How to Apply Static Masking in MySQL
Production MySQL databases contain a wealth of useful information, including information that you really don't want to appear in a vendor-managed test environment, a QA sandbox, or a developer laptop dump. The workable solution is static masking, which makes a permanently masked copy of your MySQL data so that teams can function normally without disclosing financial information, login credentials, or real identities.
Fundamentally, data masking keeps the dataset useful by substituting safe values for sensitive ones. For Personally Identifiable Information (PII) such as names, emails, phone numbers, passport IDs, and addresses—as well as internal data like salaries and customer account attributes—this is particularly crucial in MySQL.
What Static Masking Is (and How It Differs from Other Types)
Data in a copied dataset can be transformed using Static masking. The masked values are saved in the target database after the task is finished and stay masked indefinitely. This contrasts with in-place masking, which alters the original dataset directly, and dynamic data masking, which masks values only in query results.
For training environments, analytics sandboxes, and development/test pipelines where real identifiers are not needed, static masking is usually the best choice. Because you can standardize the creation and refresh of masked datasets over time, it also fits in well with test data management.
When to Use Static Masking for MySQL
Static masking is the right move when you need a “safe copy” of your MySQL data:
Dev/Test refreshes: replace production snapshots with masked equivalents before distributing them.
Vendor access: share realistic datasets without sharing real customer identities.
Analytics sandboxes: keep the schema and distributions usable while removing real values.
Training and demos: demonstrate workflows without exposing regulated data.
Even when data is masked, it should still be treated as sensitive. That means aligning with your organization’s data security policy and broader data security practices.
Preparation Checklist Before You Mask
Static masking goes smoothly when you do a little homework first:
Discover and classify sensitive fields. Use data discovery to identify which columns require protection and how they should be treated.
Decide what must stay consistent. Some test cases require stable relationships (for example, the same customer email always masking the same way). Your masking strategy should preserve usability without reintroducing risk.
Separate source and target. Always mask into a target database/schema meant for non-production usage. If you need to create a source export first, MySQL’s official documentation for mysqldump is a solid reference.
Lock down access to masked environments. Apply role-based access control (RBAC) and the principle of least privilege, even for masked datasets.
Before masking at scale, run a pilot on a small schema and validate join behavior, unique constraints, and application workflows. Fix issues early, then expand scope.
Step-by-Step: Apply Static Masking in MySQL with DataSunrise
DataSunrise provides an enterprise-ready layer for database security controls, including repeatable static masking workflows. The approach below mirrors how teams typically roll static masking into regular MySQL data refresh cycles.
Step 1: Create a New Static Masking Task
Create a new static masking task and define your source and target. The source is your original dataset (often a production snapshot). The target is the masked destination dataset used by dev/test or analytics.
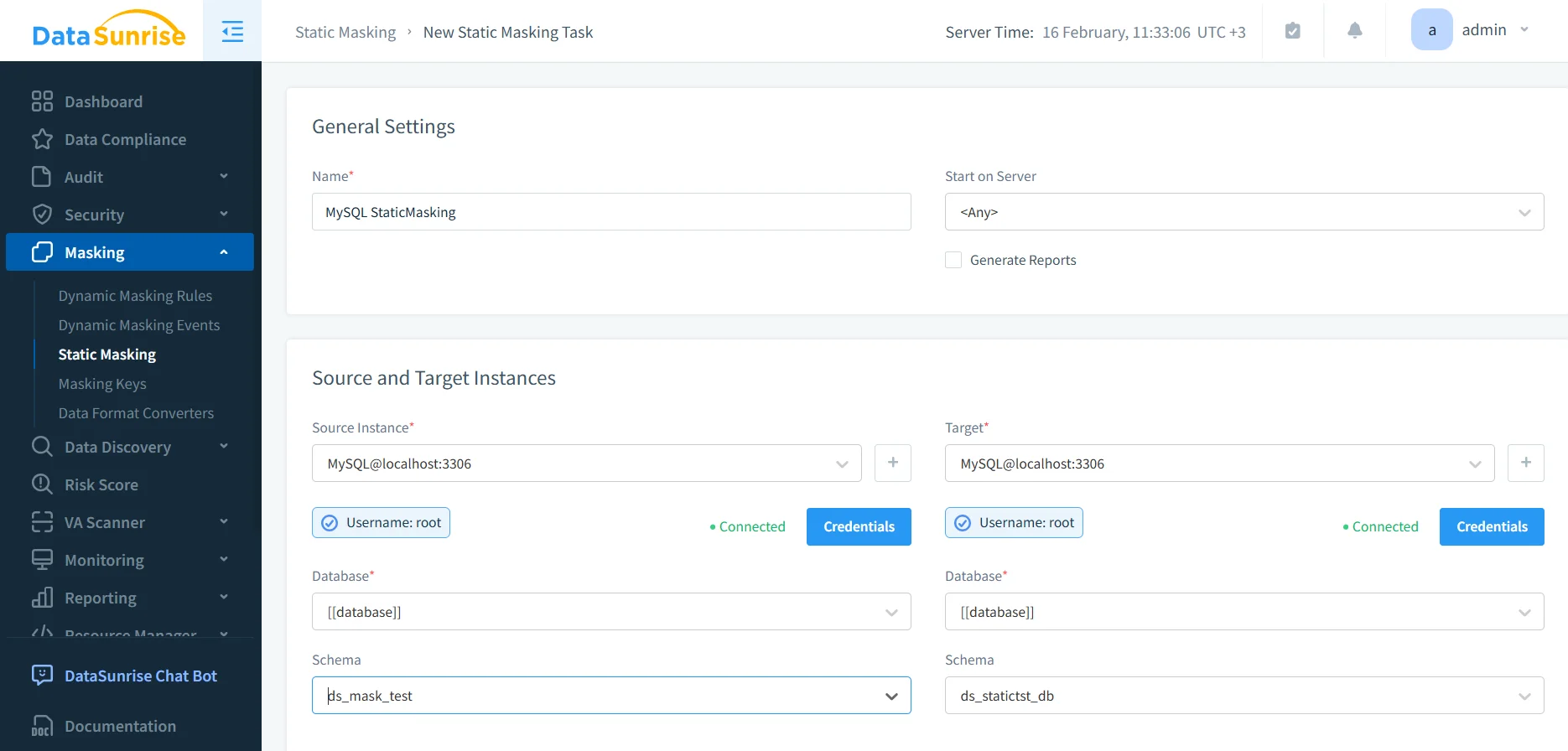
This is also the right moment to ensure your target environment is protected with controls like database encryption, especially if masked datasets are stored in shared infrastructure.
Step 2: Select Source Tables and Columns to Mask
After selecting the source and target, choose the tables and columns that should be masked. DataSunrise supports different masking methods depending on your field type and your usability requirements. If you’re deciding between redaction, substitution, shuffling, or format-preserving approaches, review masking types to match technique to risk level.
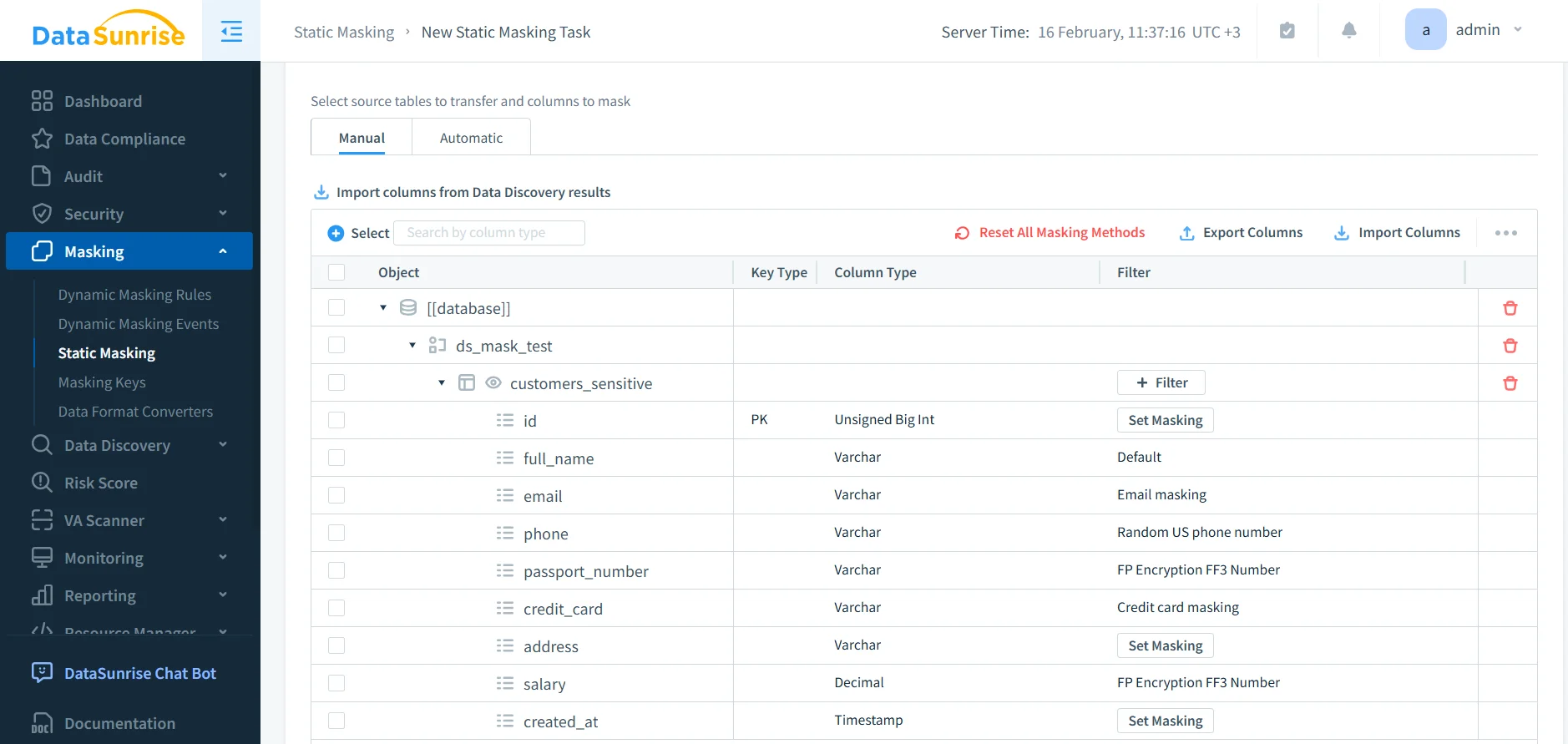
Select source tables and assign masking methods per column to control how MySQL data is transformed in the target dataset.
For MySQL environments that rely heavily on permission segmentation, it’s useful to align masking outcomes with MySQL’s role model. The official MySQL documentation on roles can help standardize who can access the masked target database.
Step 3: Run the Task and Generate Evidence
Once your masking methods are defined, run the static masking task. Many teams generate artifacts for audit and internal governance, especially when working under regulatory requirements. DataSunrise supports operational proof via audit logs and centralized data audit workflows. If you need to explain “who did what and when” to security and compliance teams, the concept of audit trails is the right framing.
For structured reporting, many deployments use report generation to standardize documentation and reduce manual compliance work.
Step 4: Validate Masked Output in the Target MySQL Database
Validation is not optional. Query the target schema and confirm that sensitive values are transformed correctly, while the schema, types, and referential structure remain usable for applications and tests.
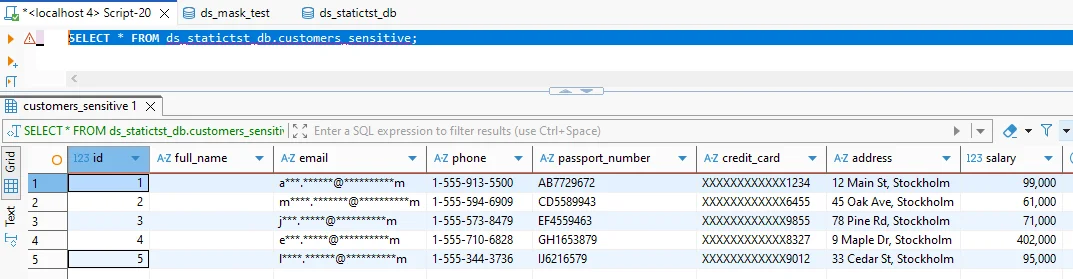
Verify masking results by querying the target MySQL schema and confirming sensitive columns are masked while data remains usable.
As part of validation, confirm that indexes, constraints, and joins behave as expected. If a field is used as a join key, choose a masking method that preserves relationships or provide a mapped substitute. This is where disciplined database activity monitoring also helps by exposing unexpected access patterns during testing.
Static masking is designed to change data permanently in the target dataset. Do not run it against production tables or shared schemas without a verified backup and an isolated target. Treat the target as irreversible.
Operational Best Practices for Static Masking in MySQL
Static masking works best when treated as a repeatable pipeline step, not a one-off project. These practices reduce breakage and reduce the chance of hidden exposures:
Schedule masking refreshes so dev/test data stays current, but always masked before distribution.
Harden permissions and access paths using centralized controls aligned with compliance regulations.
Assess MySQL security posture regularly with vulnerability assessment to find weak accounts, risky grants, and configuration drift.
Reduce query-based attacks using a database firewall and targeted security rules against SQL injections to prevent abusive extraction patterns.
Protect masked datasets like real assets with continuous data protection so you retain control over access, change history, and operational visibility.
Static Masking and Compliance: Keep It Simple, Keep It Defensible
Static masking is often driven by compliance requirements because it reduces the chance that regulated data leaks into lower-control environments. Common frameworks include GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX. Each framework has different requirements, but the theme is consistent: reduce exposure, limit access, and maintain evidence.
To keep evidence collection and reporting consistent across teams, many organizations standardize policy enforcement with the DataSunrise Compliance Manager.
Conclusion: A Practical Way to Mask MySQL Data for Dev/Test
Static masking in MySQL is one of the most practical ways to stop sensitive data from spreading into dev/test and analytics environments. The workflow is straightforward: identify sensitive fields, define masking methods, run a static masking task into a target dataset, and validate results thoroughly. From there, treat masking as a repeatable pipeline step and pair it with monitoring, access control, and reporting.
DataSunrise supports enforcement across 40+ data platforms, making it easier to apply consistent policies beyond MySQL as your environment grows. To try it in practice, start with the DataSunrise download or request a guided DataSunrise demo.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now