboration.
When paired with masking, synthetic generation creates a hybrid model: retain referential integrity for workflows that need it, and generate fully artificial records for testing, sharing, or AI training. This blended approach ensures compliance without slowing innovation.
Synthetic Data — Summary, Steps, Validation
Summary
- Goal: create privacy-safe datasets that preserve schema and statistical properties without exposing real records.
- Use when: external sharing, LLM/ML training, non-prod provisioning, or policies require zero linkage to individuals.
- Pairing: combine with masking for hybrid workflows needing referential integrity in limited areas.
Implementation Steps
- Define scope & purpose (QA, analytics, LLM training, vendor sharing).
- Catalog schema, constraints, and sensitive fields (PII/PHI/PCI) to guide generators.
- Select generation mode (built-in/policy-aware in platform, or OSS like SDV/CTGAN/Mockaroo for prototypes).
- Choose column strategies (substitution, statistical models, FPE where shape matters).
- Preserve relationships (keys/foreign keys) or simulate with deterministic rules where needed.
- Run a pilot on a subset; record parameters for reproducibility.
- Validate quality (distribution, correlations, privacy distance); adjust generators.
- Schedule jobs; log tasks and control access per governance policy.
Validation Checklist
| Check | What to verify | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Distribution | Mean/variance, percentiles match tolerance | KS test per numeric column |
| Correlations | Key pairwise correlations preserved (±Δ) | Compare corr matrices |
| Privacy | No synthetic row too close to real samples | Nearest-neighbor distance |
| Constraints | Uniqueness, formats, domains respected | Regex/range checks |
Quick Checks
- Document generators, seeds, and rules for reproducibility.
- Keep synthetic and real datasets isolated; prohibit joins across them.
- For UI/integration tests needing strict referential integrity, consider a hybrid approach (masked base + synthetic expansions).
- Apply the same access controls and retention policies to synthetic datasets used outside the organization.
DataSunrise Synthetic Data Use Cases
| Use Case | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Compliance Testing | Simulate real-world datasets to validate logic without using actual customer data. | Run fraud detection algorithms on generated banking transactions. |
| AI & ML Training | Train models on realistic but non-identifiable datasets to avoid regulatory breaches. | Build diagnostic models from synthetic medical records. |
| Staging & QA | Populate test environments with lifelike data for UI, load, or integration tests. | Fill a dev PostgreSQL cluster with synthetic user profiles. |
| Secure Collaboration | Share synthetic datasets across teams or with partners without exposing sensitive info. | Provide synthetic HR records to a third-party analytics vendor. |
What Makes DataSunrise Synthetic Data Different?
While many platforms offer artificial data generation, few integrate it directly into enterprise-grade security and compliance pipelines. DataSunrise Synthetic Data tools are tightly coupled with masking, audit, and policy enforcement features—making them ideal for real-world usage in regulated environments.
- Integrated masking fallback: Seamlessly switch between masking and generation based on access context or schema type.
- Policy-aware generation: Define generation rules that align with existing compliance filters and sensitive data tags.
- Scheduled workflows: Automate synthetic dataset creation across environments, applications, and CI/CD pipelines.
- Audit logging: Track every generation task for full traceability and audit-readiness.
Whether you’re testing internal apps or training AI models, DataSunrise Synthetic Data gives teams the flexibility to simulate production-like workloads—without risking production data.
How to Configure Synthetic Data Generation in DataSunrise
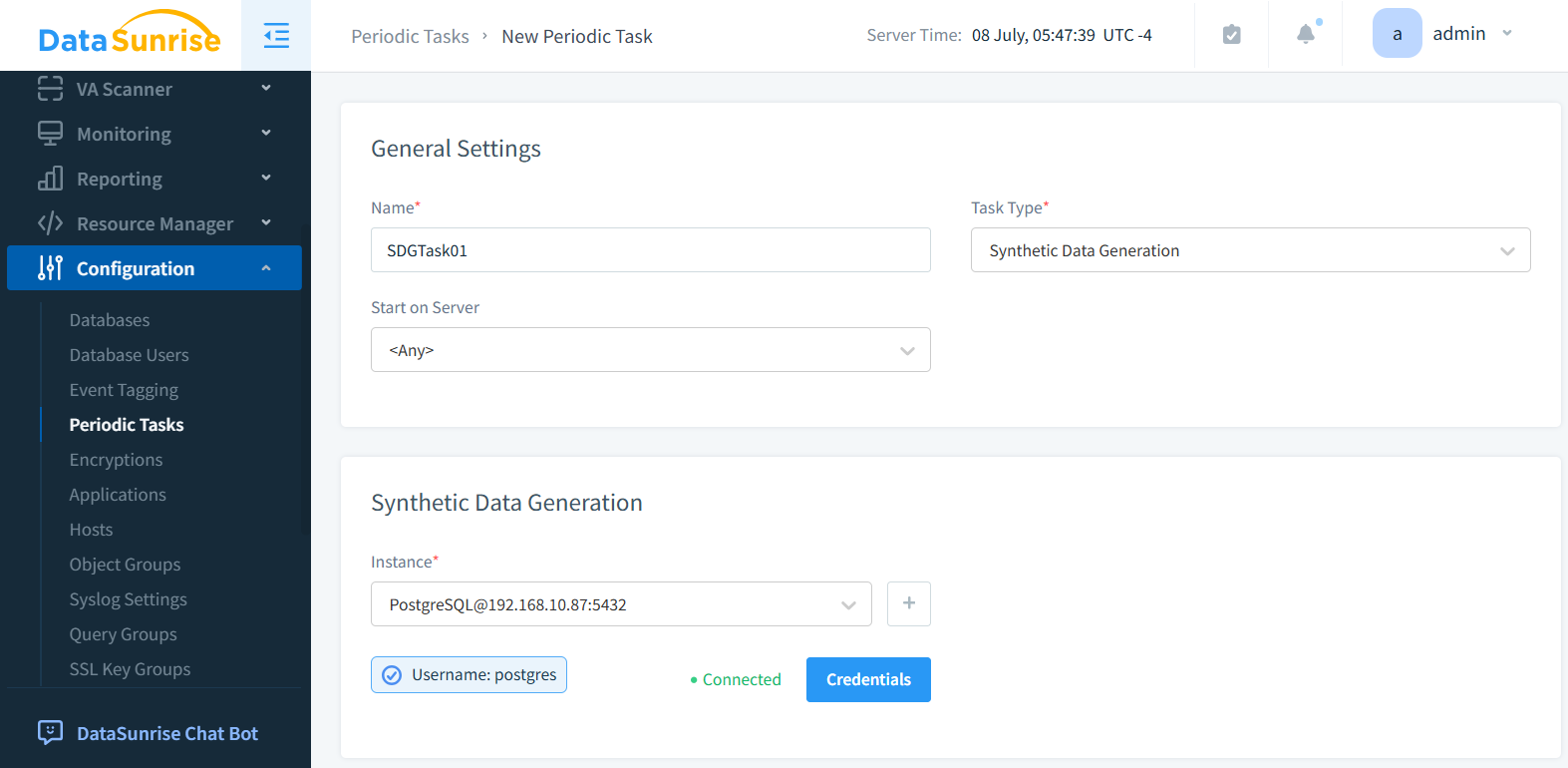
Step 1: Set General Parameters
Navigate to Configuration → Periodic Tasks and create a new task. Select “Synthetic Data Generation” as the type, and name the task accordingly.
Step 2: Select Database Instance
Choose your target instance. Below, PostgreSQL is selected as the database engine.
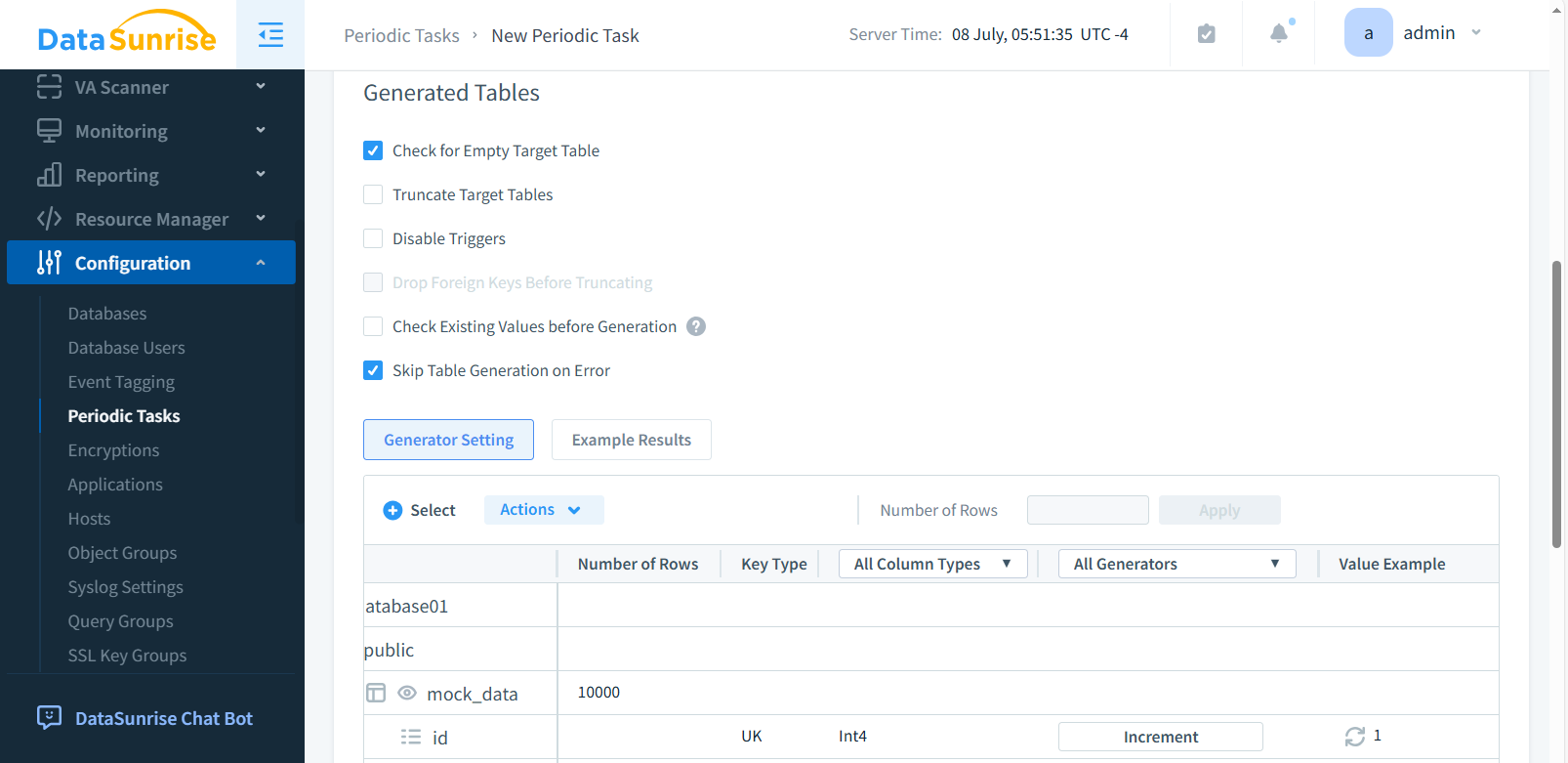
Step 3: Define Target Tables and Columns
Select the schema and tables where synthetic data will be injected. Choose specific columns, enable “Empty Table” if needed, and configure error handling behavior.
Step 4: Use Built-in or Custom Generators
Choose from built-in value generators (names, emails, numbers, dates) or define custom logic via Configuration → Generators. This is useful for matching domain-specific patterns, like simulating patient IDs or tax codes.
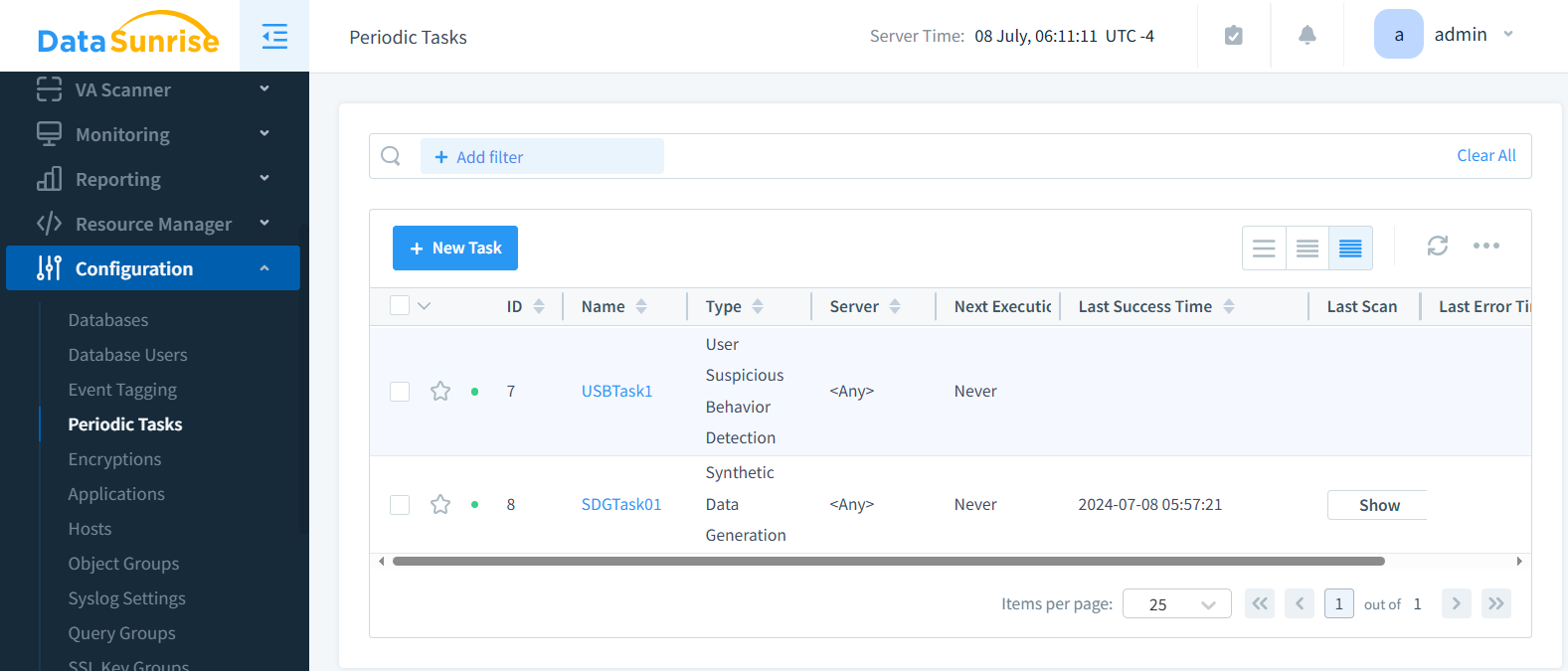
Step 5: Save, Schedule, and Run
Once saved, the task appears in your job list. You can run it on demand or schedule periodic runs for continuous data refresh.
Free Tools and Libraries for Synthetic Data
DataSunrise provides comprehensive support for synthetic generation with masking, audit, and compliance controls. But developers and data scientists also benefit from free alternatives when learning or prototyping.
SDV (Synthetic Data Vault)
SDV is an open-source Python framework that uses statistical models and GANs to generate synthetic tabular datasets. It supports relational and multi-table structures.
pip install sdv
from sdv.datasets.demo import download_demo
from sdv.single_table import GaussianCopulaSynthesizer
real_data, metadata = download_demo(modality='single_table', dataset_name='fake_hotel_guests')
synthesizer = GaussianCopulaSynthesizer(metadata)
synthesizer.fit(real_data)
synthetic_data = synthesizer.sample(num_rows=500)
print(synthetic_data.head())
CTGAN
A GAN-based model tailored for tabular data, CTGAN works well with imbalanced datasets and mixed column types. See our earlier AI data generation article for sample code.
Mockaroo
Mockaroo is a web tool for generating mock datasets in CSV, JSON, SQL, and other formats. It’s ideal for quick prototypes and supports custom field schemas. Free usage is limited to 1,000 rows per session.
Validating Synthetic Data Quality
Generating synthetic records is only half the job. You need to confirm the data behaves like the real dataset without exposing sensitive values. Common checks include:
- Distribution similarity: Compare column distributions between real and synthetic sets.
- Correlation preservation: Ensure relationships between fields remain intact.
- Privacy distance: Confirm no synthetic row is too close to a real record.
Python Example: Kolmogorov–Smirnov Test
from scipy.stats import ks_2samp
# Compare real vs synthetic column distributions
ks_stat, p_value = ks_2samp(real_data["age"], synthetic_data["age"])
if p_value > 0.05:
print("Synthetic 'age' distribution matches real data")
else:
print("Significant difference detected")
Correlation Matrix Check
import pandas as pd
real_corr = real_data.corr(numeric_only=True)
synth_corr = synthetic_data.corr(numeric_only=True)
diff = (real_corr - synth_corr).abs()
print(diff.head())
These validation steps ensure your synthetic data is useful for analytics and ML pipelines, while remaining safe for compliance.
Best Practices for Generated Data
- Match data formats to downstream expectations.
Ensure synthetic values follow the same patterns—data types, ranges, formats, and constraints—so that applications, pipelines, and analytics tools work without modification. - Preserve table relationships where needed.
Maintain key dependencies such as primary/foreign keys, hierarchies, and lookup tables to keep workflows, joins, and business logic functioning correctly. - Document generation rules for reproducibility.
Track the logic, seed values, and transformation rules used to create the dataset to support consistent regeneration, auditing, and troubleshooting. - Run sanity checks to validate logic.
Verify that distributions, ranges, and behavioral patterns look realistic—catching anomalies like out-of-range values, empty fields, or broken relationships early. - Use masking or exclusions to avoid any overlap with real data.
Confirm that synthetic values cannot be traced back to actual customer information, reducing re-identification risk and strengthening compliance.
Quick Comparison
| Tool | Best For | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| SDV | Statistical simulation of tabular data | Python-only, tuning required |
| CTGAN | Complex, imbalanced datasets | Slower training, may need GPU |
| Mockaroo | Quick CSV/JSON/SQL prototypes | Row limits, not schema-aware |
Synthetic Data in Compliance Frameworks
Synthetic data generation aligns naturally with modern regulations by removing direct identifiers while preserving analytical value. Here’s how it maps to common frameworks:
| Framework | Requirement | How Synthetic Data Helps |
|---|---|---|
| GDPR | Art. 32 — pseudonymisation and minimisation of personal data | Generates artificial records with no link to real individuals, meeting pseudonymisation and minimisation standards. |
| HIPAA | §164.514 — de-identification of PHI identifiers | Produces non-identifiable health records for research and testing while protecting PHI. |
| PCI DSS | Req. 3.4 — prevent storage of PAN in test environments | Synthetic payment records allow QA and vendor sharing without exposing real cardholder data. |
| SOX | §404 — ensure financial data integrity for audit | Provides audit-safe test data for validating financial systems without risk to production records. |
By aligning synthetic generation with these frameworks, DataSunrise helps organizations accelerate AI and analytics adoption while staying audit-ready and compliant.
When Synthetic Data Isn’t Enough: Considerations and Controls
While synthetically generated data offers strong privacy guarantees and flexibility, it’s not a universal replacement for real data or enterprise masking workflows. Certain scenarios—such as referential integrity testing, deterministic joins, or longitudinal analysis—may still require controlled access to masked or pseudonymized datasets instead.
To ensure generated data serves your goals effectively, consider these guardrails:
- Use case alignment: For model validation, use fully synthetic data. For integration or UI testing, masked production clones may be more accurate.
- Governance documentation: Track which fields were synthetically generated, which were preserved, and which tools or logic were used.
- Sampling vs. simulation: Don’t confuse random sampling of real data with synthetic generation. Only the latter breaks linkage to identifiable subjects.
- Audit readiness: Maintain logs of generation tasks, retention timelines, and access controls—especially if synthetic data enters test pipelines shared with vendors or contractors.
DataSunrise helps bridge these decisions with automation, masking fallback options, and full visibility across data types and environments. The result is safer, smarter, and faster data workflows—without compliance trade-offs.
Key Takeaways for Using Synthetic Data Effectively
- Choose synthetic data when compliance requires zero exposure to real records, or when sharing datasets externally.
- Combine synthetic generation with masking for hybrid scenarios—keeping relational integrity where needed while replacing high-risk fields entirely.
- Document generation rules, retention policies, and access controls to maintain governance and audit readiness.
- Test synthetic datasets against real-world workflows to confirm they meet performance, accuracy, and compatibility requirements.
- Automate generation tasks through scheduling and integration with CI/CD pipelines for consistent, repeatable results.
Synthetic Data FAQ
What is synthetic data?
Synthetic data is artificially generated information that mirrors the structure and statistical properties of real datasets, but contains no actual customer records. It enables safe testing, analytics, and AI training without privacy risk.
How is synthetic data different from masking?
Masking alters real values to obscure identifiers, preserving schema and referential integrity. Synthetic data, by contrast, creates fully artificial records with no link to real individuals, making it safer for external sharing and AI pipelines.
When should organizations use synthetic data?
Synthetic data is ideal for use cases where compliance requires zero exposure to real records—such as external vendor collaboration, training large language models, or populating non-production environments at scale.
Which compliance frameworks support synthetic data?
Frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS recognize pseudonymization and de-identification techniques. Synthetic generation provides an effective path to compliance when combined with governance policies.
What are the limitations of synthetic data?
It may not fully replicate complex joins, longitudinal histories, or rare outlier patterns. For those scenarios, organizations often combine masking with synthetic generation in hybrid workflows.
How does DataSunrise support synthetic data?
DataSunrise integrates synthetic data generation with masking, auditing, and compliance reporting. It provides policy-aware generators, scheduled workflows, and audit trails to ensure every dataset aligns with regulatory requirements.
Industry Applications of Synthetic Data
Synthetic data supports more than testing—it directly enables compliance and innovation across industries:
- Finance: Generate artificial transaction logs for fraud model training, meeting PCI DSS and SOX audit requirements without exposing PANs.
- Healthcare: Create de-identified patient datasets aligned with HIPAA, enabling safe research and diagnostic AI development.
- SaaS & Cloud: Provide GDPR-compliant tenant datasets for staging environments, validating multi-tenant isolation.
- Government: Share population datasets with contractors while enforcing GDPR and local privacy laws.
- Retail & eCommerce: Populate analytics pipelines with synthetic customer journeys to test personalization engines without privacy risk.
By contextualizing synthetic data for each industry, organizations accelerate innovation while staying audit-ready and privacy-safe.
The Future of Synthetic Data Generation
Synthetic data is rapidly evolving from a testing utility into a core component of enterprise data strategy. As organizations strive to innovate responsibly, next-generation synthetic data platforms will combine AI-driven generation, data quality validation, and automated compliance controls to create realistic yet fully anonymized datasets at scale. These systems will not only reproduce statistical accuracy and structural integrity but will also dynamically adapt to changing data models, privacy requirements, and evolving regulatory landscapes.
Future solutions will offer seamless integration with complementary technologies such as data masking, database activity monitoring, and sensitive data discovery. This interoperability will allow organizations to fluidly transition between real, masked, and synthetic datasets based on context—enabling safe analytics, model training, and external collaboration without exposing regulated information. Over time, this adaptive data ecosystem will make privacy-preserving innovation a default, not an exception. Capabilities like compliance automation will further ensure that synthetic datasets consistently meet regulatory and organizational requirements.
For highly regulated sectors such as finance, healthcare, and government, synthetic data will redefine the balance between compliance and innovation. Enterprises will be able to accelerate AI adoption, collaborate securely with third parties, and maintain verifiable proof that no authentic customer data ever left controlled environments. Ultimately, the future of synthetic data generation lies in intelligent automation and continuous compliance, turning privacy into an enabler of progress rather than a constraint.
Conclusion
Synthetic data has become a key component of modern privacy-first data management strategies, providing a secure and regulation-friendly alternative to using real production datasets for development, testing, analytics, and machine learning. By mirroring the structure, statistical characteristics, and relationships of real-world data—without retaining any personally identifiable or proprietary information—it enables organizations to innovate, collaborate, and analyze safely. This privacy-by-design approach minimizes compliance risks, reduces legal liabilities, and supports ethical AI deployment across sectors such as finance, healthcare, telecommunications, and the public domain.
DataSunrise incorporates synthetic data generation within its comprehensive data security and governance platform. Through automated policy enforcement, advanced masking logic, and detailed audit trails, the platform ensures that synthetic datasets comply with both internal governance frameworks and external standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, SOX, and PCI DSS. This allows enterprises to produce realistic yet fully anonymized data suitable for AI training, software testing, and third-party collaboration—without risking exposure of sensitive or confidential content.
When integrated with solutions like Database Activity Monitoring (DAM), data discovery, and dynamic masking, synthetic data becomes a powerful enabler of secure digital transformation. It allows organizations to accelerate innovation while maintaining transparency and compliance, supporting responsible experimentation and continuous improvement. As privacy regulations evolve and AI technologies advance, synthetic data will remain a foundational element of secure, ethical, and scalable data-driven innovation.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now