How to Ensure Compliance for Amazon OpenSearch
Amazon OpenSearch is a workhorse for log analytics, observability, SIEM-style security monitoring, and search-driven applications. That also makes it a magnet for regulated data: authentication events, customer identifiers, operational logs, and application payloads tend to end up indexed “temporarily”… and then live there forever.
The compliance problem is simple: once regulated data lands in OpenSearch, you are responsible for proving it is governed. AWS provides the managed service and security building blocks, but compliance ownership stays with the organization operating the data. For reference, see the service overview at Amazon OpenSearch Service.
This guide explains how to build a defensible compliance posture for Amazon OpenSearch: how to discover sensitive data, enforce least-privilege access, reduce exposure with masking, collect audit-ready evidence, and automate reporting — without breaking your search workloads.
What “Compliance” Means in an OpenSearch Environment
Compliance for OpenSearch is not a single feature toggle. It’s a set of continuous controls that let you answer auditor-grade questions:
- Where is sensitive data? (inventory and classification across indices)
- Who accessed it? (user identity, role, access path, and scope)
- What was exposed? (returned fields, visibility controls, masking rules)
- Can you prove enforcement? (audit trails + reports that are repeatable)
If you can’t produce consistent evidence, you don’t have compliance — you have a collection of configuration screens and good intentions.
Step 1: Discover and Classify Sensitive Data in Indices
OpenSearch environments typically grow organically: new apps ship logs, pipelines enrich documents, and indices multiply. Sensitive fields often appear in unexpected places (headers, tokens, error messages, free-text payloads). Before you can enforce compliance, you need visibility.
Start with automated discovery using Data Discovery. This enables organizations to scan OpenSearch content for patterns and classify regulated elements such as Personally Identifiable Information (PII). Once you have classification results, you can scope controls precisely (by index patterns, fields, and sensitivity categories) instead of guessing.
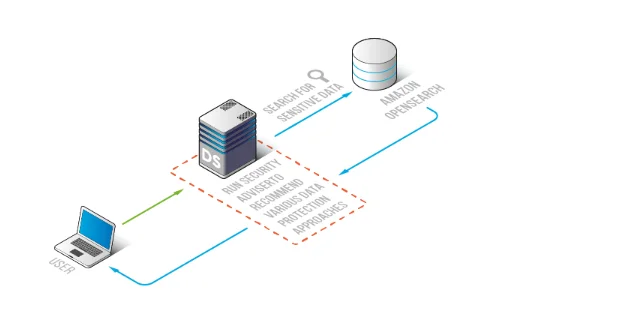
Sensitive data discovery flow: DataSunrise inspects OpenSearch content to identify regulated fields and build a compliance scope.
Discovery also reduces compliance drift. You don’t want a “one-time scan” that becomes obsolete the moment a new index appears.
Step 2: Enforce Governance and Least-Privilege Access
Most OpenSearch risk comes from over-broad access: shared accounts, wide index patterns, and permissive roles meant to “unblock analytics.” Compliance requires the opposite — role-scoped access with clear ownership.
A practical governance baseline includes:
- Define roles based on job function using Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
- Centralize permissions and review paths via Access Controls
- Align policy with the Least Privilege Principle (no “read everything” roles)
This step is where you stop treating OpenSearch like a public utility and start treating it like a regulated system. Roles and access policies should map to business intent, not convenience.
Step 3: Reduce Exposure With Masking (Because “Authorized” Doesn’t Mean “Needs Raw Data”)
Access control alone is not sufficient when users legitimately need to search, aggregate, and troubleshoot — but do not need raw sensitive values. That’s the difference between “access allowed” and “exposure allowed.”
To reduce exposure while keeping search usable:
- Apply runtime redaction using Dynamic Data Masking so sensitive fields are protected in query results
- Create safer datasets for analytics and lower environments with Static Data Masking
Masking is one of the fastest ways to improve compliance posture because it directly limits data leakage blast radius — even when credentials or roles are misused.
Step 4: Capture Audit-Ready Evidence (Not Just System Logs)
Auditors want traceability: who searched what, which indices were queried, which sensitive fields were touched, and whether policies were enforced. OpenSearch can emit logs, but compliance evidence typically requires structured auditing with consistency across environments.
Build auditing around three layers:
- Formalize audit objectives using an Audit Guide approach (what you log, why, and how long you retain it)
- Collect structured events via Audit Logs that are suitable for investigations and audits
- Maintain immutable traceability with Audit Trails that support compliance evidence requirements
For OpenSearch-specific auditing realities and configuration considerations, AWS documents audit logging options here: Amazon OpenSearch Service audit logs. (Use it as a baseline — but don’t confuse “enabled logs” with “audit-ready compliance evidence.”)
To make audit data operational (not just archived), connect it to ongoing oversight using Database Activity Monitoring. This provides continuous visibility into access patterns and supports faster detection of policy violations or suspicious querying behavior.
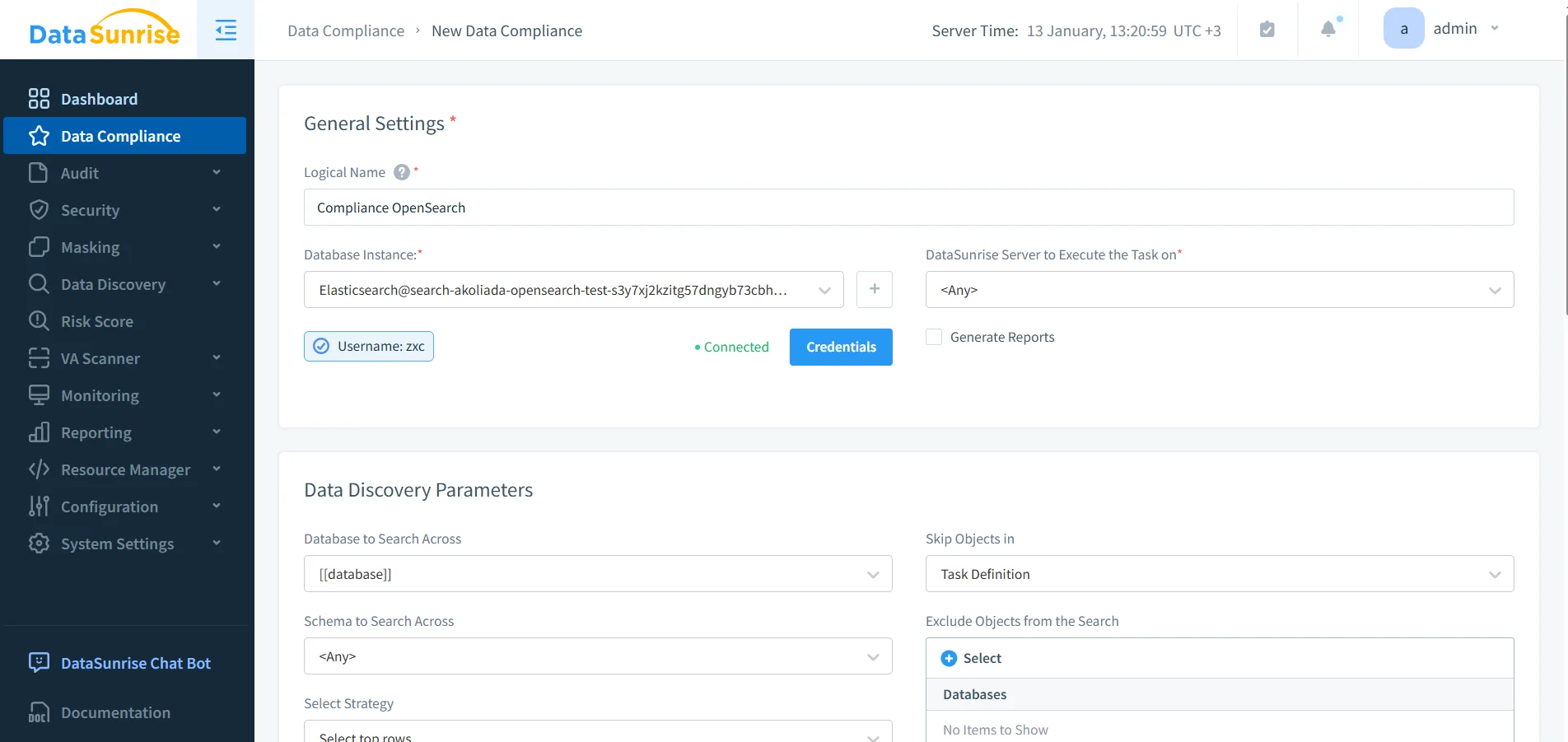
Configuring compliance rules for Amazon OpenSearch in DataSunrise to standardize enforcement and evidence collection.
Compliance Checklist Table: Controls You Need vs. Evidence You Must Produce
Use the matrix below to sanity-check whether your OpenSearch compliance program is actually defensible:
| Compliance Control | What You Implement in OpenSearch | Evidence Auditors Expect | How DataSunrise Helps |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Inventory | Identify indices and fields containing regulated data | Discovery results, scope definition, classification outputs | Automated compliance-aligned data classification |
| Access Governance | Restrict who can query which indices and fields | Role mappings, access reviews, least-privilege documentation | Centralized policies aligned to GDPR expectations |
| Exposure Reduction | Prevent sensitive values from being returned in clear text | Masking policies, test results, enforcement proof | Masking workflows supporting HIPAA safeguards |
| Auditability | Log user activity with context and retention | Who/what/when logs, retention policy, tamper resistance | Audit reporting aligned with PCI DSS traceability |
| Reporting | Produce repeatable compliance reports for audits | Standardized reports, recurring evidence packages | Automated reporting via Report Generation |
Step 5: Automate Compliance Reporting and Operational Response
Compliance fails when it becomes a manual quarterly ritual. Reporting and governance must be continuous and repeatable. Use automated compliance workflows through DataSunrise Compliance Manager to standardize evidence generation and simplify audit preparation across environments.
To avoid “we didn’t know this index existed” incidents, implement periodic discovery tasks and align remediation processes to risk. Pair compliance workflows with security enforcement capabilities like Database Firewall and continuous posture review using Vulnerability Assessment.
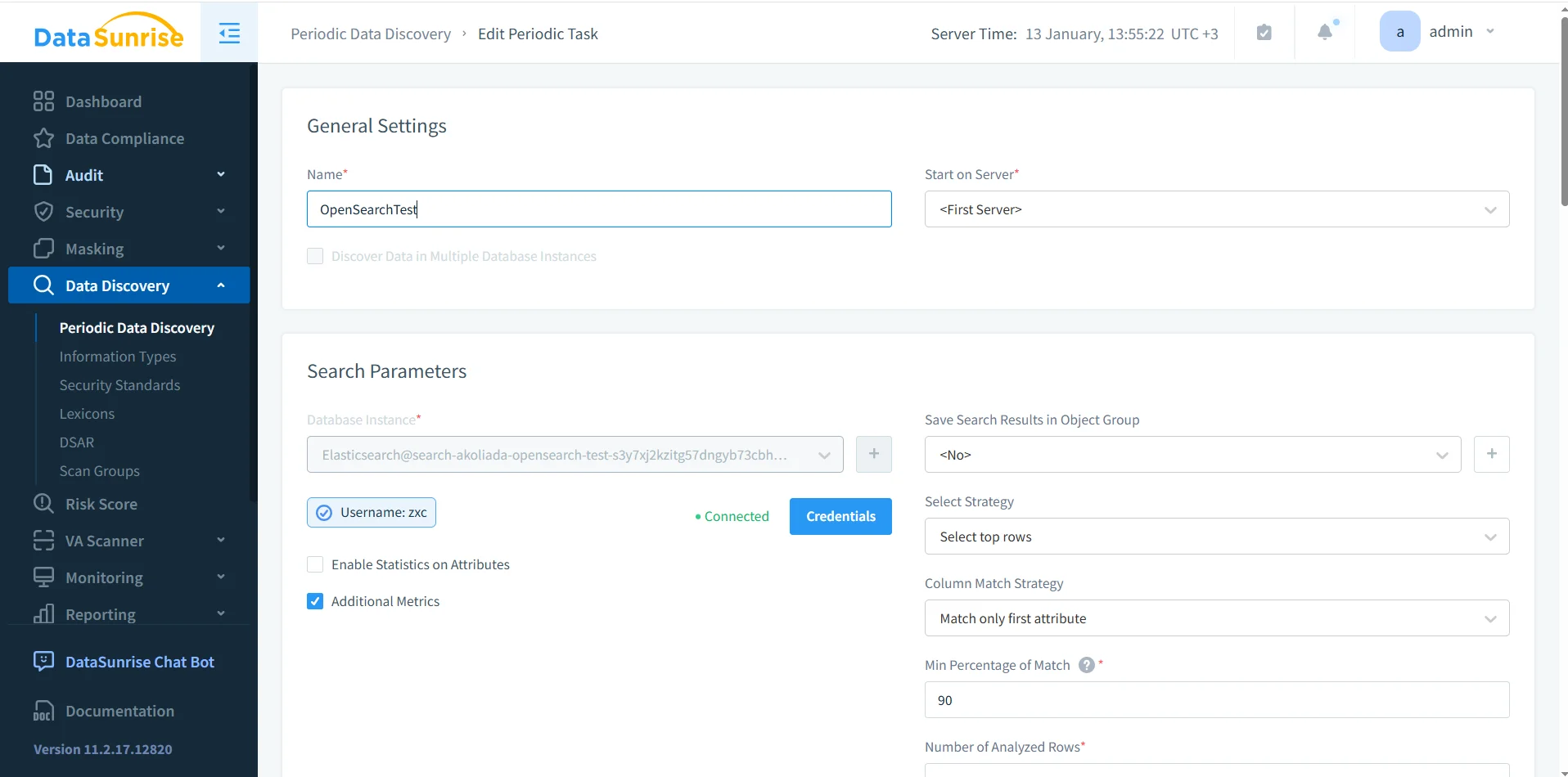
Periodic discovery task configuration: recurring scans keep OpenSearch compliance scope current as indices evolve.
Do not treat OpenSearch as “just logs.” If an index contains user identifiers or payload data, regulators will treat it as a regulated data store. Compliance must be enforced at the query level, not after an incident.
Conclusion: Make OpenSearch Compliance Continuous, Not Heroic
Ensuring compliance for Amazon OpenSearch is ultimately about operational discipline: discover sensitive data continuously, enforce least privilege, reduce exposure with masking, collect audit-ready evidence, and automate reporting. OpenSearch can be a compliant component of your architecture — but only if it is governed like a regulated datastore, not a dumping ground for “temporary” logs.
DataSunrise enables that governance with centralized discovery, policy enforcement, auditing, reporting, and supporting security controls across regulated environments, including those subject to SOX requirements via SOX Compliance.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now