Dynamic Data Masking in Amazon OpenSearch
Dynamic data masking in Amazon OpenSearch is one of the fastest ways to reduce sensitive data exposure while keeping search, observability, and security analytics fully operational. OpenSearch indexes often contain user identifiers, IP addresses, session tokens, customer references, and operational payloads that were never intended to become searchable “data assets.” Once those values are queryable, you need controls that protect what users see, not just how data is stored.
AWS delivers the managed infrastructure for Amazon OpenSearch Service, but compliance responsibility still sits with the organization operating the cluster and the data flowing into it. This article explains how dynamic masking works in OpenSearch workloads and how DataSunrise can enforce masking policies, collect audit evidence, and keep reporting consistent across environments.
Why Dynamic Data Masking Matters in Amazon OpenSearch
OpenSearch is commonly deployed as a “read-heavy” system for logs and analytics. That usage pattern creates a familiar compliance problem: many people need access to search results, but very few people should see raw sensitive values. Even if OpenSearch permissions are configured correctly, broad read roles are often granted to avoid breaking dashboards, SIEM rules, or incident response workflows.
Dynamic masking closes the gap between “can access the index” and “should see the raw value.” Instead of blocking access entirely, masking transforms sensitive fields in the response so teams can troubleshoot and analyze without exposing regulated data. This reduces the blast radius of over-permissioning and supports privacy-by-design controls described in What is Data Masking.
Dynamic vs. Static Masking: Picking the Right Control
Masking is not a single technique. A mature program uses both dynamic and static approaches, depending on the workflow:
- Dynamic masking applies transformations at query time, based on identity, role, or context. It is designed for production access paths and real-time analytics. See Dynamic Data Masking.
- Static masking transforms data for downstream copies (non-production, exports, QA datasets) to reduce risk outside the primary environment. See Static Data Masking.
For Amazon OpenSearch, dynamic masking is usually the first priority because it protects day-to-day searches, dashboards, and investigations without forcing teams to redesign ingestion pipelines or rebuild indices.
Architecture: Enforcing Masking Without Breaking Search Workloads
Dynamic masking works best when it is enforced close to the access path—where queries can be evaluated consistently and outputs can be controlled before they reach users, dashboards, or automated tools. DataSunrise provides a centralized layer to implement masking policies across OpenSearch environments, while also supporting discovery, auditing, and reporting.
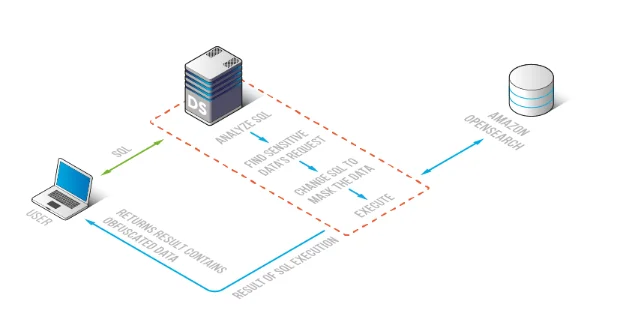
This approach is particularly useful for OpenSearch because sensitive values often appear across multiple indices and document structures. A centralized enforcement layer reduces “policy drift” between teams and prevents masking from becoming a one-off configuration exercise.
Step-by-Step: Implement Dynamic Masking for OpenSearch with DataSunrise
1) Discover sensitive fields across indices
You cannot mask what you cannot reliably identify. OpenSearch data is often semi-structured (JSON) and may include sensitive values inside message fields or nested attributes. Automated discovery helps you find regulated patterns and build a defensible scope.
DataSunrise supports automated data discovery to identify sensitive content such as PII. Discovery results can be used to prioritize which indices and fields require masking, and to reduce blind spots caused by manual assumptions.
2) Define roles and access boundaries
Dynamic masking is most effective when it is role-aware. Observability engineers might need to see request routes and error codes, but not customer emails. Support analysts might need activity context, but not full card numbers. That separation is the practical version of least privilege.
Build a consistent access model using role-based access control (RBAC) and centralized access controls. Then align masking outcomes with the principle of least privilege so sensitive values are visible only when the business purpose clearly requires it.
3) Create dynamic masking rules for OpenSearch fields
Once you know what to protect and who should see it, define the masking behavior. Dynamic rules specify which fields are masked and how the output is transformed (redaction, partial reveal, normalization, or other masking methods). In practice, start with the highest-risk fields: emails, phone numbers, IDs, and authentication-related values.
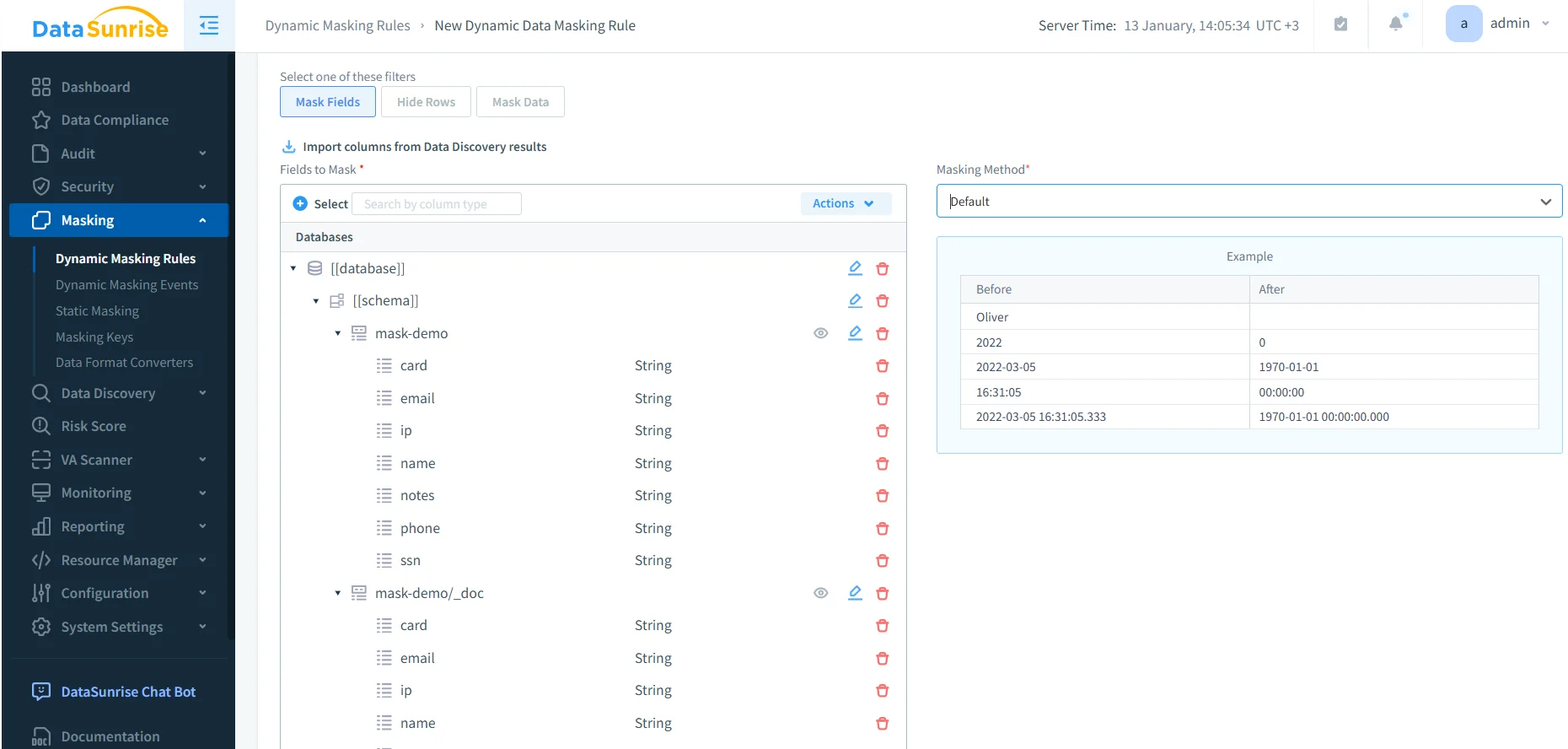
Masking policies scale best when they are part of a broader governance program. DataSunrise supports centralized policy management through Compliance Manager, helping organizations apply consistent controls across environments.
Where multiple controls may apply to the same request, deterministic behavior matters. Use rules priority to avoid ambiguous outcomes and ensure masking remains predictable for both users and auditors.
4) Validate outputs and track masking events
After deploying rules, validate that masking preserves the utility of search results. The right implementation masks the sensitive portion while retaining enough structure for troubleshooting, analytics, and correlation (for example, partial reveal, tokenized formats, or consistent placeholders).
Operational teams also need visibility into when masking triggers and whether any errors occur. Tracking masking events helps confirm that policies are working in real workloads and provides a useful audit signal during incident reviews.
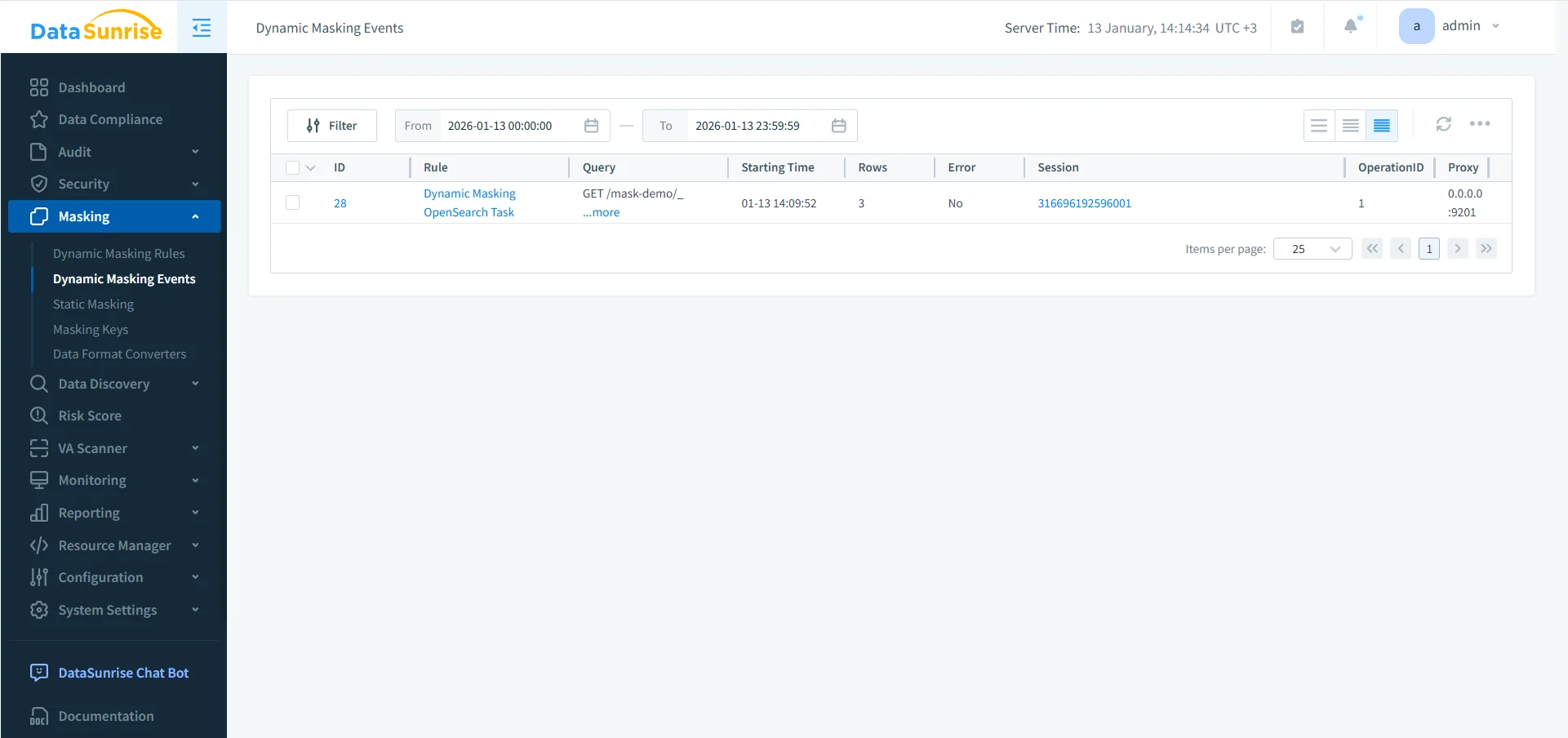
Dynamic masking events: visibility into masked requests, time windows, and execution outcomes supports continuous compliance operations.
Auditing and Compliance Evidence for Masked Queries
Masking reduces exposure, but compliance requires evidence: who accessed governed indices, what policy applied, and what the system returned. DataSunrise supports centralized auditing using Data Audit, detailed audit logs, and immutable audit trails to support investigations and regulatory reviews.
For continuous oversight and anomaly detection, integrate masking with database activity monitoring to spot suspicious access patterns (bulk extraction attempts, unusual query spikes, repeated lookups of sensitive fields). As a baseline reference for platform-native logging, see Amazon OpenSearch audit logs.
To convert activity and policy enforcement into audit-ready artifacts, use report generation. Reporting becomes significantly easier when discovery, masking policies, and audit records live in the same system.
Dynamic masking is also easier to defend when aligned with standard obligations and internal controls. Start with a structured overview of data compliance regulations, then map outputs to programs such as GDPR compliance, HIPAA compliance, PCI DSS compliance, and SOX compliance.
Hardening the Masking Program
Masking is a strong control, but it should not be the only control. Hardening focuses on preventing abusive access and detecting drift:
- Database firewall rules help block suspicious query patterns and reduce scraping risk.
- Vulnerability assessment helps detect misconfigurations that undermine governance.
- Continuous data protection ensures controls remain effective as indices and pipelines change.
Start dynamic masking with the “high-risk, high-frequency” fields first (email, phone, IDs, IPs), then expand using discovery results. Keep rules role-aware and deterministic so dashboards still work and audit evidence stays clean.
Do not rely on masking to fix unsafe ingestion. If secrets (tokens, API keys, passwords) or regulated identifiers are indexed broadly, search becomes an exfiltration accelerator. Prevent sensitive ingestion where possible and enforce scoped access plus auditing immediately.
Conclusion: Dynamic Masking as an Operational Compliance Control
Dynamic data masking in Amazon OpenSearch is a practical way to protect sensitive values while preserving the speed and utility of search-driven workflows. The strongest implementations are discovery-driven, role-aware, and continuously auditable—so masking remains effective as OpenSearch evolves.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now