
Static Data Masking
Introduction
Static data masking safeguards sensitive information by generating a secure, anonymized copy of production data in which confidential fields are replaced with realistic but fictitious values. Because the resulting dataset maintains the original schema, relationships, and data format, it remains fully usable for testing, analytics, software development, and machine learning—without exposing personally identifiable information, financial records, or healthcare data to unauthorized individuals. This approach allows organizations to balance data utility with stringent privacy and compliance requirements. Guidance from standards such as the ISO/IEC 27559 data protection framework further emphasizes the importance of robust anonymization practices.
This article explores the key principles of static data masking, explains how it differs from dynamic masking, and examines its critical role in compliance management, privacy assurance, and risk reduction. It also demonstrates how DataSunrise simplifies deployment through automated workflows, ensures referential integrity across complex datasets, and supports heterogeneous database environments—both on-premises and in the cloud. In addition, static masking is invaluable for secure data sharing with third-party vendors, research partners, or test teams, as well as for enabling safe cloud migration processes where only anonymized, compliance-ready datasets leave the protected production perimeter.
Static vs Dynamic Masking: Key Differences
Both techniques protect sensitive fields, but they serve different operational needs.
Static data masking generates a new masked copy of the database where sensitive content is replaced with synthetic values—ideal for dev/test, vendor handoffs, and safe data sharing.
By contrast, dynamic masking operates at runtime—masking query results based on access context without modifying stored data—best for live access control inside applications.
| Feature | Static Masking | Dynamic Masking |
|---|---|---|
| How it Works | Makes a masked database copy | Alters query output at runtime |
| Use Case | Dev/test, external access | Live production access control |
| Performance | No runtime impact | Applied on the fly |
| Data Safety | Safe for export/sharing | Needs runtime protection policies |
When to Use Static Masking
Static data masking is especially valuable when sensitive information needs to be moved outside its original production environment. It allows teams to work with realistic datasets while ensuring that no personally identifiable or regulated data is exposed. Typical use cases include:
- Developer and testing environments: Enable developers and engineers to build, debug, and optimize features using data that reflects real-world complexity—without revealing actual customer identities, payment details, or confidential records.
- Quality assurance and staging systems: Replicate production conditions for functional, performance, or integration testing without introducing compliance or privacy risks.
- Employee training and onboarding: Provide new hires and support teams with realistic examples that improve learning outcomes while fully safeguarding sensitive information.
- External collaboration: Safely share datasets with consultants, outsourced teams, researchers, or vendors without granting access to regulated data.
- Cloud migrations, backups, and archival: Transfer or store masked datasets to reduce exposure risks during movement, replication, or long-term retention.
With DataSunrise, these workflows can be standardized and automated. Format-preserving masking ensures analytical and relational consistency, referential integrity is maintained across tables and schemas, and scheduled masking jobs guarantee that every generated dataset remains compliant over time. Additionally, integrated auditing and policy controls help organizations validate the masking process and demonstrate compliance to auditors and regulators.
How DataSunrise Applies Static Data Masking
DataSunrise supports static masking across SQL Server, Oracle, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, and cloud databases like Amazon Redshift. It operates via the DataSunrise server (no schema changes). Setup defines four areas: source/target instances, transferred tables, scheduling frequency, and optional cleanup rules.
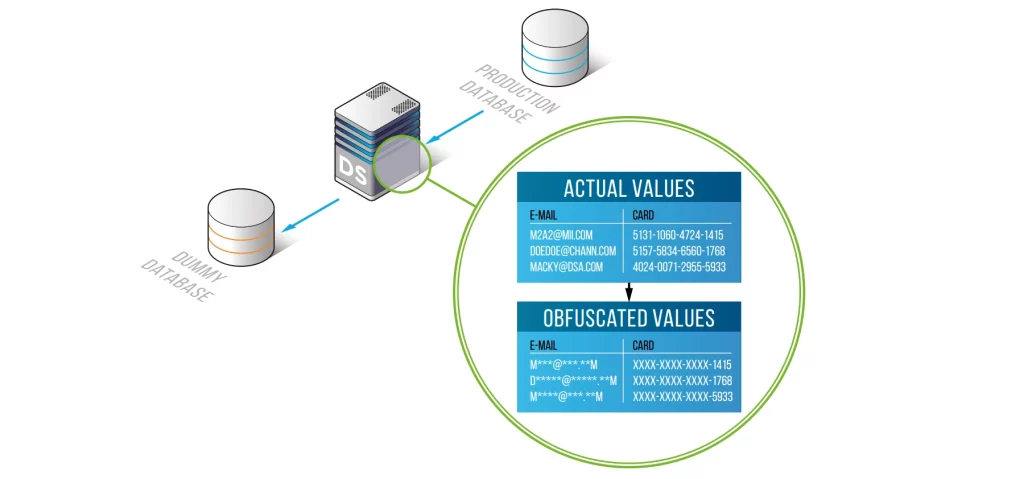
Common masking functions & when to use them
| Function | Example Input | Masked Output | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| FPE (AES-FFX) | 4111 1111 1111 1111 | 4129 6034 5821 4410 | Credit-card simulations |
| Substring Redact | [email protected] | al***@***.com | Emails, usernames |
| Date Shuffle (+/- 365d) | 1990-05-09 | 1990-12-17 | Birth dates |
| Dictionary Swap | Chicago | Frankfurt | City / country fields |
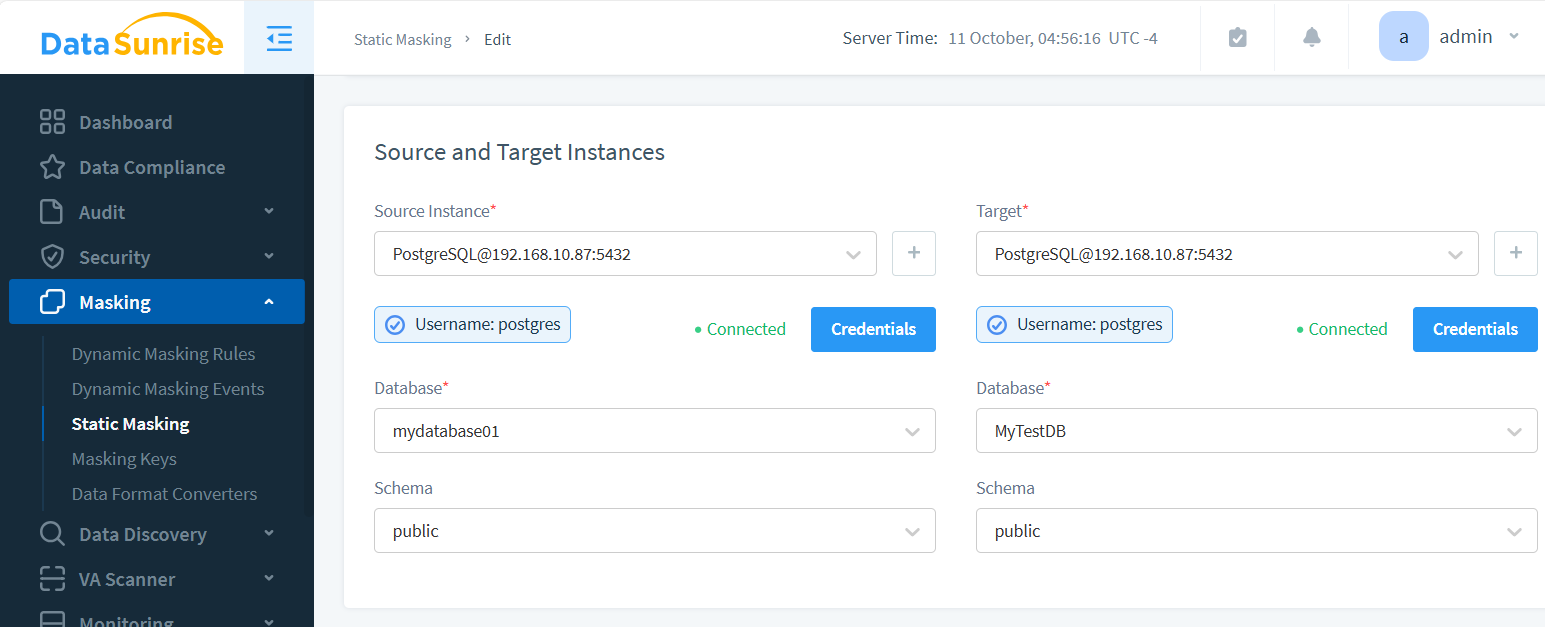
Source and Target Instances
The masking process generates a new instance with masked data. The source contains the original content; the target is where the obfuscated data will reside.
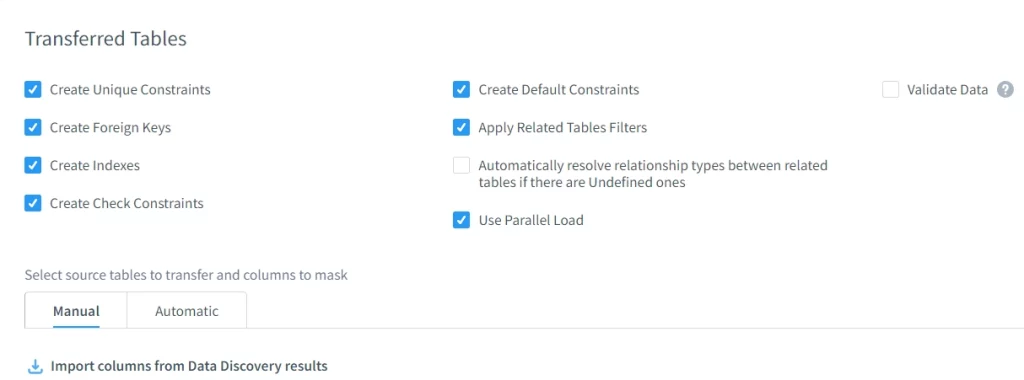
Transferred Tables
DataSunrise preserves referential integrity, constraints, indexes, and relationships across masked tables—keeping data usable after obfuscation.
Startup Frequency
Run tasks manually, schedule once, or configure recurring intervals. This automates data refresh pipelines and keeps test environments current.
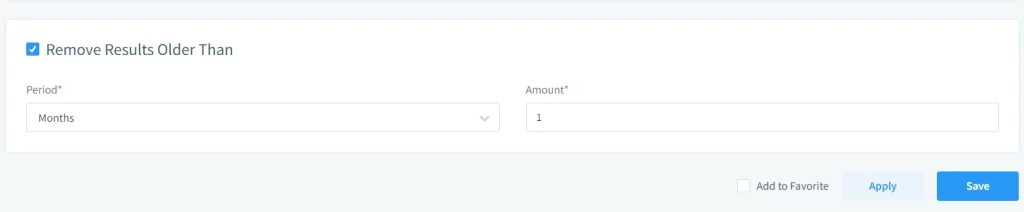
Remove Results Older Than
Apply retention to remove outdated masked databases. This saves storage and reduces operational clutter.
Simulating Static Masking in PostgreSQL
Here’s how you might simulate static masking manually without automation:
-- Step 1: Create masked copy of a table
CREATE TABLE customers_masked AS
SELECT
id,
name,
email,
'XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-' || RIGHT(card_number, 4) AS card_number
FROM customers;
-- Step 2: Mask email format
UPDATE customers_masked
SET email = CONCAT(LEFT(email, 2), '***@***.com');
This works for small-scale masking, but lacks format-preserving logic, foreign key enforcement, and audit logging. DataSunrise automates and scales this workflow across platforms.
Practical Example: PostgreSQL + DataSunrise
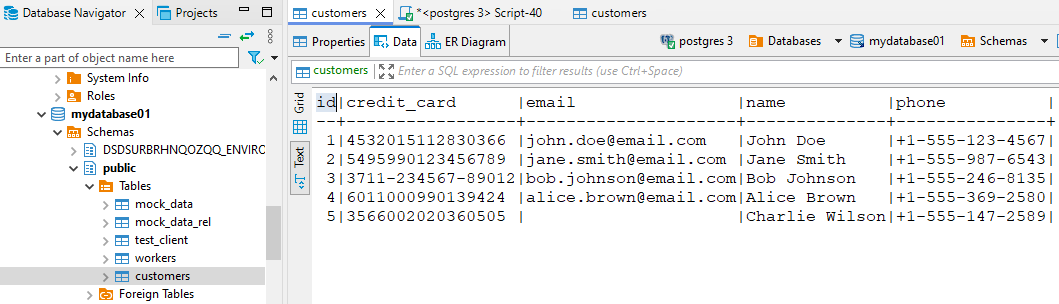
Consider a PostgreSQL database with customer data including names, emails, and card numbers. Unmasked view:
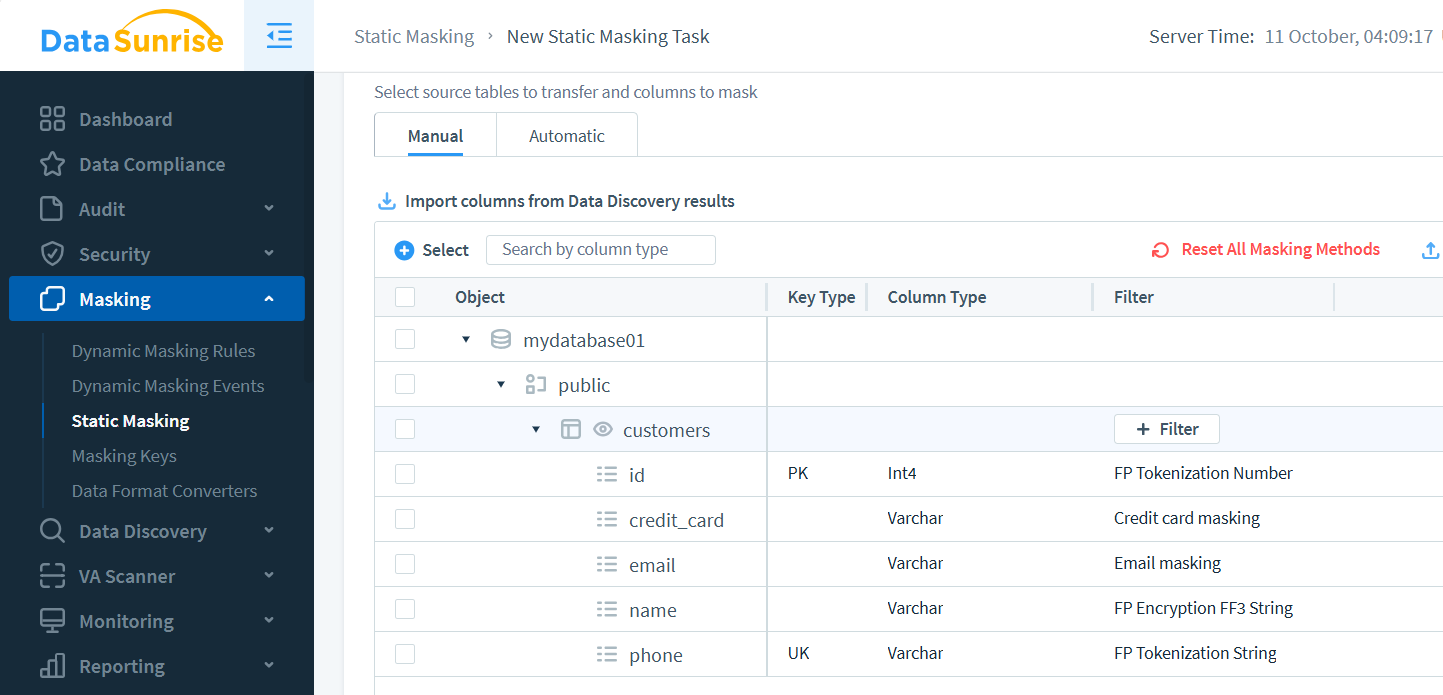
In DataSunrise, configure a task via the Static Masking panel. Select instances, define tables, and choose masking methods per column:
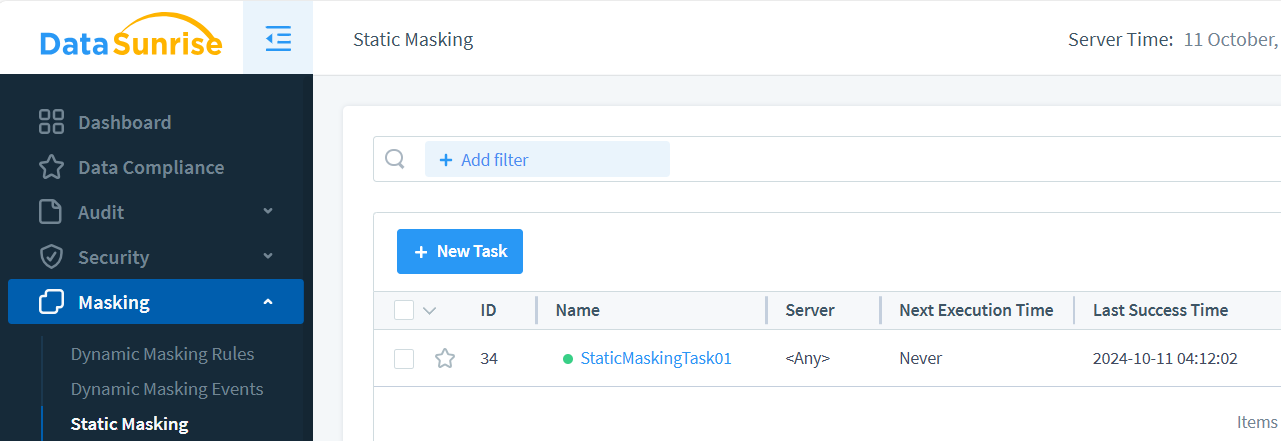
Once the task completes, you’ll see confirmation in the task status:
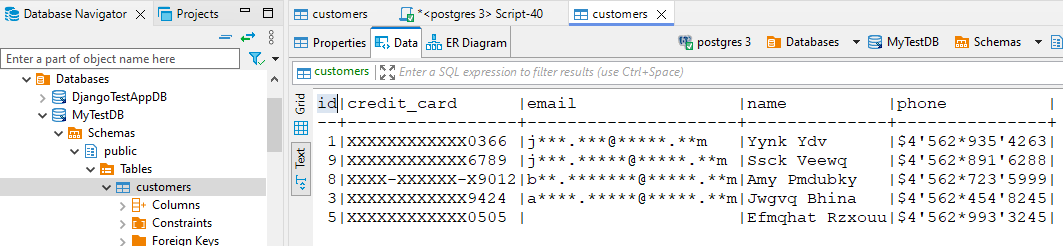
The target instance now contains a fully masked version of the data:
Static Masking with DataSunrise: Key Advantages
- Realistic data for dev/test
- Format-preserving obfuscation
- Referential integrity maintained
- Zero impact on source systems
- GDPR/PCI/HIPAA-ready
Best Practices for Static Data Masking
Even with the right tool, effectiveness depends on precise implementation. Use these practices to keep masking secure, scalable, and audit-ready:
- Mask at the column level: Target only fields that pose risk (names, emails, card numbers) to preserve usability.
- Prefer format-preserving methods for analytics: Keep length, type, and referential patterns for BI, joins, and exports.
- Mask before offloading: Export masked copies to S3, cold storage, or vendors to reduce liability.
- Document every job: Track source/target, affected tables, methods, and schedules—DataSunrise logs this for review.
- Quarterly policy reviews: Update configurations as schemas and regulations evolve.
Integrate static masking into CI/CD so each build environment pulls sanitized data automatically. This removes brittle scripts, enforces consistent logic, and keeps test environments aligned with production—without exposing sensitive content.
Done right, static masking becomes a repeatable, embedded control in your SDLC—not a one-off task.
Why Use Static Data Masking with DataSunrise
- Protect sensitive fields like PII, financials, and credentials before external use.
Static masking irreversibly transforms confidential values, ensuring that exported or shared datasets cannot reveal real customer information—even if they leave your secure environment. - Meet mandates including GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS.
By anonymizing sensitive elements at the source, organizations satisfy regulatory requirements around data minimization, safe sharing, and protection of personal information. - Share data safely with contractors, analysts, and third parties.
Masked datasets enable collaboration without exposing live production data, reducing the risk of insider misuse or accidental disclosure. - Reduce risk while supporting realistic test data environments.
Developers and QA teams can work with high-fidelity datasets that maintain statistical value and business logic—without the danger of handling real identities or financial details. - Preserve referential integrity across complex schemas.
DataSunrise masking maintains consistent relationships between tables and fields, ensuring that applications, analytics, and test pipelines continue to function correctly after anonymization.
Conclusion
Static Data Masking (SDM) remains a fundamental element of modern data security frameworks, offering a reliable and efficient method to anonymize sensitive information while preserving the structure, integrity, and usability of datasets. By substituting confidential values with realistic yet non-identifiable equivalents, organizations can safely leverage production-like data for testing, development, analytics, and AI model training without risking exposure of personal, financial, or proprietary details. This approach not only ensures compliance with global regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, SOX, and PCI DSS but also maintains an optimal balance between privacy, functionality, and efficiency across DevOps pipelines and enterprise data ecosystems.
Beyond meeting compliance obligations, static masking plays a crucial role in complex operations like cloud migrations, third-party collaborations, and interdepartmental data exchange. Its centralized management and automation capabilities guarantee consistent policy enforcement across hybrid and multi-cloud environments—reducing human error and ensuring complete traceability throughout the data lifecycle. When integrated with complementary technologies such as dynamic masking, Database Activity Monitoring (DAM), and intelligent data discovery, SDM becomes a vital component of a unified data governance strategy.
Within comprehensive platforms like DataSunrise, static masking not only prevents unauthorized data exposure but also enhances operational flexibility by enabling secure data sharing, testing automation, and innovation at scale. Through real-time monitoring, automated compliance enforcement, and centralized audit visibility, it transforms data privacy from a reactive obligation into a proactive force for trust, resilience, and sustainable digital transformation.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now