
MongoDB Audit Log

The MongoDB Audit Log is a critical component for organizations that need to monitor, secure, and ensure compliance across their database environments. It captures detailed information about database operations, user activities, and system events, serving not only as a forensic record but also as a foundation for proactive threat detection, compliance reporting, and operational analysis.
A well-designed audit log implementation can help organizations identify suspicious behavior early, support regulatory audits, and improve database security posture. With advancements in real-time monitoring, dynamic masking, and data discovery, the MongoDB Audit Log can be transformed from a passive archive into an active defense tool.
Why the MongoDB Audit Log Matters
In industries such as finance, healthcare, and government, regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS require organizations to record and retain detailed access logs. These logs provide accountability by showing which users accessed sensitive collections and when, assist in incident investigation to determine the scope and impact of unauthorized actions, and offer operational intelligence for improving database performance and refining security controls. Without a robust audit strategy, organizations risk compliance violations, reputational damage, and longer incident response times.
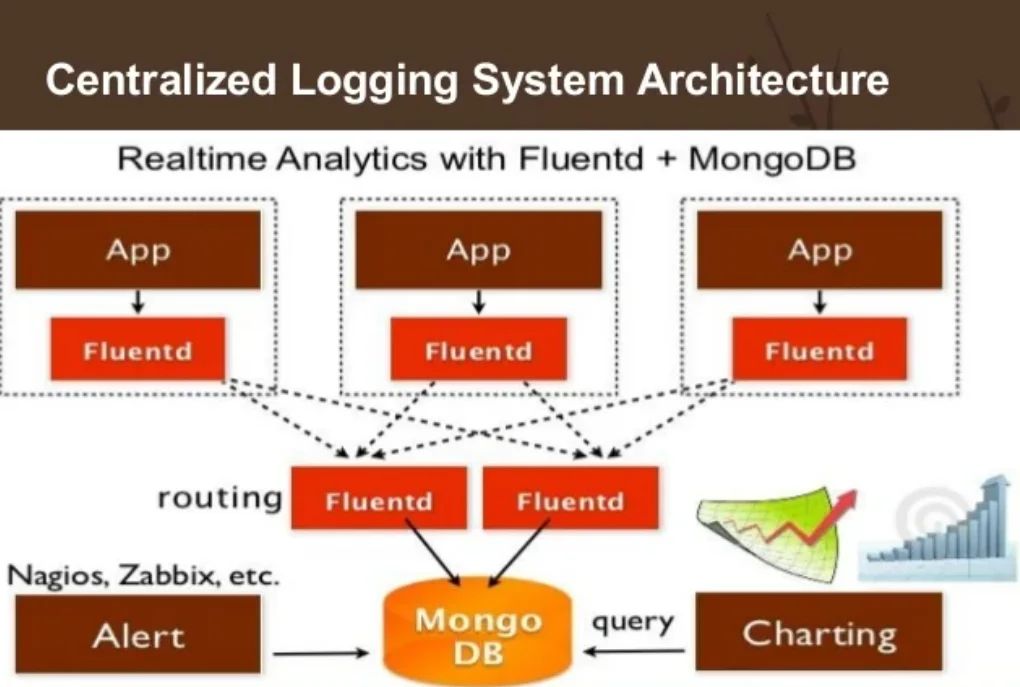
Real-Time Audit and Threat Detection
Static logs are useful for post-event reviews, but modern cybersecurity demands real-time auditing. With Database Activity Monitoring, MongoDB audit events can be sent to SIEM systems like Splunk or Elastic, where correlation rules instantly detect anomalies. This capability can identify unexpected bulk data extraction after business hours, privilege escalation attempts, or access from unusual geographic locations. The MongoDB auditing documentation explains how to integrate logs with monitoring tools for this purpose.
Dynamic Masking for Sensitive Data
Even with auditing in place, sensitive data exposure can occur if fields are left unprotected. Dynamic masking hides sensitive values in query results without altering the underlying data. For example, customer service staff may see masked credit card numbers while still being able to perform their tasks:
{
"customer_name": "John Doe",
"credit_card": "XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-1234"
}
This approach ensures compliance with data protection regulations while maintaining business functionality.
Data Discovery for Better Audit Precision
Data Discovery scans and classifies sensitive data across MongoDB collections. This allows administrators to focus auditing efforts on high-risk data, implement targeted monitoring for compliance, and improve the relevance of alerts while reducing noise. When integrated with audit policies, discovered data classifications can trigger stricter logging and alerting rules automatically.
Configuring Native MongoDB Audit Log (Enterprise Edition)
It’s important to note that native audit logging is only available in MongoDB Enterprise Edition. This feature is not included in the Community Edition. In Enterprise deployments, auditing is enabled through the mongod configuration file. Here’s an example configuration:
auditLog:
destination: file
format: BSON
path: /var/log/mongodb/auditLog.bson
filter: '{ atype: { $in: [ "authCheck", "createCollection", "dropDatabase" ] } }'
After enabling auditing, you can review log data with:
bsondump /var/log/mongodb/auditLog.bson | grep "atype"
Configuration options include choosing between file and syslog destinations, specifying output formats (BSON or JSON), and applying filters to capture only relevant events. Storing logs on a dedicated disk helps prevent performance degradation, and regular rotation ensures compliance with retention requirements. More details can be found in the official MongoDB Audit Log reference and the auditing guide.
Enhancing Auditing with DataSunrise
DataSunrise extends MongoDB’s native capabilities with centralized management for multiple instances, granular rules that log only under specific conditions, and integrated masking or blocking for high-risk queries. It also offers automated compliance reporting to speed up audit preparation.
For example, a DataSunrise rule can log all queries to the payments collection by contractors while automatically masking credit card data:
WHEN user_role = 'contractor' AND collection = 'payments'
THEN log_event AND apply_masking('credit_card')
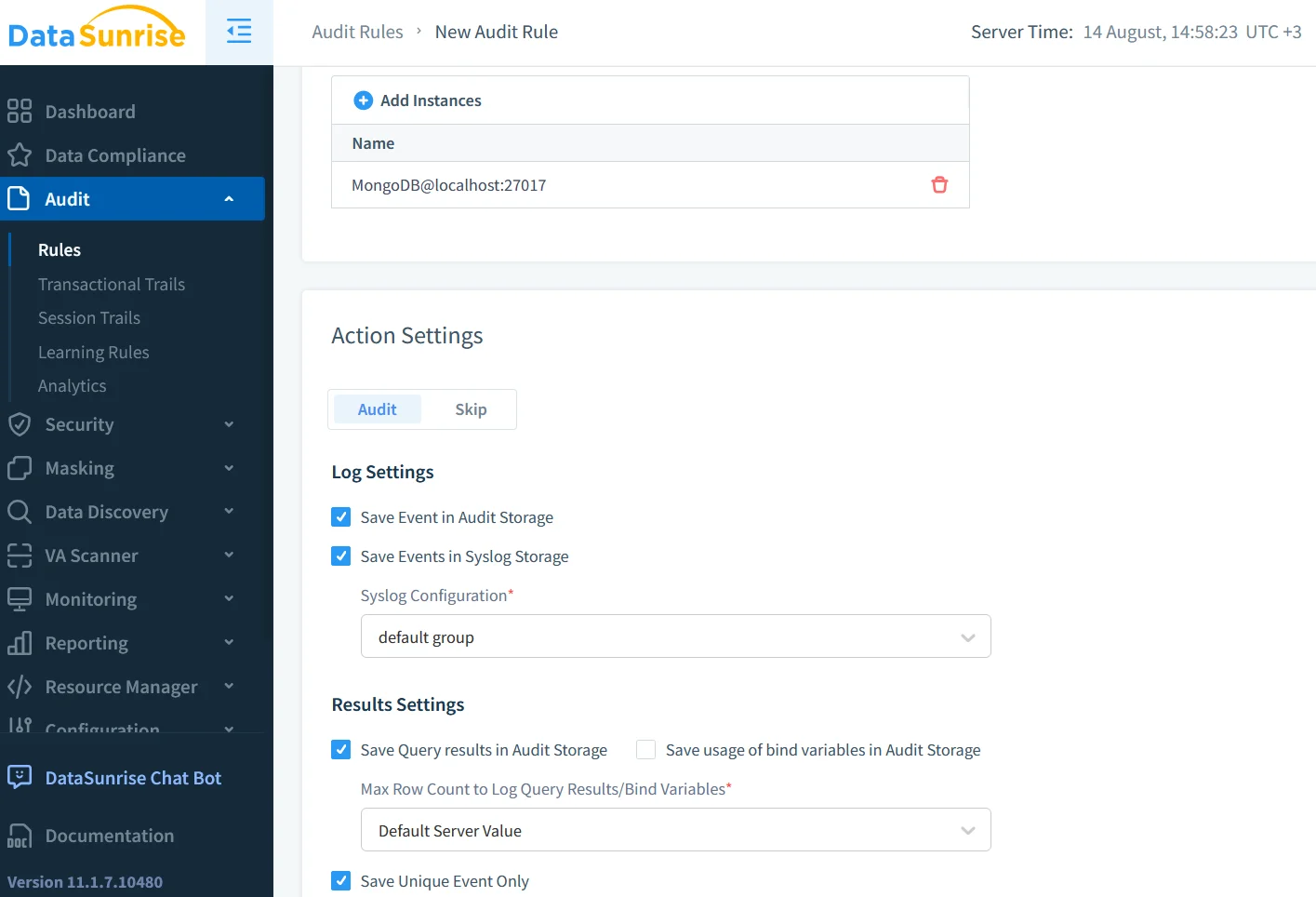
This ensures only relevant events are recorded, while sensitive values remain protected.
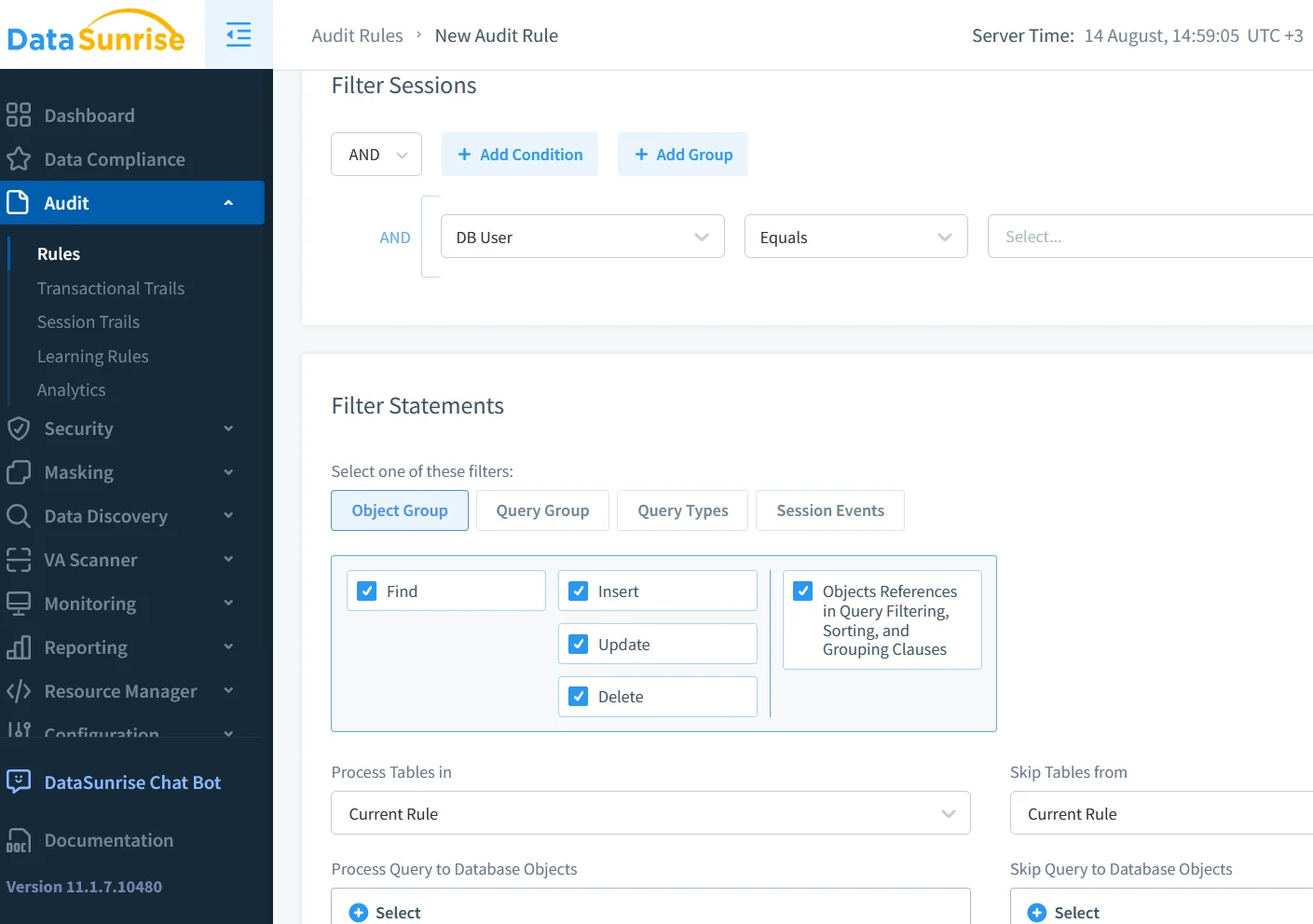
Security and Compliance Synergy
Combining MongoDB’s native audit log with DataSunrise creates a layered defense. Native logging captures immutable, low-level events, while DataSunrise adds context-aware enforcement and real-time protection. This combination accelerates compliance reporting for SOX, GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS, strengthens security posture, and reduces audit complexity.
Final Thoughts
The MongoDB Audit Log is more than a regulatory checkbox—it is a core element of proactive data security. With real-time monitoring, dynamic masking, and data discovery, it becomes a powerful mechanism for detecting and preventing threats. Organizations that integrate native MongoDB auditing with DataSunrise gain comprehensive visibility and actionable intelligence, ensuring compliance, protecting sensitive assets, and improving incident response readiness.
For more insights, explore MongoDB security best practices, the MongoDB auditing guide to design a framework that meets both operational and compliance goals.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now