How to Apply Data Governance for Amazon OpenSearch
How to apply data governance for Amazon OpenSearch becomes a real requirement once OpenSearch is used beyond basic search workloads. Over time, OpenSearch turns into a central aggregation point for application events, infrastructure logs, user activity records, and operational metadata. As a result, OpenSearch often contains sensitive or regulated data—even when it was never intended to be a system of record.
Applying data governance for Amazon OpenSearch means moving beyond basic access controls and building a structured framework that defines what data exists, who can access it, how exposure is limited, and how evidence is produced for audits. AWS provides the managed service and security primitives, but governance remains the responsibility of the organization operating the data. For baseline context, see the official Amazon OpenSearch Service overview.
This article explains how to apply data governance for Amazon OpenSearch in practice, using discovery, policy enforcement, auditing, masking, and reporting—without disrupting search performance or operational workflows.
Why Data Governance Matters for Amazon OpenSearch
Unlike relational databases, OpenSearch is optimized for flexible, semi-structured data. Teams index JSON documents, free-text fields, and enriched payloads with minimal upfront schema discipline. This flexibility accelerates analytics but introduces governance risk:
- Sensitive fields appear in unexpected locations inside documents
- Indices are created dynamically by pipelines and applications
- Access roles are often broad to avoid breaking dashboards
- Audit evidence is fragmented across logs and systems
Once OpenSearch contains personal, financial, or operationally sensitive data, governance must align with data compliance regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and internal controls frameworks like SOX compliance.
How to Apply Data Governance for Amazon OpenSearch with Discovery
Effective data governance always starts with visibility. You cannot govern what you cannot identify. In OpenSearch environments, sensitive data is rarely confined to a single index or field—it often appears inside log messages, request payloads, or nested attributes.
Using automated data discovery, organizations can scan OpenSearch content to identify regulated elements such as Personally Identifiable Information (PII), account identifiers, tokens, and other high-risk patterns. Discovery results establish a defensible governance scope and prevent blind spots caused by manual assumptions.
Discovery should not be a one-time activity. OpenSearch environments evolve continuously, so discovery must be repeatable and policy-driven.
How to Apply Data Governance for Amazon OpenSearch by Scoping Objects
After discovery, governance policies must be scoped precisely. Applying controls globally across all indices often creates operational friction. Instead, governance should target specific indices, fields, and document patterns that actually contain sensitive data.
DataSunrise allows administrators to select OpenSearch objects explicitly and exclude non-relevant datasets. This approach reduces noise while ensuring regulated data remains under governance control.
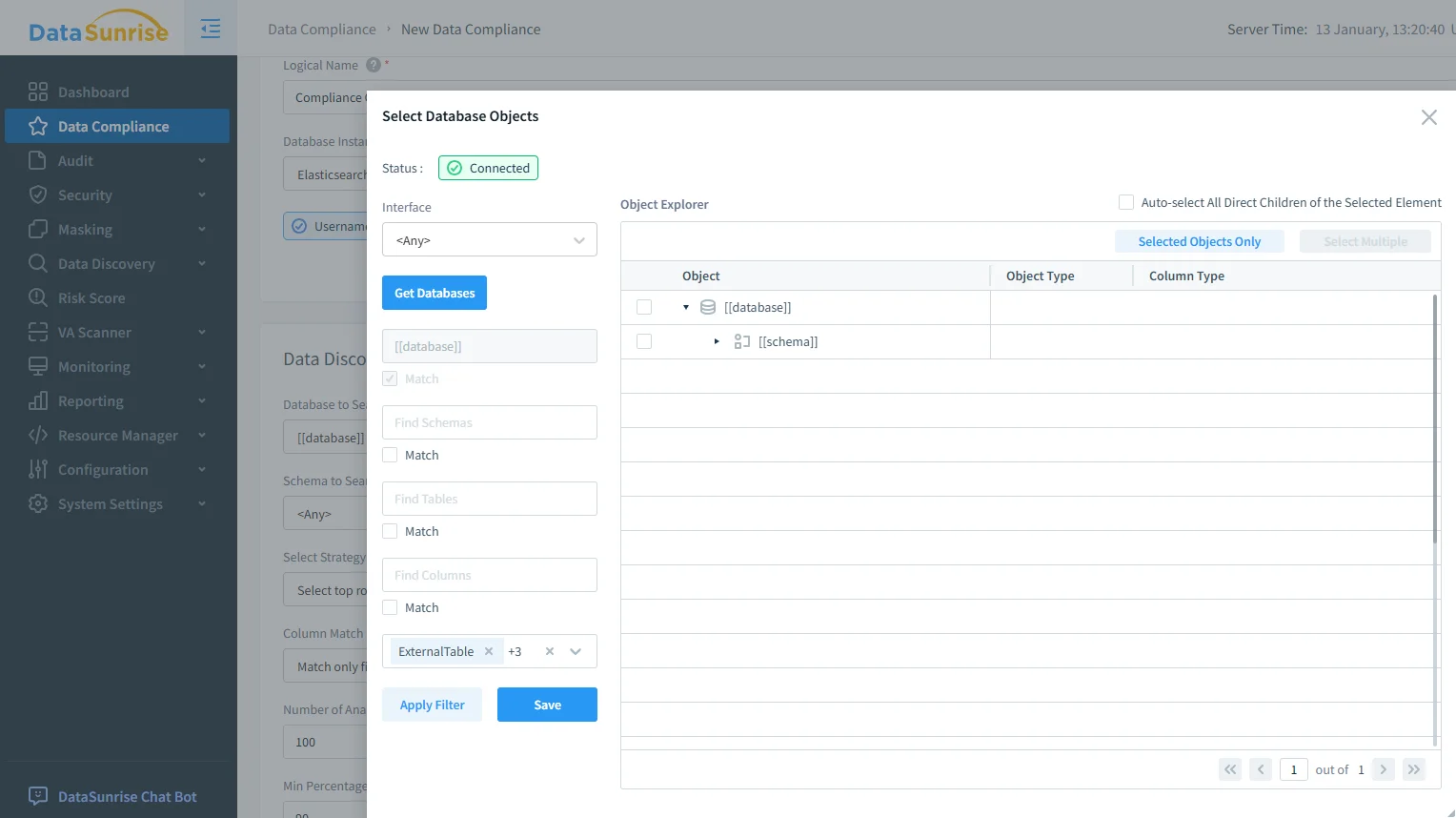
Selecting OpenSearch objects and defining governance scope ensures that policies apply only where required. Clear scoping also simplifies ownership. Security teams define policies, data owners validate scope, and platform teams ensure enforcement aligns with operational requirements.
Step 3: Enforce Access Governance and Least Privilege
Data governance fails quickly when access controls are overly permissive. OpenSearch often supports diverse users: SREs, security analysts, developers, support teams, and business analysts. Each role requires different visibility levels.
A governance-ready access model includes:
- Structured role-based access control
- Centralized access controls applied consistently
- Operational enforcement of the principle of least privilege
Access governance should align with business intent. Analysts may need aggregated insights, while support teams rarely need raw identifiers. Governance policies should reflect those distinctions explicitly.
Step 4: Reduce Data Exposure with Masking
Access control alone does not guarantee minimal exposure. Even authorized users may not need to see full sensitive values. Data governance therefore includes exposure reduction techniques.
DataSunrise supports multiple masking approaches:
- Dynamic data masking to redact sensitive fields in real time
- Static data masking for safe copies and non-production use
- Synthetic data generation for analytics and testing workflows
Masking is particularly effective in OpenSearch because it preserves search functionality while limiting the visibility of regulated fields. This significantly reduces the blast radius of accidental exposure or credential misuse.
Step 5: Capture Audit-Ready Activity Evidence
Auditable governance requires detailed traceability. Organizations must be able to demonstrate who accessed governed data, when access occurred, and whether policies were enforced.
DataSunrise enables this through:
- Centralized data audit controls
- Structured audit logs suitable for compliance reviews
- Immutable audit trails aligned with regulatory expectations
- Continuous database activity monitoring
- Queryable database activity history
AWS provides native OpenSearch audit logging as a baseline reference: Amazon OpenSearch audit logs. However, governance requires consistent evidence across environments and workloads, not just platform-level events.
How to Apply Data Governance for Amazon OpenSearch with Compliance Tasks
To scale governance, policies must be formalized and automated. Ad hoc controls do not survive platform growth or audit scrutiny.
Using Compliance Manager and automated compliance reporting, organizations can define governance policies once and apply them consistently across OpenSearch domains and environments.
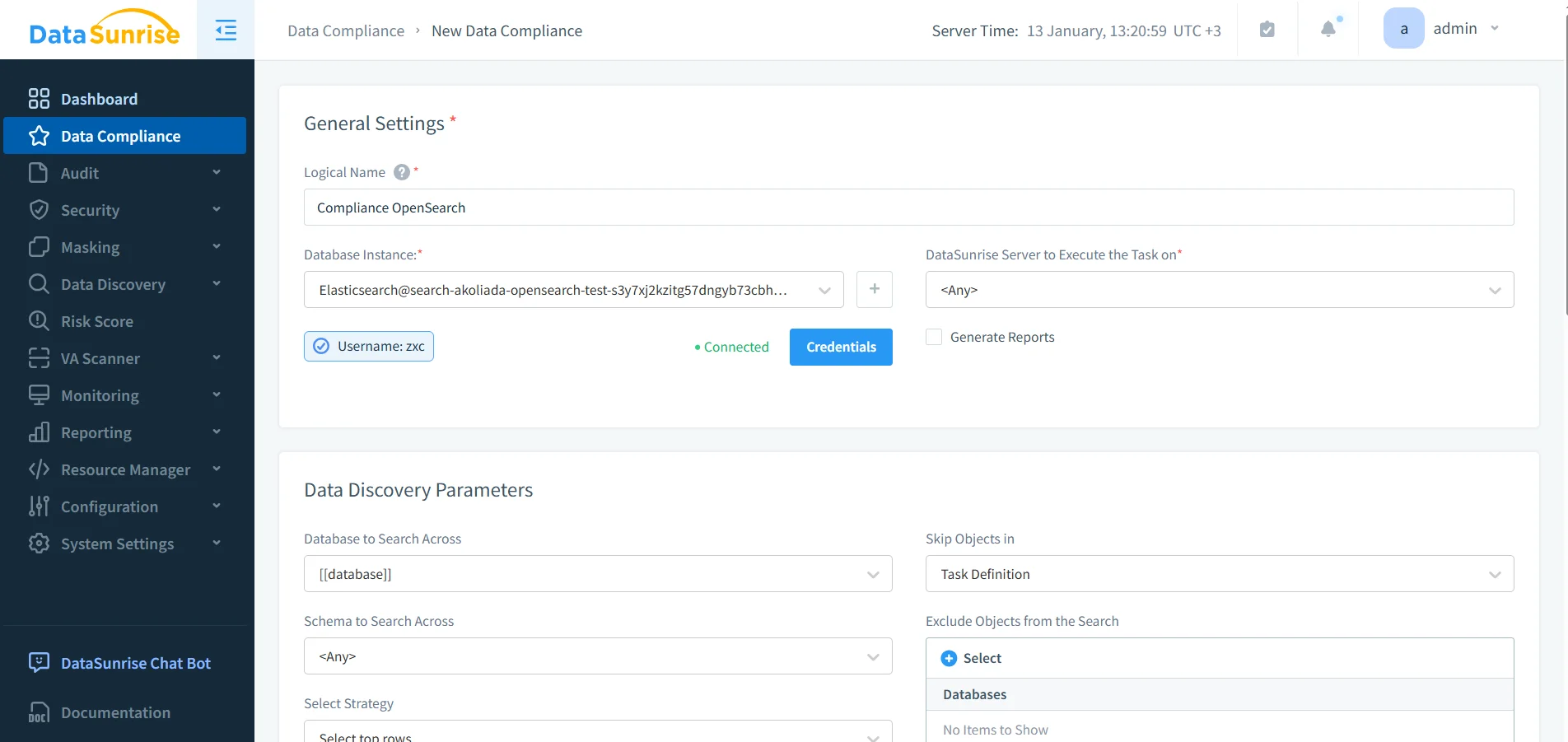
Policies can trigger auditing, alerts, and reports automatically, transforming governance from a manual process into an operational control.
Step 7: Monitor Governance Drift and Security Posture
Data governance is not static. New indices, pipelines, and applications constantly change the OpenSearch landscape. Governance must therefore include continuous monitoring and validation.
DataSunrise supports ongoing assurance through:
- continuous data protection
- vulnerability assessment
- Security enforcement via database firewall
- Structured reporting with report generation
These controls help detect misconfigurations, policy drift, and emerging risks before they turn into audit findings.
Do not treat OpenSearch as “just logs.” If an index contains user identifiers or payload data, regulators will treat it as a governed data store. Data governance must be enforced at the query level, not retroactively after an incident.
Conclusion: Applying Governance Without Breaking OpenSearch
How to apply data governance for Amazon OpenSearch comes down to a repeatable workflow: discover and classify sensitive data, define precise governance scope, enforce least-privilege access, reduce exposure through masking, collect audit-ready evidence, and automate reporting. When implemented correctly, governance enhances trust and compliance without sacrificing performance or usability.
DataSunrise provides an integrated governance layer for OpenSearch, supporting discovery, access governance, auditing, masking, and reporting from a single platform. With structured policies and continuous enforcement, OpenSearch becomes a governed asset rather than an unmanaged risk.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now