Database Audit for Amazon OpenSearch
Database audit for Amazon OpenSearch plays an important role when search clusters evolve from simple log indexes into shared data platforms. In many organizations, Amazon OpenSearch is no longer used solely for operational telemetry. It stores customer identifiers, security events, application payloads, and business metadata accessed by engineers, analysts, automated services, and third-party tools, as described in the Amazon OpenSearch Service overview.
As this usage expands, traditional perimeter controls become inadequate. Teams need continuous visibility into database-level activity: which users and applications connect to OpenSearch, which indices they access, what operations they execute, and whether those actions align with internal security policies and regulatory obligations.
This article explains how to implement a database audit for Amazon OpenSearch using DataSunrise. It focuses on audit architecture, rule design, transactional analysis, and compliance alignment, using real DataSunrise interface screenshots to demonstrate how auditing works in practice.
Why Database Auditing Is Different for Amazon OpenSearch
Although OpenSearch is not a relational database, it behaves like one from a governance perspective. It accepts structured requests, processes queries, modifies stored data, and returns results that may include sensitive fields. For that reason, OpenSearch activity must be audited with the same rigor applied to traditional databases, especially when access occurs through the OpenSearch REST APIs.
However, several characteristics make OpenSearch auditing more complex:
-
API-based database access
OpenSearch exposes its functionality through HTTP APIs rather than SQL. Index creation, document updates, and search queries arrive as REST requests with JSON payloads. A database audit must therefore inspect protocol-level operations instead of relying on SQL logs, aligning with AWS guidance on securing Amazon OpenSearch Service. -
Shared clusters and mixed workloads
The same OpenSearch cluster often serves production applications, analytics dashboards, CI pipelines, and troubleshooting tools. Without a centralized audit layer, it becomes difficult to distinguish routine operational access from risky or unauthorized activity. -
High-impact bulk operations
Bulk indexing and update APIs can modify thousands of documents in a single request. From an audit perspective, these operations carry higher risk than individual queries and must be tracked with full context. -
Regulated data inside search indices
Email addresses, IPs, identifiers, and behavioral attributes frequently appear in indexed documents. Once this data is present, audit requirements tied to GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX automatically apply, consistent with guidance from the NIST privacy and security frameworks.
Database Audit Architecture for Amazon OpenSearch
DataSunrise implements database auditing for Amazon OpenSearch by inserting a transparent control layer between client applications and the OpenSearch service. All database interactions pass through this layer, allowing DataSunrise to observe, evaluate, and record activity in real time, following principles similar to AWS Zero Trust architecture.
This architecture does not require changes to OpenSearch indices or application code. Instead, it standardizes auditing across environments and integrates OpenSearch into broader database activity monitoring strategies.
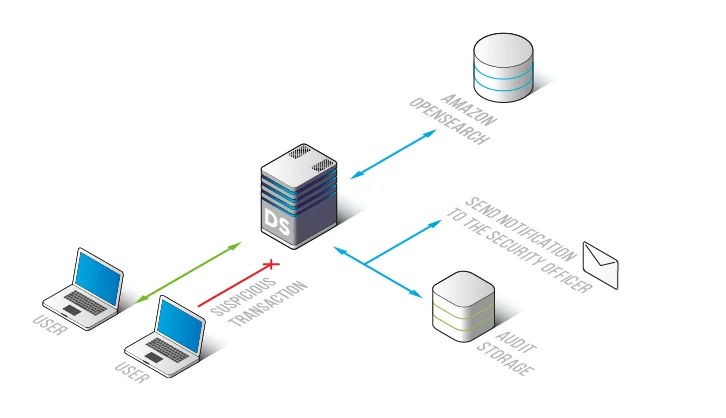
Through this approach, every OpenSearch request becomes part of a centralized audit trail that can be reviewed, filtered, and correlated with activity from other databases and platforms.
Configuring Database Audit Rules for Amazon OpenSearch
Database audit rules define which OpenSearch operations must be recorded and how those records are handled. Effective rule design balances visibility with performance by focusing on meaningful database actions.
Typical audit rule criteria include:
- Index patterns containing sensitive or regulated data
- HTTP methods associated with data modification or extraction
- Database users, service accounts, or source networks
- Session context and execution outcomes
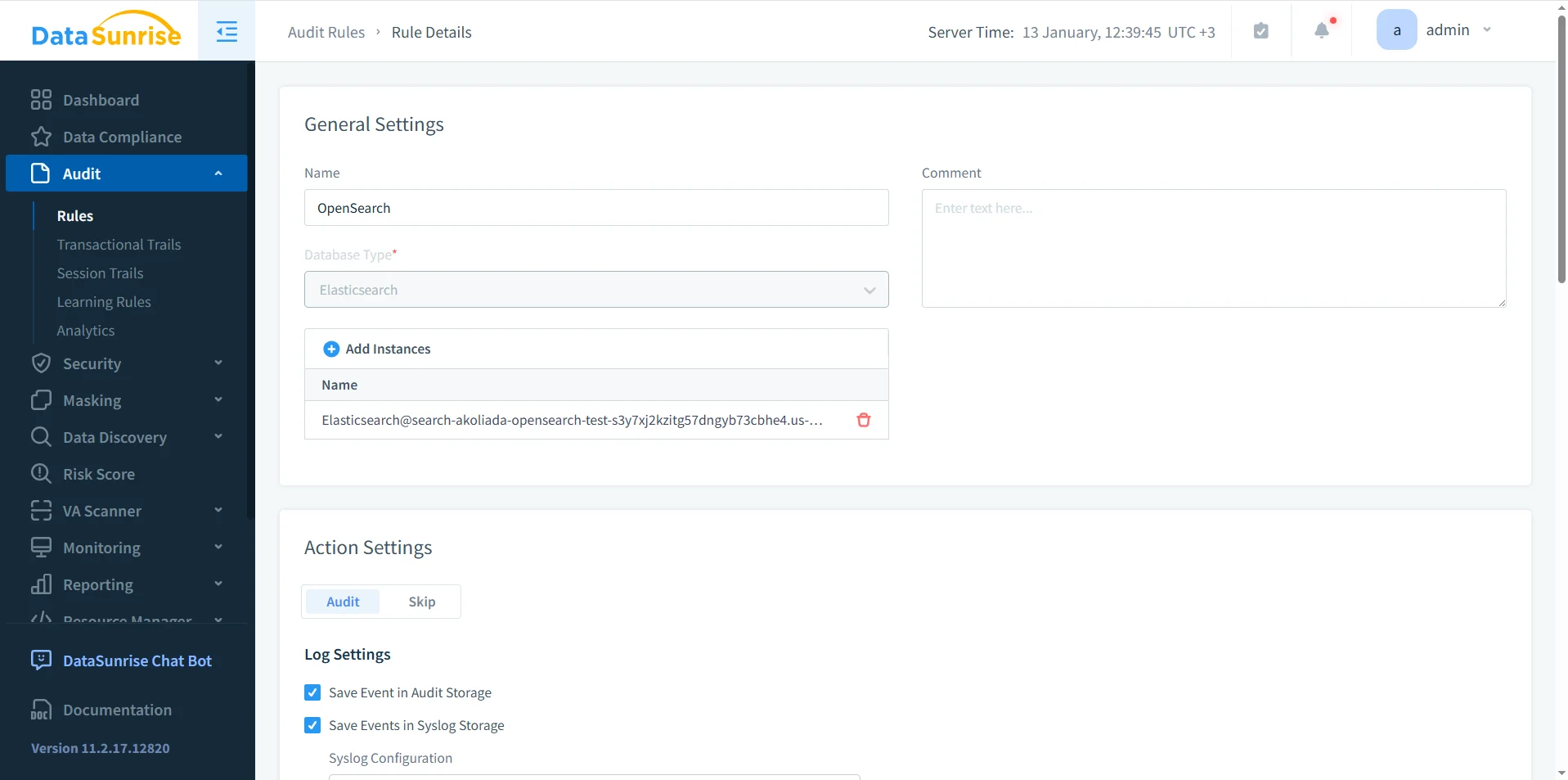
Rule prioritization allows stricter auditing for sensitive indices while applying lighter policies to low-risk operational traffic. This capability is essential for large OpenSearch deployments where raw logging would otherwise overwhelm storage and analysts.
Transactional Database Audit Trails
Once database audit rules are activated, DataSunrise records OpenSearch activity in structured transactional trails. Instead of isolated log entries, related requests are grouped into sessions and transactions.
This structure enables security and compliance teams to reconstruct complete database interaction flows, which is a core requirement in incident response practices outlined by CISA incident response guidance. A database audit for Amazon OpenSearch should present these sequences as coherent narratives.
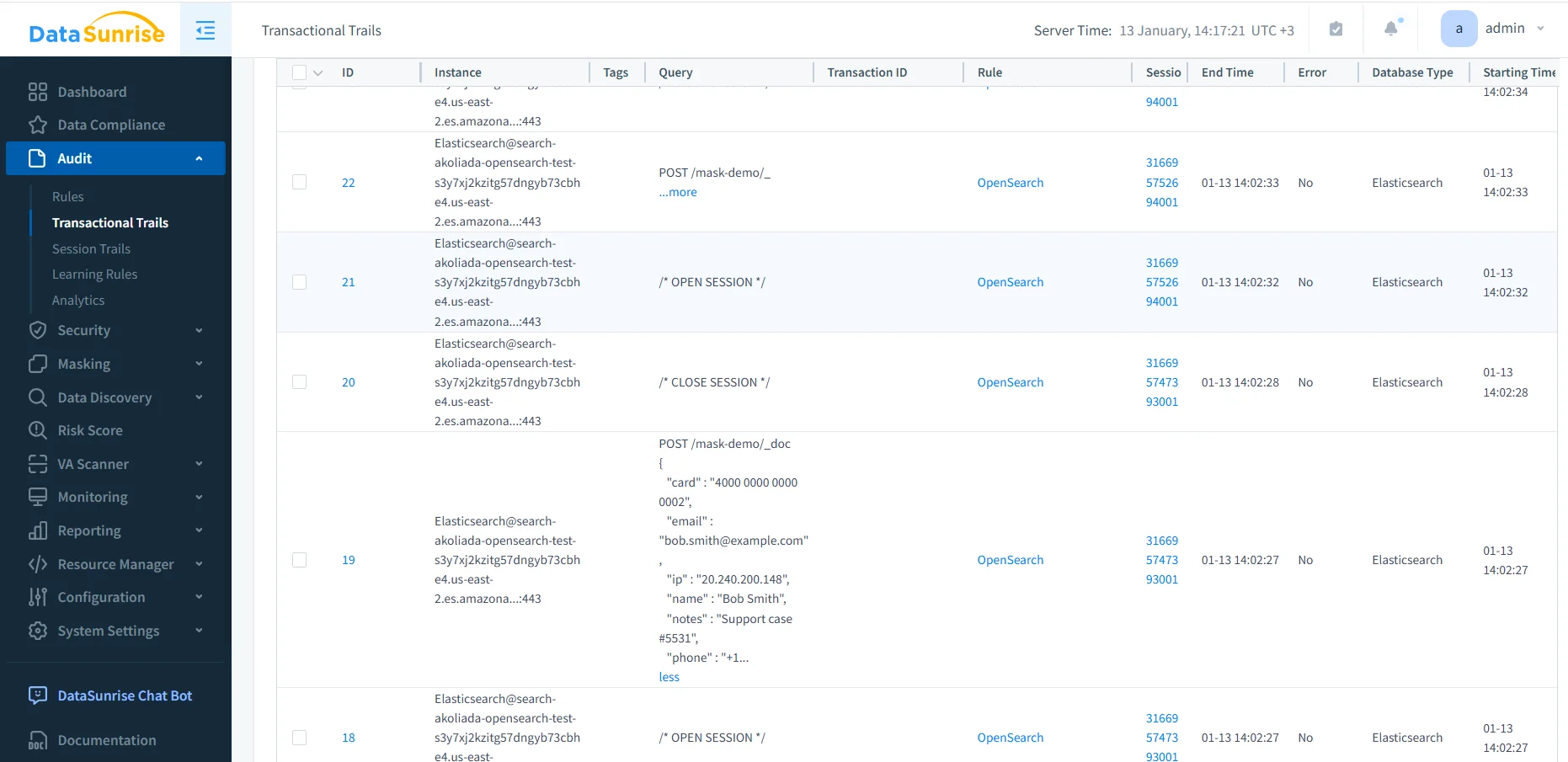
Each audit record typically includes:
- Database endpoint and index name
- HTTP method and request type
- Session and transaction identifiers
- Source IP and user context
- Timestamps, execution time, and error status
This level of detail supports incident response, insider investigations, and compliance evidence collection.
What a Database Audit Covers for Amazon OpenSearch
A comprehensive database audit for Amazon OpenSearch should answer both security and operational questions. DataSunrise audit coverage typically includes:
- Index creation, deletion, and configuration changes
- Document insertion, update, and deletion operations
- Search and aggregation queries that expose stored data
- Bulk indexing and bulk update requests
- Session open and close events
- Failed or denied database operations
Audit events can be stored locally, forwarded to SIEM systems, or integrated into centralized data security workflows for correlation with alerts from other systems.
When defining a database audit for Amazon OpenSearch, start by auditing bulk operations and access to sensitive indices. These actions carry the highest risk and deliver the most value during investigations.
Extending Database Audits with Preventive Controls
Database auditing provides visibility, but visibility alone does not prevent data exposure. DataSunrise complements auditing with preventive and corrective controls that operate on the same traffic.
Dynamic Data Masking
Audit trails often reveal that users without a clear business need still access sensitive fields. With dynamic data masking, sensitive values are obfuscated at query time based on user role or context.
Security Rules and Behavioral Analysis
Unusual OpenSearch usage patterns—such as aggressive scanning or repeated bulk requests—can indicate abuse or automation issues. DataSunrise applies security rules and behavioral analysis to identify and respond to suspicious database activity before it escalates.
Discovery-Driven Audit Scope
Auditing everything equally is inefficient. Data discovery helps identify which indices contain sensitive or regulated data, allowing audit rules to focus on the most critical assets.
Compliance Alignment and Reporting
Database auditing for Amazon OpenSearch directly supports regulatory compliance. Once OpenSearch stores regulated data, organizations must demonstrate control and traceability.
DataSunrise maps database audit evidence to common frameworks, including GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX. Audit records can be packaged into reports using built-in report generation workflows.
| Regulation | Database Audit Requirement | DataSunrise Capability |
|---|---|---|
| GDPR | Trace access to personal data | Centralized audit trails and searchable evidence |
| HIPAA | Monitor PHI access | Session-level database audit logs |
| PCI DSS | Log access to payment data | Immutable audit storage and reporting |
| SOX | Accountability for administrative actions | Change tracking and compliance reports |
Automated workflows through the Compliance Manager further reduce manual effort during audits and reviews.
Conclusion: Database Audit for Amazon OpenSearch in Practice
Amazon OpenSearch delivers speed and flexibility, but it also introduces governance challenges once sensitive data enters search indices. Without a structured database audit, organizations risk losing visibility into how that data is accessed and modified.
A well-designed database audit for Amazon OpenSearch transforms raw REST traffic into structured, reviewable evidence. DataSunrise provides centralized audit trails, session-aware monitoring, and compliance-ready reporting that integrate OpenSearch into enterprise-wide security and governance programs.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now