Amazon Redshift Audit Tools
Amazon Redshift is a distributed, columnar data warehouse designed for large-scale analytics. It excels at query performance and concurrency; however, auditing in Redshift is not a first-class, centralized capability. Instead, audit data is fragmented across system tables, exported logs, and cluster-level metadata, as described in the official Amazon Redshift documentation.
As organizations scale analytics workloads, onboard more users, and integrate BI tools and automated pipelines, understanding who accessed what data, when, and how becomes a strict operational requirement. In regulated environments, this visibility is not optional; rather, it directly affects security posture, compliance readiness, and incident response capabilities. Consequently, this need is closely tied to broader practices such as database activity monitoring and maintaining a reliable data activity history.
Therefore, audit tools for Amazon Redshift exist to close this gap. Specifically, they provide structured visibility into database activity, reconstruct execution timelines, and enable governance over distributed analytical workloads. As a result, this approach builds on core principles behind audit logs and extends Redshift into a compliance-ready system suitable for security investigations and regulatory audits.
What Are Audit Tools?
Audit tools are systems designed to collect, organize, and preserve evidence of database activity in a form suitable for investigation, governance, and compliance. Unlike basic logging mechanisms, they focus on context, sequence, and accountability rather than isolated technical events; therefore, they align with the principles behind a structured database audit trail.
In analytical platforms such as Amazon Redshift, audit tools play a critical role because activity is inherently distributed. For example, queries execute across multiple nodes, sessions may span long-running workloads, and operational metadata is scattered across internal structures. As a result, audit tools correlate these signals into coherent records that show how actions unfolded over time, which users or roles initiated them, and what data objects were involved, forming a complete database activity history.
Rather than replacing native telemetry, audit tools operate on top of it. At the same time, they transform low-level system records into structured audit trails that can be reviewed, retained, searched, and presented as evidence during internal investigations or external audits, thereby supporting broader data audit and governance initiatives.
Native Amazon Redshift Auditing Capabilities
Amazon Redshift provides foundational auditing through internal system tables and optional log exports. These mechanisms expose low-level telemetry and allow administrators to retrieve detailed information about database operations.
System Tables for Activity Tracking
Amazon Redshift records detailed execution metadata in a set of internal system tables prefixed with STL, SVL, and STV. These tables expose low-level information about query execution, user sessions, authentication events, and object access. Together, they form the primary native source for reconstructing database activity after execution.
Query Execution Metadata (STL_QUERY)
The STL_QUERY table is the central source for understanding executed SQL statements. It records query text, execution timing, user identity, and execution outcome.
Typical use cases include identifying slow queries, tracing user activity, and reconstructing execution timelines.
SELECT
query,
userid,
starttime,
endtime,
total_exec_time,
aborted
FROM stl_query
ORDER BY starttime DESC
LIMIT 20;
This query returns recent statements along with execution duration and failure status. Each row represents a query fragment executed on a specific node, which means a single logical query may appear multiple times.
Authentication and Connection Events (STL_CONNECTION_LOG)
The STL_CONNECTION_LOG table captures connection-level activity, including successful logins, failed authentication attempts, and session lifecycle events.
This table is commonly used to audit access patterns and identify suspicious login behavior.
SELECT
event,
recordtime,
remotehost,
remoteport,
username,
database
FROM stl_connection_log
ORDER BY recordtime DESC
LIMIT 20;
It provides visibility into who connected, from where, and when, forming the basis for access auditing and security investigations.
Schema and Object Changes (STL_DDLTEXT)
DDL operations such as CREATE, ALTER, and DROP statements are recorded in STL_DDLTEXT. This table is essential for tracking structural changes to the database.
SELECT
userid,
starttime,
sequence,
text
FROM stl_ddltext
ORDER BY starttime DESC
LIMIT 20;
Each DDL statement may be split across multiple rows, requiring ordering by sequence to reconstruct the full command. This table is commonly used during forensic reviews to determine when schemas or tables were modified and by whom.
Data Access and Table Scans (STL_SCAN)
The STL_SCAN table provides insight into how queries interact with data at the storage level. It records table scan operations, row counts, and data volume accessed.
SELECT
query,
tbl,
rows,
bytes
FROM stl_scan
ORDER BY query DESC
LIMIT 20;
This information is particularly valuable for understanding which tables were accessed, how much data was scanned, and whether sensitive datasets were involved during query execution.
Operational Context and Limitations
While these system tables provide deep visibility, they are designed for internal diagnostics rather than centralized auditing. Records are distributed across nodes, retention is limited, and correlation across tables must be performed manually. As a result, administrators often rely on custom queries or external tools to assemble a coherent activity history.
Audit Log Export to Amazon S3
In addition to system tables, Amazon Redshift supports exporting audit logs to Amazon S3. This mechanism extends retention and enables integration with external analytics, monitoring, and archival systems.
Exported logs typically include:
- User activity logs
- Connection and authentication logs
- Login successes and failures
Audit log export is configured at the cluster level and continuously writes log files to a designated S3 bucket.
-- Example: verify logging configuration
SELECT *
FROM svv_logging;
Once enabled, Redshift periodically delivers log files to S3, where they can be consumed by log processing pipelines, SIEM platforms, or custom analytics workflows.
# Example: list exported Redshift audit logs in S3
aws s3 ls s3://my-redshift-audit-logs/
These logs provide a persistent, externally accessible record of database activity and are commonly used for long-term retention, compliance archiving, and offline analysis.
Practical Usage
In practice, organizations often combine system table queries for short-term, detailed analysis with S3-exported logs for long-term retention and cross-system correlation. Together, these mechanisms form the native auditing foundation for Amazon Redshift, although they typically require additional tooling to achieve centralized visibility and compliance-ready reporting.
Centralized Amazon Redshift Auditing with DataSunrise
To build a consistent and operationally usable audit process, organizations often deploy centralized audit platforms that consolidate Redshift activity into a single governed audit stream.
DataSunrise integrates with Amazon Redshift using non-intrusive deployment modes, including reverse proxy and native log ingestion. This approach allows the platform to capture SQL traffic, authentication events, and execution metadata without requiring application changes or query rewriting.
Unified Audit Trail Construction
DataSunrise reconstructs Amazon Redshift activity by correlating multiple execution dimensions into a single, coherent audit narrative. Query execution flows are linked with user and role context, session lineage, accessed objects, and sensitivity classification, all anchored by precise execution timestamps. This correlation process transforms fragmented, node-level events into a chronological, query-aware audit trail that can be reliably used for forensic investigations, operational oversight, and regulatory audits.
Granular Audit Rules
Rather than capturing all database activity indiscriminately, DataSunrise applies fine-grained audit rules that precisely define what should be monitored. Audit policies can be scoped to specific schemas, tables, users, roles, or data categories, allowing organizations to focus on high-risk or regulated assets. This selective approach ensures that critical activity is captured with high fidelity while minimizing noise and storage overhead. Audit rules can be aligned with internal governance policies or mapped directly to external regulatory requirements.
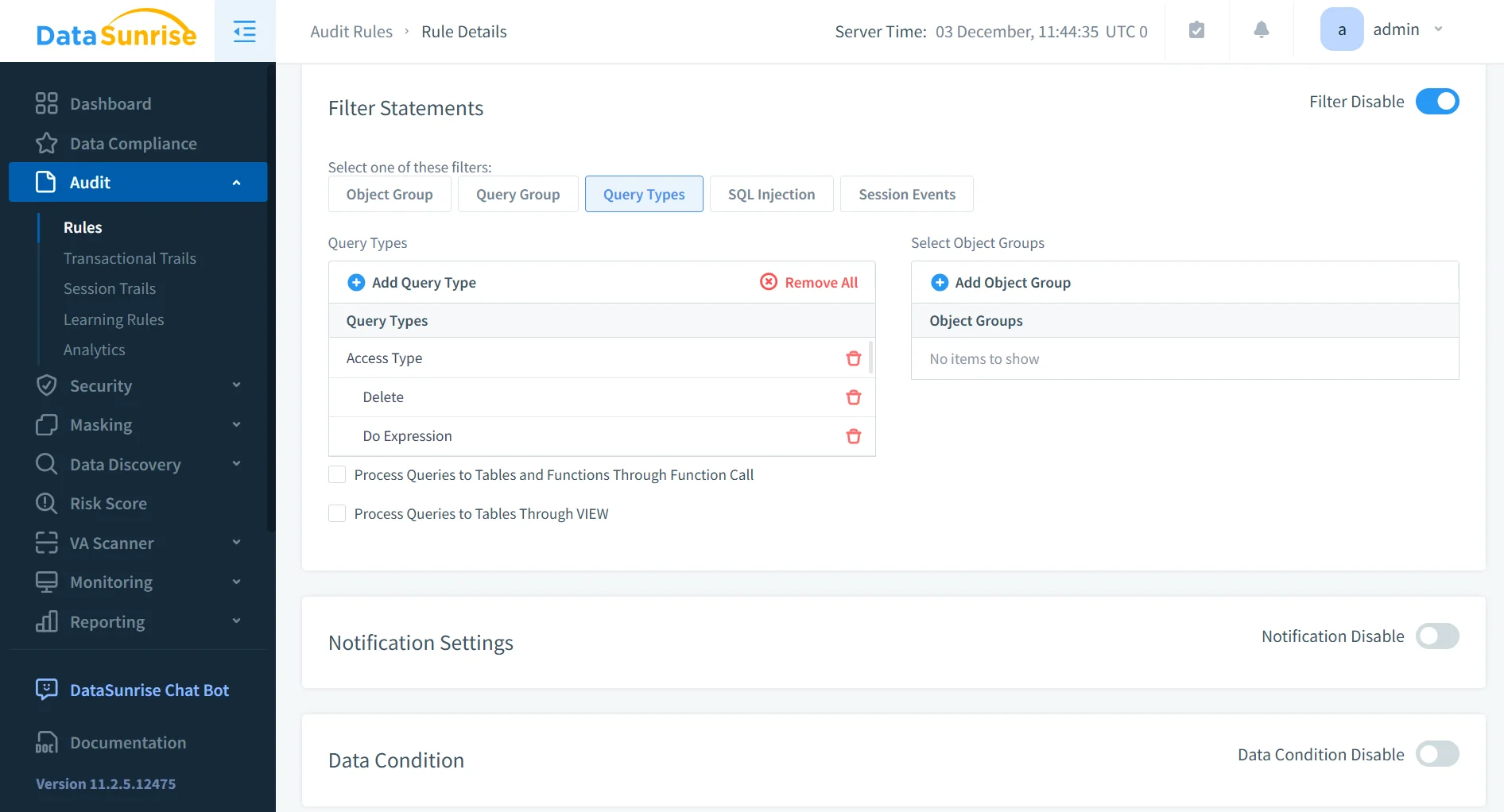
Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts
Beyond historical analysis, DataSunrise provides continuous, real-time visibility into Amazon Redshift activity. Database actions are monitored as they occur, enabling immediate detection of abnormal behavior, suspicious access patterns, or policy violations. Integrated alerting and external security system integrations allow security teams to respond quickly to potential incidents, shifting auditing from a purely retrospective function to an active security control.
Compliance Alignment for Amazon Redshift
Audit tooling plays a central role in maintaining regulatory compliance for Amazon Redshift environments. DataSunrise aligns database activity with the requirements of frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX by retaining, classifying, and structuring audit records according to compliance expectations. Predefined reporting templates and automated evidence generation significantly reduce the manual effort required to prepare for audits and inspections, while ensuring consistency and accuracy across compliance workflows.
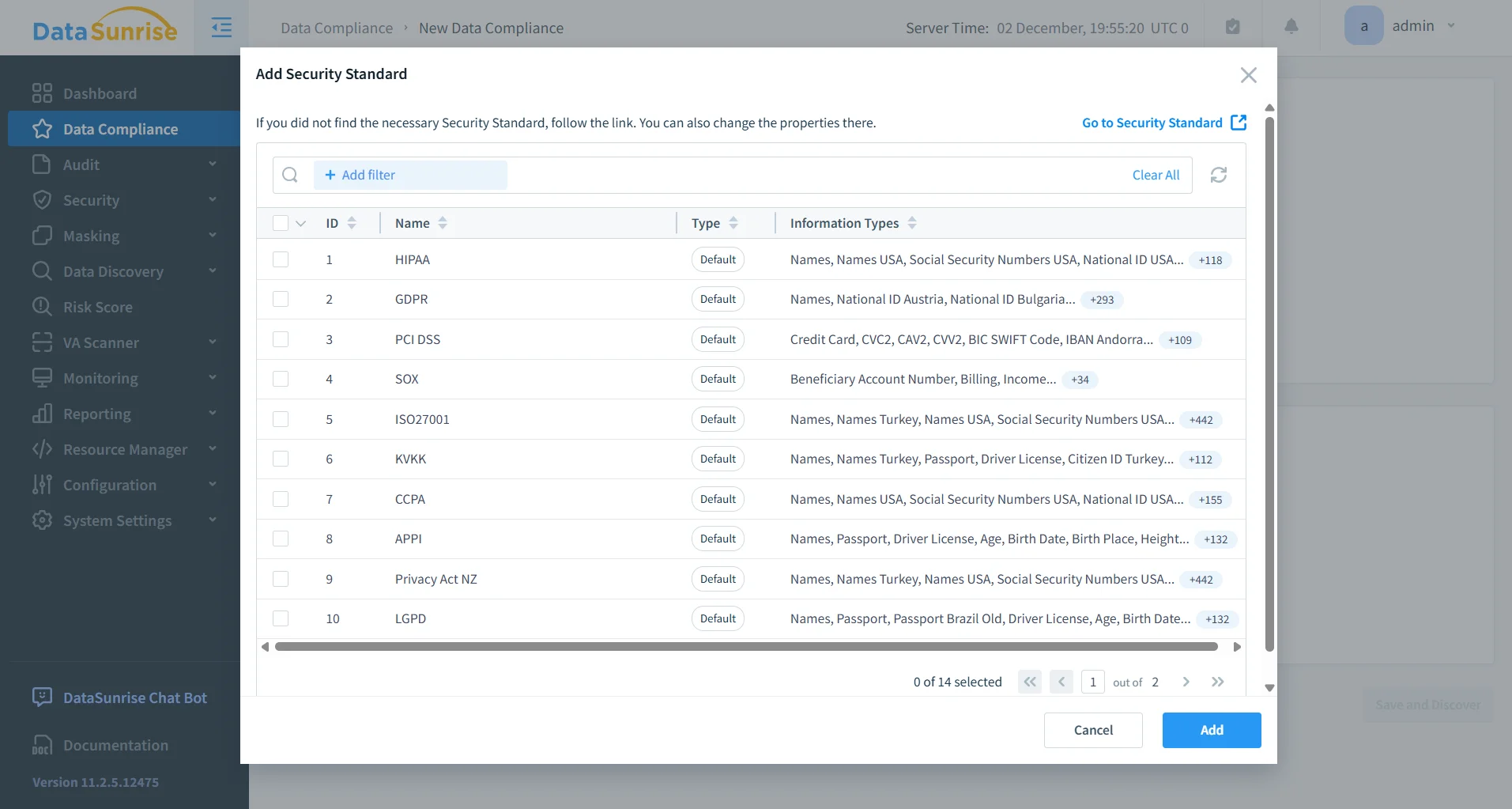
Key Advantages of DataSunrise
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Accelerated Investigation | Fast reconstruction of Redshift activity from a single audit trail. |
| Simplified Compliance | Audit-ready records mapped to regulatory requirements. |
| Clear Accountability | Precise tracking of users, sessions, and accessed objects. |
| User Behavior Insight | Detection of abnormal and risky access patterns. |
Conclusion
Amazon Redshift provides native mechanisms for capturing database activity through system tables and exported logs, forming a basic foundation for auditing. However, without correlation and execution context, this data remains fragmented and difficult to use at enterprise scale.
DataSunrise addresses these gaps by centralizing Redshift activity into unified, query-aware audit trails with real-time visibility. Capabilities such as database activity monitoring and structured database audit trails enable effective investigations and governance enforcement.
By aligning audit records with compliance workflows, DataSunrise simplifies regulatory oversight through automated reporting, centralized data audit, and consistent audit logs. Maintaining a unified database activity history ensures long-term accountability across Redshift environments.
As a result, organizations transform Amazon Redshift into a transparent, governed, and audit-ready analytics platform.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now