How to Mask Sensitive Data in MariaDB
MariaDB powers transactional systems, customer-facing applications, analytics workloads, and internal tools across many organizations. As these environments scale, the same database often serves developers, analysts, support engineers, and automated services at the same time. Consequently, teams face a recurring challenge: allowing access to real data structures while preventing exposure of sensitive values.
To address this issue, organizations use data masking to transform sensitive fields such as emails, personal identifiers, or payment data before query results reach end users. Unlike encryption, masking does not alter how applications store data. Instead, it controls what users see at query time or through controlled access paths. As a result, masking becomes a practical extension of broader data security strategies.
In this article, we explain how teams can implement sensitive data masking in MariaDB using native mechanisms. Additionally, we show how centralized platforms such as DataSunrise extend masking into a policy-driven, auditable, and compliance-aligned process.
What Is Data Masking?
Data masking replaces sensitive values with obfuscated, truncated, or tokenized representations while preserving the original data in storage. Instead of exposing full values, the system returns masked results only to users or processes that do not require complete data visibility.
Unlike encryption, masking focuses on controlling data exposure rather than protecting stored data. Internally, the database continues to operate on real values. Meanwhile, it selectively transforms query results based on access context. Because of this, organizations frequently apply masking as part of broader data security strategies in shared database environments.
In practice, organizations use data masking to protect personally identifiable information (PII) in shared environments. At the same time, masking enables safe access for analytics, testing, and support teams. Moreover, it helps reduce insider risk without redesigning schemas or applications and supports alignment with regulatory requirements such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS within a structured data compliance program.
Organizations can apply masking either statically or dynamically. Static masking permanently alters stored values, which teams usually apply in non-production copies. In contrast, dynamic masking transforms values at query time. Therefore, sensitive data remains intact while access stays strictly controlled.
Native Approaches to Data Masking in MariaDB
MariaDB does not include a built-in, policy-driven dynamic masking engine. Instead, masking is typically implemented using SQL constructs and access design patterns that control how data is exposed. These approaches are often used as part of basic data masking strategies in environments without centralized enforcement.
Views with Transformed Columns
A common technique is to expose sensitive data through SQL views that apply masking transformations.
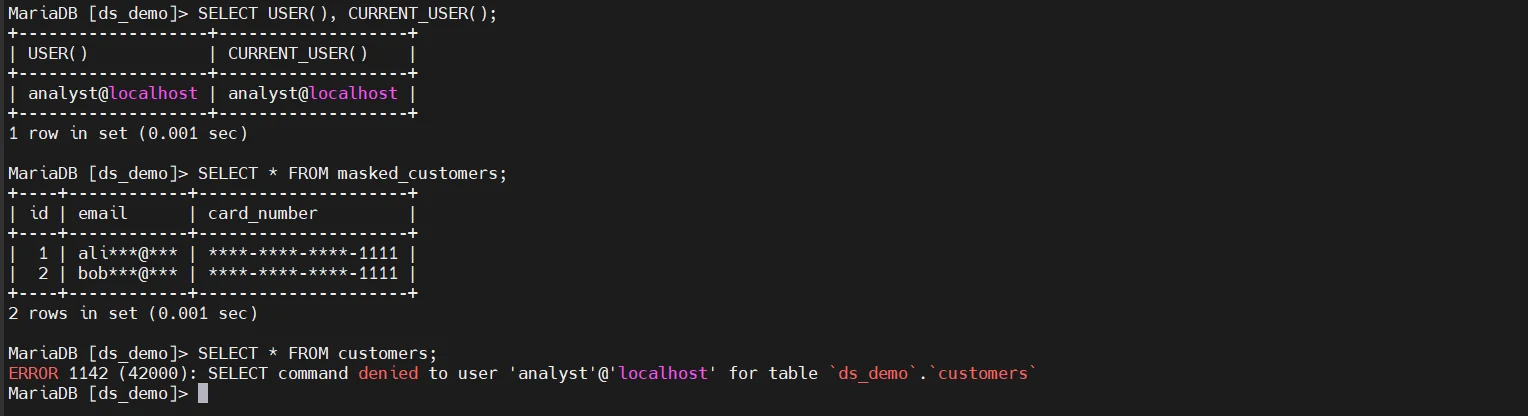
Applications and users query the view instead of the base table and receive masked output, while the original data remains unchanged. This method is frequently combined with access controls to restrict direct table access.
Stored Functions for Conditional Masking
Masking logic can also be encapsulated in stored functions and reused across queries or views.
/*CREATE FUNCTION mask_email(val VARCHAR(255))
RETURNS VARCHAR(255)
DETERMINISTIC
RETURN CONCAT(LEFT(val, 2), '***@***');*/
This approach centralizes formatting logic but still depends on consistent usage across applications and queries, especially in environments without role-based access control (RBAC) enforcement.
Separate Masked Copies of Data
Another pattern involves creating separate tables or schemas with permanently masked values. This is commonly used for development, testing, or analytics environments.
/*INSERT INTO customers_masked
SELECT
id,
CONCAT(LEFT(email, 3), '***@***'),
NULL
FROM customers;*/
The masked dataset can be shared safely without exposing production data, particularly in workflows related to test data management.
Centralized Data Masking for MariaDB with DataSunrise
DataSunrise introduces a centralized masking layer in front of MariaDB that enforces masking independently of SQL structure, views, or application logic. This approach removes the need to embed masking logic into database objects or application queries.
All SQL traffic is processed by the DataSunrise engine before reaching MariaDB. Masking rules are applied in real time based on contextual attributes such as user identity, role, source IP, session parameters, and accessed columns. The database schema and stored data remain unchanged, which allows masking policies to be introduced or modified without impacting existing applications.
Because masking enforcement occurs outside the database engine, the same rules can be applied consistently across multiple MariaDB instances and environments as part of a centralized data security
strategy.
Defining Masking Rules for MariaDB
A typical masking workflow in DataSunrise includes:
- connecting the MariaDB instance to the DataSunrise platform
- identifying sensitive tables and columns, often based on automated data discovery
- defining masking formats appropriate for each data type
- assigning visibility rules for users, roles, or groups
Masking rules are evaluated dynamically at query time. Once enabled, they take effect immediately without database restarts or application changes. This makes it possible to adjust data exposure policies on demand, for example during audits, incident response, or role changes.
Compliance-Driven Masking Use Cases
Dynamic masking in MariaDB directly supports regulatory scenarios where sensitive data exposure must be strictly controlled and demonstrable.
GDPR
Personal data such as names, emails, and identifiers can be dynamically masked for non-privileged users, supporting data minimization and role-based access principles required by GDPR.HIPAA
Patient identifiers and regulated attributes remain protected in operational systems while still enabling clinical, reporting, and analytical workflows without duplicating data.PCI DSS
Cardholder data is masked during query execution, preventing unauthorized exposure while preserving the integrity of stored payment records.
By combining real-time masking with automated compliance reporting,
DataSunrise reduces the operational effort required to demonstrate adherence during audits and regulatory reviews.
Real-Time Enforcement and Visibility
Each query processed through the masking layer is captured as part of a unified audit stream. This creates direct traceability between access attempts and applied masking behavior.
Security and compliance teams can clearly determine:
- which users accessed sensitive columns
- what masking rules were triggered
- when and from where access occurred
Masking and monitoring operate as a single control plane rather than separate mechanisms, allowing teams to correlate data access, masking decisions, and user behavior within a single investigative context. This tight integration with database activity monitoring supports both security investigations and compliance evidence collection.
Key Advantages of DataSunrise
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Centralized Policy Enforcement | Masking rules are defined and enforced from a single control plane, ensuring consistent data protection across all MariaDB instances and environments. |
| Real-Time Dynamic Masking | Sensitive data is masked at query time based on user identity, role, and context, without modifying schemas or stored values. |
| Compliance-Ready Visibility | Masking actions are fully traceable and correlated with user activity, simplifying audit preparation and regulatory evidence collection. |
| Operational Simplicity | Masking policies can be introduced, updated, or revoked instantly without database restarts or application changes. |
Conclusion
MariaDB provides flexible SQL tools that allow teams to implement data masking through views, functions, and controlled data copies. These techniques are effective for targeted use cases and isolated environments, especially when combined with foundational data security practices.
For organizations operating MariaDB in shared or regulated contexts, centralized masking platforms such as DataSunrise extend these capabilities into a policy-driven protection layer. By enforcing masking independently of applications and schemas, organizations gain consistent visibility, stronger control, and alignment with modern compliance requirements.
In practice, this transforms MariaDB from a permissive data store into a governed platform where sensitive data exposure is intentional, measurable, and auditable.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now