How to Apply Dynamic Masking in MySQL
MySQL is fast, familiar, and everywhere. It’s also a magnet for accidental exposure: analysts export query results, support teams run wide SELECT, and production data slips into dev/test. Dynamic data masking reduces that risk by masking sensitive values at query time, while keeping the underlying data intact. It complements static masking and in-place masking, but it is usually the safest first step for production MySQL.
What Dynamic Masking Means in MySQL
Data masking replaces sensitive values with safe substitutes. Dynamic masking does it in real time: the same query can return different results depending on the user, role, client, or network context. That makes it ideal for protecting PII in production MySQL without copying or rewriting the database.
Dynamic masking should be treated as one layer of database security. Back it with a clear data security policy, strong permissions, and auditable enforcement.
Where is masking implemented?
DataSunrise functions as a reverse proxy in numerous environments. DataSunrise connects to SQL clients, BI tools, and apps and applies masking rules before returning results. The schema and query shape remain unchanged since masking takes place at query time. This lessens the possibility of applications and dashboards breaking.
Step 1: Discover and Classify Sensitive Columns
Accurate scope is the first step in dynamic masking. To find high-risk fields like emails, phone numbers, passport IDs, card numbers, and addresses, use data discovery . Then, in order to match masking policies with actual usage, map them to business roles and environments.
Free-text fields and "notes" should not be disregarded. These are frequently overlooked during manual reviews and frequently contain embedded financial or personal data.
Step 2: Define Who Gets Masked and Who Doesn’t
Before creating rules, define visibility by role. Combine RBAC with the principle of least privilege, and enforce explicit access controls for sensitive schemas. As a baseline, allow raw access only to approved privileged roles and mask everyone else.
On the MySQL side, align privileges with that model. MySQL supports role-based privilege assignment; reference: MySQL roles.
Start with discovery and classification, then apply dynamic masking to production read access and static masking for dev/test copies. This reduces risk quickly without breaking workflows.
Step 2.5: Choose Masking Methods That Preserve Usability
Only when dynamic masking preserves data and maintains application functionality does it work. Determine the masked output for each sensitive column. In order for downstream systems to still recognize the value type, you will typically combine format-preserving substitutions, partial reveal (keeping a small suffix or prefix), and redaction (hiding everything). Masking types. provide a quick reference for common methods.
| Column | Common dynamic masking output | Why it helps |
|---|---|---|
| Mask local-part, keep domain (e.g., a***@example.com) | Preserves routing context while hiding identity | |
| Phone | Keep last 2–4 digits, mask the rest | Supports support verification without full disclosure |
| Card number | Show last 4 digits only | Maintains reconciliation workflows and reduces risk |
| Salary | Bucketize (e.g., 50–75K) or mask entirely | Enables analytics while reducing personal exposure |
Step 3: Create a Dynamic Masking Rule in DataSunrise
In DataSunrise, dynamic masking is set up as a rule that applies to a database instance. Choose MySQL as the database type, give the rule a name, and link the target MySQL instance.
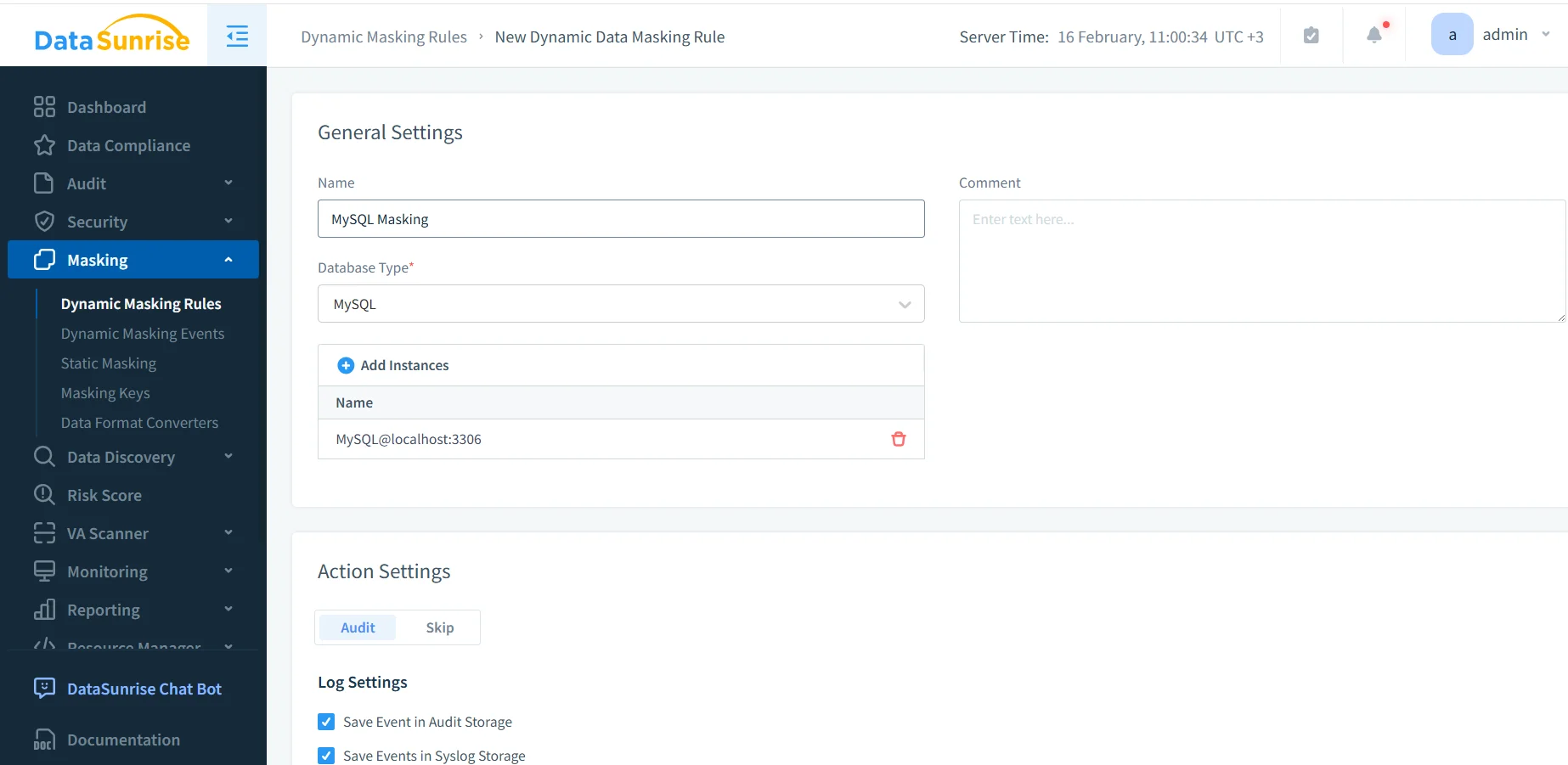
Step 4: Activate the Rule and Manage Priority
Make sure that the rule is turned on for the right MySQL instance. Ordering is important when you use more than one rule. DataSunrise lets you prioritize evaluations so that the most specific rule wins when conditions are the same. Check the rules priority rules priority.
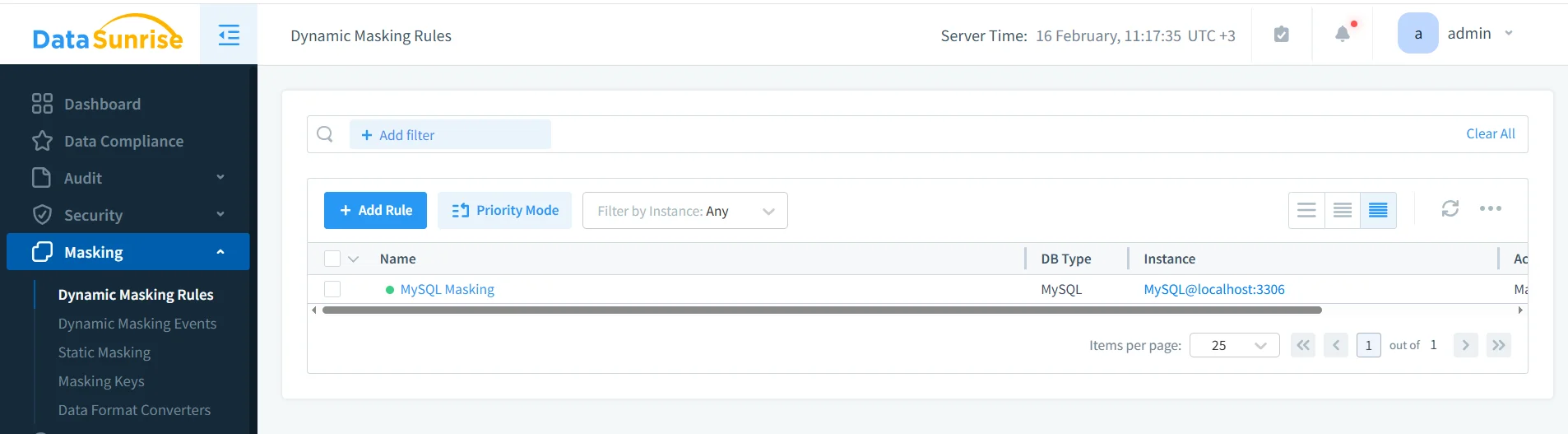
The MySQL instance has dynamic masking rule turned on, and you can see it in the DataSunrise Dynamic Masking Rules list.
Turn on logging along with masking. This lets you track things down with audit logs and helps with a centralized data audit workflow.
Step 5: Validate Masked Output with Real Queries
Validation should use real clients and real queries. Compare results for privileged vs. non-privileged users. For least-privilege accounts in MySQL, you’ll use GRANT and REVOKE; reference: GRANT statement.
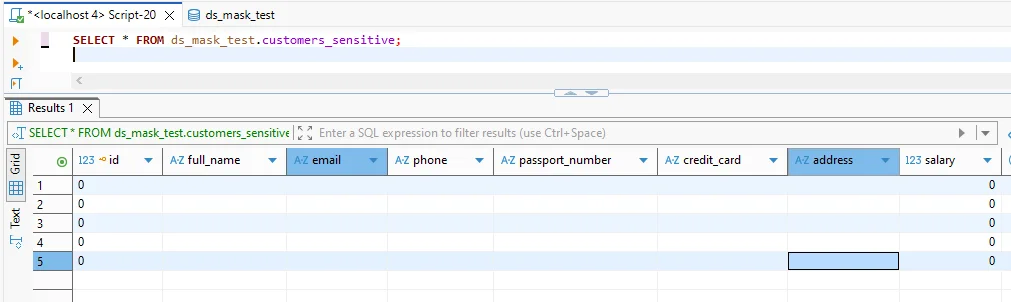
Validation query after masking: sensitive MySQL columns return masked values while the query structure remains unchanged.
For strong accountability, maintain an auditable history using audit trails. Also verify that applications don’t break due to unexpected NULLs, type shifts, or formatting changes.
Operational Best Practices for Dynamic Masking
Monitor sensitive access: Use database activity monitoring to detect bulk exports and unusual query behavior.
Harden the environment: Run vulnerability assessment and reduce attack paths with a database firewall plus security rules against SQL injections.
Protect data at rest: Pair masking with database encryption and operational continuous data protection, especially for replicas and backups.
Don't think of masking as your only way to control. If attackers get privileged access, they can still get to private information. Use masking along with least-privilege access, monitoring, encryption, and regular audits.
Compliance: Turning Masking into Evidence
Compliance programs care about preventing unnecessary exposure and proving controls work. Map dynamic masking to compliance regulations and common frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX.
To standardize reporting and evidence collection, use the DataSunrise Compliance Manager.
Conclusion: Apply Dynamic Masking in MySQL Without Breaking Apps
One of the quickest methods for lowering MySQL exposure without having to rebuild systems is dynamic masking. Find sensitive columns, specify visibility based on roles, enforce query path masking, and use actual client behavior to validate results.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now