Amazon OpenSearch Compliance Management
Amazon OpenSearch compliance management is the discipline of controlling, monitoring, and proving how sensitive data is handled inside OpenSearch indices. OpenSearch is often deployed for log analytics, observability, security analytics, and application search, which means it inevitably collects user identifiers, request metadata, and operational telemetry that can fall under regulatory scope.
AWS provides the managed service and security features, but compliance ownership stays with you. If you store regulated data in OpenSearch, you must demonstrate that access is governed, exposure is minimized, activity is auditable, and evidence can be produced on demand. For baseline service context, see Amazon OpenSearch Service.
This guide explains how to build Amazon OpenSearch compliance management as a repeatable program: discover sensitive data, define policy boundaries, audit and monitor access, protect data in motion with masking, and automate compliance reporting using DataSunrise.
Amazon OpenSearch Compliance Management: What You Must Control
Compliance management is not a single setting. It is a control system built around four questions:
- What data is stored? OpenSearch documents can contain structured fields and unstructured payloads, so classification must be automated.
- Who can access it? Access must be enforced with least privilege and clear ownership.
- What is exposed in results? Even authorized users should not automatically see full sensitive values.
- Can you prove it? You need consistent audit records, retention, and reports for regulators and internal audits.
These expectations map directly to common requirements across data compliance regulations including GDPR, HIPAA technical safeguards, PCI DSS, and SOX compliance.
Compliance Management Challenges in Amazon OpenSearch
OpenSearch introduces governance challenges that look different from traditional databases:
- Sensitive data sprawl inside logs and payloads. “Just logs” often contain emails, IP addresses, session identifiers, tokens, and customer IDs.
- Fast-changing index landscapes. New pipelines, index templates, and enrichment jobs create new fields without explicit review.
- Overbroad access for operational convenience. Teams commonly grant wide read access to avoid breaking dashboards, which conflicts with least privilege.
- Evidence fragmentation. Platform logs, application logs, and security tools may all hold partial truth, making audit responses slow and inconsistent.
Effective compliance management therefore requires controls that sit close to the data access path and produce centralized evidence.
Implementing Amazon OpenSearch Compliance Management with DataSunrise
DataSunrise provides a unified layer for security and compliance controls that can be applied consistently across OpenSearch environments. The goal is to turn compliance management into an operational workflow rather than an ad-hoc audit scramble.
1) Discover and classify sensitive data in OpenSearch
Start with visibility. Use Data Discovery to scan indices and identify sensitive fields, including PII. Discovery results create a defensible scope for policy enforcement and prevent blind spots caused by manual assumptions.
For a sustainable program, run discovery on a schedule and treat classification as continuous, not a one-time inventory exercise.
2) Define compliance policy boundaries and ownership
Compliance policies should reflect business intent: who needs access, which indices are in scope, and which actions require auditing. DataSunrise supports centralized policy workflows through Compliance Manager and security baselines aligned with data security and database security programs.
Enforce least privilege using role-based access control and structured access controls. When multiple rules apply, define deterministic outcomes using rules priority so enforcement remains predictable. To reduce compliance drift at scale, align policies with your organization’s data security policy.
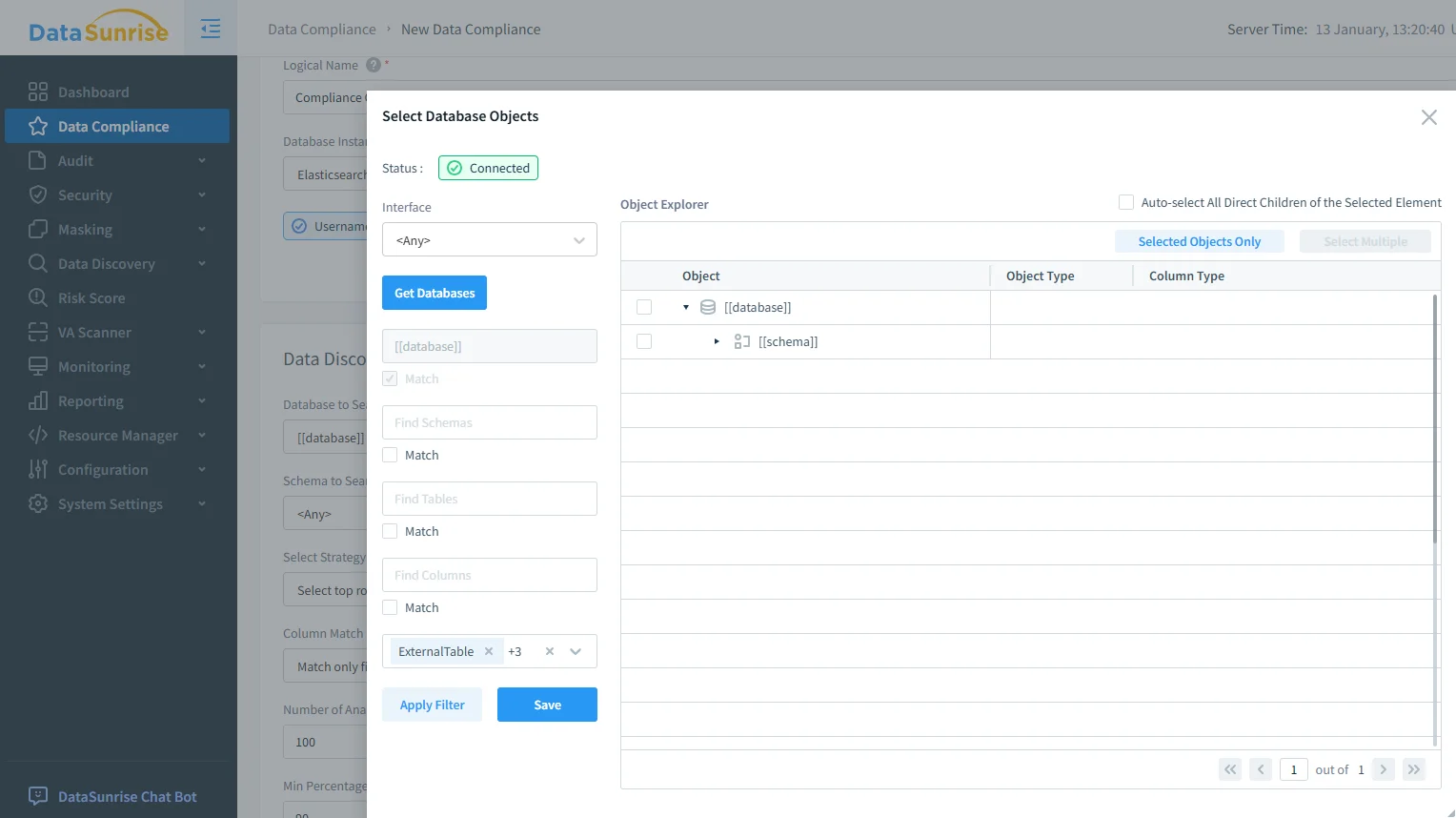
Scoping governance: selecting OpenSearch objects ensures compliance rules apply to the right indices and fields.
3) Audit, monitor, and retain evidence
Auditors expect traceability: who accessed what, when, and under which policy. DataSunrise provides centralized Data Audit with detailed audit logs and immutable audit trails. Pair this with database activity monitoring to spot abnormal patterns and support investigations with context-rich records.
Audit evidence also needs storage discipline. Plan retention and performance using guidance on audit storage so logging does not become a bottleneck.
As a baseline for native service logging, AWS documents OpenSearch audit logs here: Amazon OpenSearch audit logs.
4) Reduce exposure with masking and threat controls
Compliance management is not only about who can query, but also what the query returns. Use dynamic data masking to redact sensitive values at query time and static data masking to generate safer datasets for non-production use. Where teams need realistic datasets without real identifiers, consider synthetic data generation to reduce exposure while preserving analytical value.
To strengthen the access path against abusive patterns, apply a database firewall and validate configurations with vulnerability assessment practices. This helps prevent compliance drift caused by misconfiguration and unreviewed changes.
5) Automate compliance reporting
Compliance programs fail when reporting is manual. DataSunrise supports evidence packaging via report generation and automated compliance reporting, enabling repeatable exports for internal audits, external auditors, and regulator requests. For additional resilience, fold audit evidence into continuous data protection practices so governance remains consistent across operational changes.
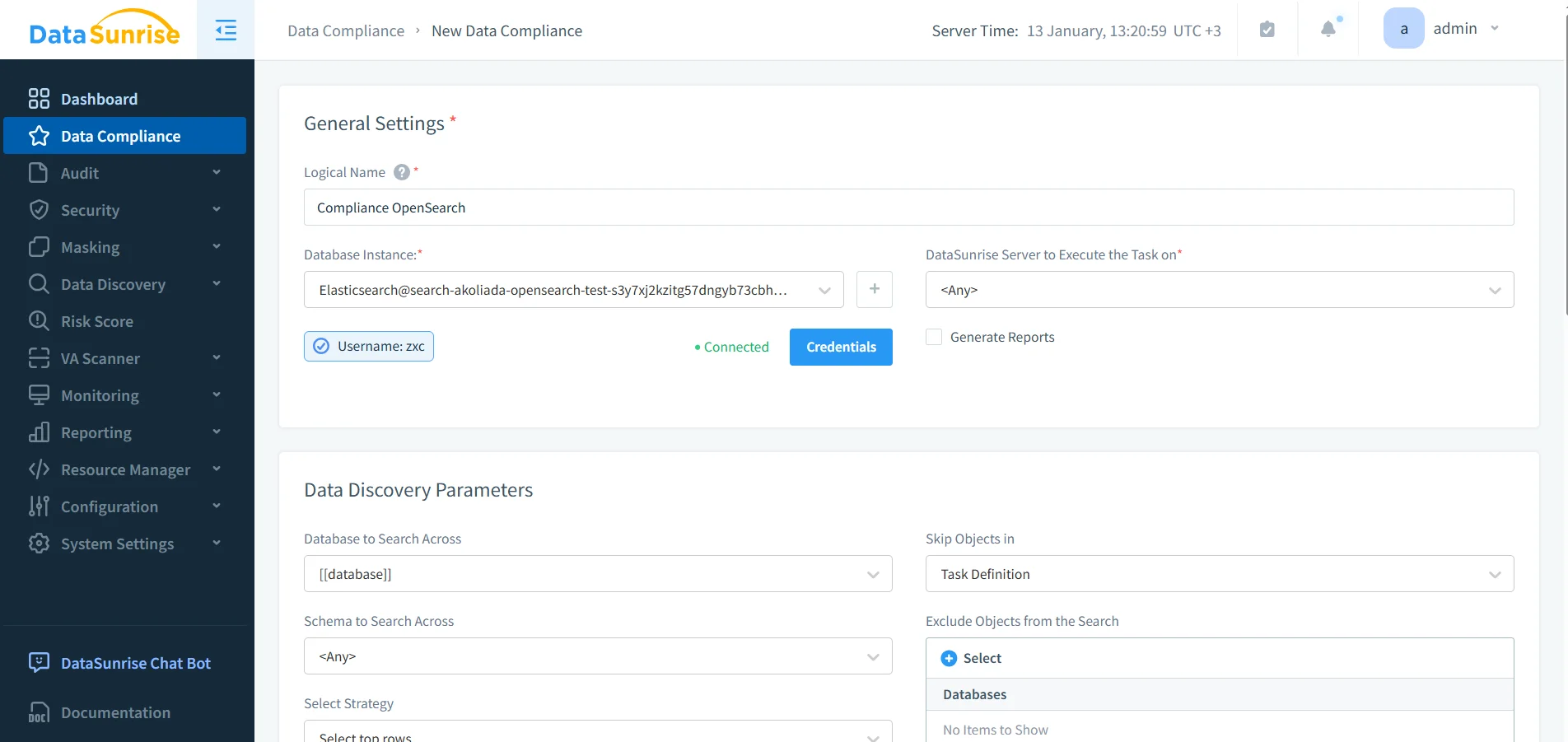
Compliance rules: defining OpenSearch policies in DataSunrise standardizes enforcement and reporting.
Compliance Management Controls at a Glance
| Control area | What it achieves for OpenSearch | What you should be able to prove |
|---|---|---|
| Discovery and classification | Identify regulated fields and index scope | Evidence of what sensitive data exists and where it lives |
| Access governance | Restrict access by role and intent | Least-privilege policy boundaries and ownership |
| Auditability | Log who accessed what and when | Audit logs and trails that reconstruct activity reliably |
| Exposure reduction | Prevent raw sensitive values from being returned | Masking rules, enforcement evidence, and exceptions |
| Reporting and retention | Generate audit-ready evidence packages | Repeatable reports and retention controls |
Do not treat OpenSearch as “just logs.” If an index contains user identifiers or payload data, regulators will treat it as a governed data store. Build compliance management around discovery, least privilege, and query-level exposure controls.
Do not index secrets or authentication artifacts (API keys, session tokens, passwords) into OpenSearch and assume encryption “solves it.” If those values appear in searchable documents, you have created an easy exfiltration path and a compliance incident waiting to happen.
Conclusion: Make Compliance Management Continuous
Amazon OpenSearch compliance management works when it is continuous: discover what is stored, govern access with least privilege, minimize exposure with masking, record auditable evidence, and automate reporting. With a unified platform approach, OpenSearch can remain highly usable for analytics and search while meeting compliance obligations in a way that is defensible under audit pressure.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now