
How to Audit MongoDB

Auditing MongoDB is essential for organizations that handle sensitive or regulated data. It enables tracking of user actions, detection of anomalies, and compliance with standards like GDPR and HIPAA. This guide covers native MongoDB audit configuration — available in MongoDB Enterprise edition — and enhancements with DataSunrise, along with strategies for real-time monitoring, dynamic masking, discovery, and compliance.
Why Audit Matters
Audit logs are the forensic backbone of database security. They record who accessed what, when, and how. This information helps in investigations, confirms compliance with data protection regulations, and supports operational transparency. Without auditing, malicious actions could remain hidden until significant damage is done. This is especially important in industries such as finance, healthcare, and government, where breaches can cause regulatory penalties, reputational loss, and operational disruption.
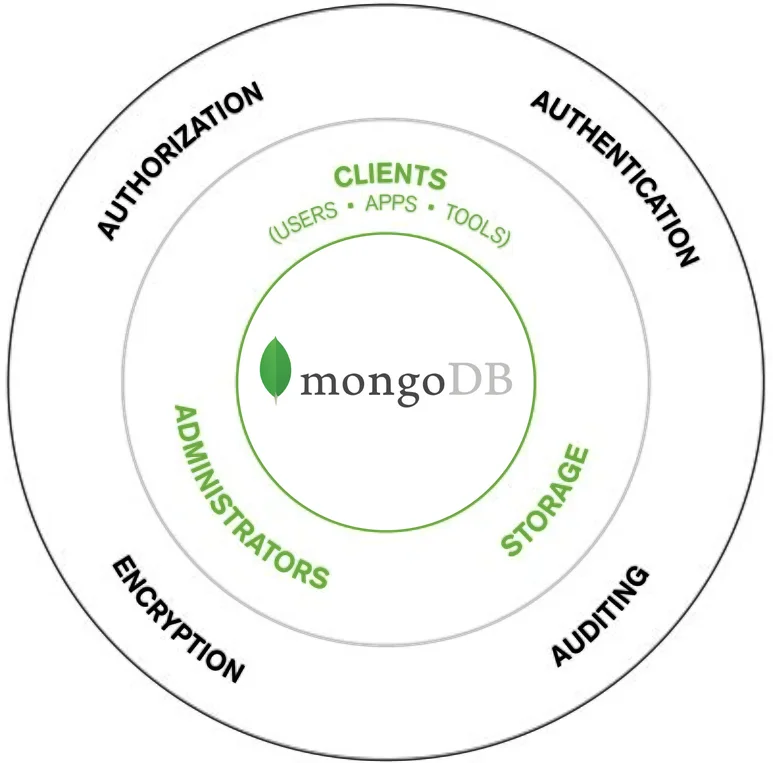
Native MongoDB Audit Configuration (Enterprise)
MongoDB’s native auditing system is only available in MongoDB Enterprise and MongoDB Atlas. It captures database events using flexible filters. To enable auditing, edit mongod.conf with the desired log destination, output format, and event filters:
auditLog:
destination: file
format: BSON
path: /var/log/mongodb/auditLog.bson
filter: '{ atype: { $in: ["createCollection", "update", "insert", "remove"] } }'
Start MongoDB with:
mongod --config /etc/mongod.conf
Convert BSON logs to JSON for analysis:
bsondump /var/log/mongodb/auditLog.bson > auditLog.json
Configuration Examples
Start with command-line flags:
mongod \
--auditDestination file \
--auditFormat BSON \
--auditPath /var/log/mongodb/auditLog.bson \
--auditFilter '{ atype: { $in: ["insert","update","remove"] } }' \
--config /etc/mongod.conf
Send audit events to syslog:
auditLog:
destination: syslog
format: JSON
systemLog:
destination: syslog
verbosity: 0
Filter by namespace:
auditLog:
destination: file
format: JSON
path: /var/log/mongodb/audit.json
filter: '{ "param.ns": { $regex: "^sales\\." }, atype: { $in: ["insert","update","remove"] } }'
Filter admin actions for a user:
auditLog:
destination: file
format: JSON
path: /var/log/mongodb/audit-admin.json
filter: '{ "users.user": "admin", atype: { $in: ["createUser","updateUser","grantRolesToUser","dropUser","authCheck"] } }'
Atlas/Enterprise event example:
{
"atype": "createUser",
"ts": { "$date": "2025-08-15T11:04:12.901Z" },
"local": { "ip": "127.0.0.1", "port": 27017 },
"remote": { "ip": "192.0.2.15", "port": 56024 },
"users": [{ "user": "admin", "db": "admin" }],
"param": { "db": "sales", "user": "reporter", "roles": [{ "role": "read", "db": "sales" }] },
"result": 0
}
Advanced filtering allows targeting of specific users, roles, or operations. For runtime configuration:
db.adminCommand({
setParameter: 1,
auditAuthorizationSuccess: true
})
See MongoDB Audit Log Documentation and Percona Audit Logging Guide.
Real-Time Monitoring
Native auditing often serves post-incident review. Pair it with Database Activity Monitoring to detect suspicious actions instantly, block risky queries, and send alerts through integrated channels.
DataSunrise enhances native auditing with centralized multi-database support, customizable rules, and real-time enforcement. Deploy as a reverse proxy, define monitored actions, set notifications, and activate.
Masking, Compliance and Discovery
Dynamic masking hides sensitive fields without altering stored data. Data discovery scans collections for sensitive fields, enabling targeted audits. For PCI DSS, SOX, or HIPAA compliance, DataSunrise maps audit policies to regulations, generates reports, and automates delivery.
Combined Example
A retail company uses native auditing to log price updates and DataSunrise to block excessive changes, mask supplier data, and alert managers. Keep filters specific to reduce load, secure logs, automate reviews with SIEM, integrate with threat detection, and test configurations regularly. See MongoDB audit manual and Atlas Security Documentation.
Feature Comparison Table
| Feature | Native MongoDB Enterprise Audit | DataSunrise Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Availability | Enterprise / Atlas only | Supports over 40 databases |
| Event Filtering | Yes, via config or CLI | Yes, with GUI and advanced logic |
| Real-Time Alerts | No | Yes |
| Data Masking | No | Dynamic & Static masking |
| Data Discovery | No | Built-in sensitive data scanning |
| Compliance Mapping | Manual | Automated with Compliance Manager |
| Integration | Syslog, file | Email, Slack, MS Teams, SIEM |
Conclusion
Knowing how to audit MongoDB means using Enterprise auditing for detail and DataSunrise for prevention, masking, and compliance automation. Together, they create a robust, layered approach to database security.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now