Sensitive Data Protection in MongoDB
Sensitive Data Protection in MongoDB is no longer optional. Modern MongoDB deployments handle customer identities, payment information, healthcare records, authentication tokens, and operational telemetry at scale. As cyber threats grow more sophisticated and regulatory requirements become stricter, organizations must implement protection strategies that go far beyond basic access controls. According to IBM’s latest Cost of a Data Breach Report, the financial and reputational impact of data exposure continues to rise globally (https://www.ibm.com/reports/data-breach). In parallel, regulatory pressure such as the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (https://gdpr.eu/) reinforces the need for structured and enforceable data governance frameworks.
MongoDB includes strong native security features such as authentication mechanisms, encryption at rest, TLS encryption in transit, and role-based access controls. These capabilities provide an essential security baseline. However, enterprise environments require more advanced safeguards, including Sensitive Data Discovery, Context-Aware Protection, Zero-Trust Data Access, and automated governance aligned with regulatory frameworks. Strengthening overall database security posture (https://www.datasunrise.com/knowledge-center/database-security/) and implementing continuous data protection strategies (https://www.datasunrise.com/knowledge-center/continuous-data-protection/) are critical components of this evolution.
In the following sections, we examine how MongoDB protects sensitive data using native tools, where these controls may fall short in complex environments, and how DataSunrise enhances MongoDB security with Autonomous Compliance Orchestration and Zero-Touch Data Masking.
Understanding Sensitive Data in MongoDB
MongoDB stores structured and semi-structured information in BSON documents, which often contain highly sensitive business and personal data. This may include Personally Identifiable Information (PII), payment card details, protected health information (PHI), authentication credentials, API tokens, and behavioral or analytics identifiers used for tracking user activity. You can explore more about sensitive data categories in the context of Personally Identifiable Information (PII) and how organizations treat data as a critical asset in data value management. In modern applications, multiple categories of sensitive data frequently coexist within the same document structure, increasing the potential impact of a single exposure event.
Without structured protection mechanisms, this information can be unintentionally exposed. Overprivileged roles may grant broader access than required, especially if the Principle of Least Privilege is not properly enforced. Debug queries in production environments can reveal full document contents. Third-party integrations may retrieve more data than necessary. Insider misuse remains a persistent risk, particularly when visibility into database interactions is limited. Misconfigured APIs can also unintentionally expose sensitive fields to external consumers, creating significant security threats.
Effective protection in MongoDB therefore requires a layered security model. Encryption safeguards data at rest and in transit. Role-Based Access Controls restrict who can access specific collections and operations. Field-level protection mechanisms help limit visibility of sensitive attributes. Continuous monitoring provides insight into access patterns and suspicious behavior. Finally, structured compliance reporting ensures that protection measures align with regulatory requirements and audit expectations.
Native Sensitive Data Protection in MongoDB
MongoDB provides strong foundational security capabilities designed to protect sensitive information at multiple levels. These built-in mechanisms establish a security baseline for production environments. However, understanding how each component works — and where its boundaries lie — is essential for designing a comprehensive protection strategy.
1. Role-Based Access Controls (RBAC)
MongoDB enforces privilege boundaries through granular role-based access controls. Administrators can define custom roles that restrict operations to specific databases and collections, ensuring that users only perform permitted actions.

RBAC effectively limits who can query specific collections and perform administrative tasks. However, once access is granted, MongoDB typically allows full visibility of all fields within the permitted documents. Field-level visibility restrictions are not inherently enforced through RBAC alone.
For deeper governance concepts, see:
https://www.datasunrise.com/knowledge-center/role-based-access-control-rbac/
2. Encryption at Rest
MongoDB Enterprise supports encryption at rest through storage engine encryption. This mechanism protects data stored on disk by encrypting database files and snapshots, significantly reducing risk in cases of physical theft, lost storage media, or unauthorized access to underlying infrastructure.
Encryption at rest is essential for meeting regulatory requirements such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS, where protecting stored data is mandatory. However, this control focuses only on data persistence. It does not manage runtime exposure. Once a query is executed and data is decrypted in memory, authorized users can still access sensitive fields in plaintext.
Example configuration in mongod.conf:
security:
enableEncryption: true
encryptionKeyFile: /etc/mongodb-keyfile
In this configuration:
enableEncryptionactivates storage-level encryption.encryptionKeyFilespecifies the local key file used by the storage engine.
For environments requiring external key management integration, MongoDB can also be configured to use KMIP servers for centralized key lifecycle control.
Learn more about encryption strategies:
https://www.datasunrise.com/knowledge-center/database-encryption/
3. Client-Side Field Level Encryption (CSFLE)
MongoDB supports Client-Side Field Level Encryption (CSFLE), which allows specific fields to be encrypted on the client before being transmitted to the database server. This ensures that even database administrators cannot view protected values without access to encryption keys.
Example schema configuration:
{
"bsonType": "object",
"properties": {
"ssn": {
"encrypt": {
"bsonType": "string",
"algorithm": "AEAD_AES_256_CBC_HMAC_SHA_512-Deterministic"
}
}
}
}
CSFLE provides strong cryptographic protection and can support deterministic encryption for searchable fields. However, implementing it requires application-level modifications, integration with a secure key management system, and coordination between development and security teams.
In large legacy systems or distributed architectures, this approach may introduce operational complexity and deployment challenges.
4. Audit Logging
MongoDB Enterprise includes native audit logging for tracking security-relevant events. Administrators can configure logging to capture authentication attempts, CRUD operations, and administrative commands.
Example configuration:
auditLog:
destination: file
format: JSON
path: /var/log/mongodb/audit.json
Native audit logging provides visibility into user actions and system events. It supports JSON output for easier parsing and integration with log analysis tools.
However, audit logs are instance-bound and require external systems for centralized aggregation, correlation, long-term storage, and advanced analytics. Without centralized monitoring, analyzing distributed clusters can become operationally complex.
More on audit strategies:
https://www.datasunrise.com/knowledge-center/database-activity-monitoring/
Autonomous Sensitive Data Protection for MongoDB with DataSunrise
Modern MongoDB environments rarely operate in isolation. They are embedded in distributed microservice architectures, cloud-native platforms, analytics pipelines, and hybrid infrastructures. As a result, sensitive data flows dynamically between applications, clusters, cloud regions, and external integrations. Protecting this ecosystem requires more than static configuration — it requires adaptive, automated governance capable of operating consistently across environments.
DataSunrise extends MongoDB’s native capabilities by introducing a compliance-first architecture built around automation, centralized policy management, and real-time enforcement. Instead of relying on fragmented security controls applied at individual database nodes, the platform establishes unified visibility and consistent protection policies across the entire data landscape. This approach reduces operational complexity while strengthening security posture.
By combining Sensitive Data Discovery, Zero-Touch Data Masking, ML-powered monitoring, and Compliance Autopilot into a single framework, DataSunrise transforms MongoDB security from reactive configuration into proactive, continuous protection.
Zero-Touch Solution Framing
DataSunrise deploys Autonomous Compliance Orchestration to deliver seamless Sensitive Data Protection in MongoDB with zero-touch implementation. The platform integrates without requiring application rewrites or architectural disruption, allowing organizations to enhance security without slowing development cycles.
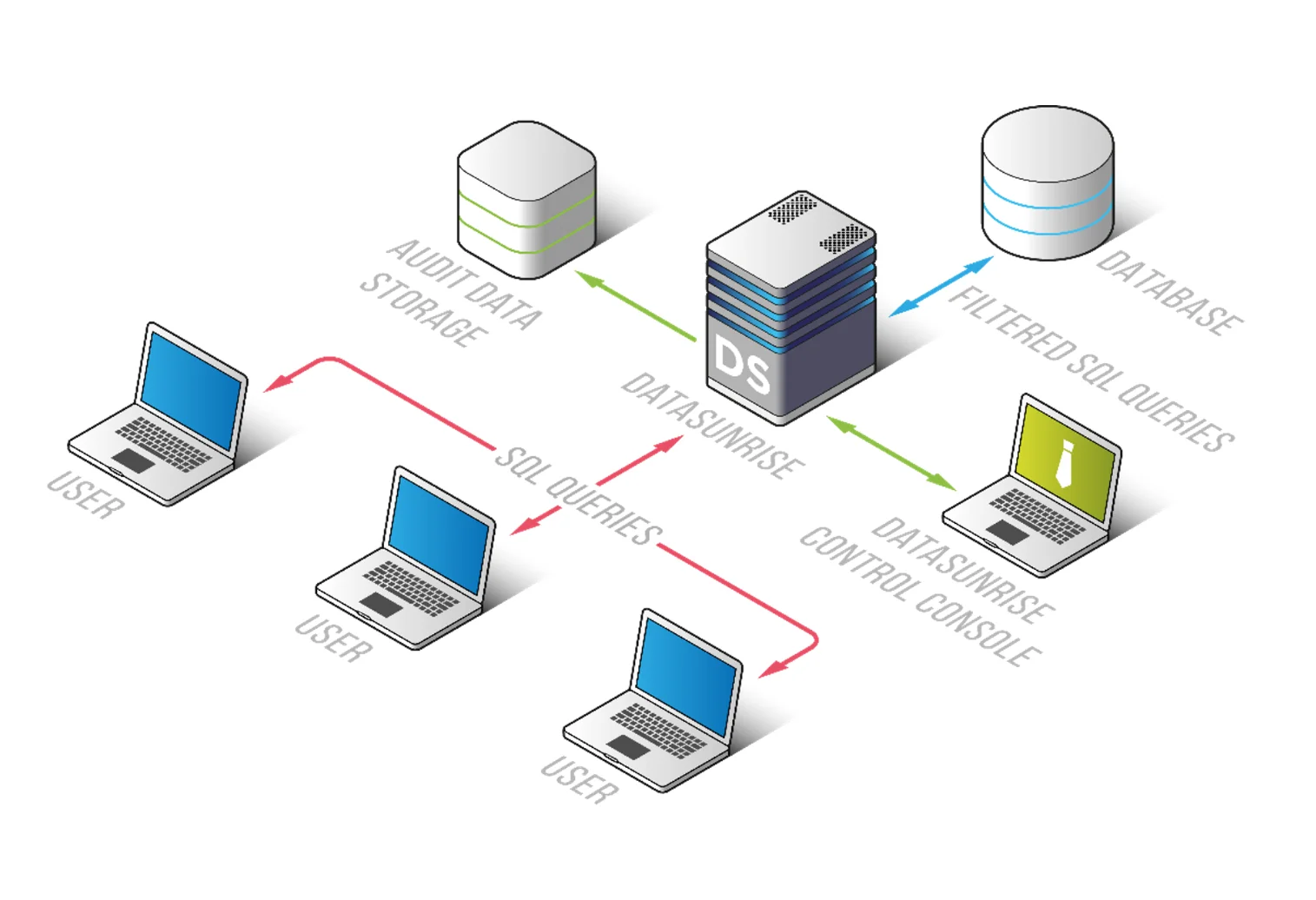
Through Flexible Deployment Modes — including proxy mode, sniffer mode, and native log trailing — DataSunrise integrates non-intrusively into MongoDB environments operating across on-premise clusters, AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, and hybrid architectures. This deployment flexibility ensures consistent policy enforcement regardless of infrastructure complexity.
No application modification is required, which significantly reduces operational friction and accelerates time-to-compliance.
Sensitive Data Discovery & Auto-Discover & Mask
DataSunrise performs automated Sensitive Data Discovery using multiple detection mechanisms. These include NLP-driven discovery for contextual analysis, pattern-based detection for structured identifiers, ML-assisted classification for adaptive recognition, and OCR image scanning to extract sensitive information from unstructured image content.
The platform identifies sensitive information across structured MongoDB collections, nested JSON fields, operational logs, file systems, and cloud storage platforms such as Amazon S3, Azure Blob Storage, and Google Cloud Storage.
Unlike manual tagging approaches that require continuous human input, this automated discovery framework enables Automatic Policy Generation. Protection rules are dynamically aligned with discovered data categories, reducing configuration overhead and minimizing compliance gaps.
Zero-Touch Data Masking
DataSunrise implements multiple masking strategies tailored to different operational needs. These include dynamic masking applied at query runtime, in-place masking for persistent transformation, static masking for non-production datasets, and context-aware transformations based on user identity, role, or access context.
Masking is enforced transparently at runtime without altering the original stored data. Applications continue to function normally while sensitive fields are transformed according to defined policies.
Unlike solutions that require continuous manual rule tuning, DataSunrise delivers Continuous Compliance Alignment across environments. Policies adapt to evolving regulatory requirements and changing data landscapes.
ML Audit Rules & Behavior Analytics
DataSunrise enhances MongoDB protection with Machine Learning Audit Rules and ML-based Suspicious Behavior Detection. The platform incorporates UEBA monitoring implementation to analyze user and entity behavior patterns over time.
It continuously monitors access activity and flags anomalies such as potential data exfiltration attempts, privilege misuse scenarios, and unusual query volumes that deviate from baseline behavior.
Real-Time Notifications ensure that security teams are immediately informed of critical events, enabling faster response and incident containment.
Compliance Autopilot & Continuous Regulatory Calibration
DataSunrise provides Compliance Autopilot aligned with major regulatory frameworks including GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, SOX, ISO 27001, and SOC 2. This alignment ensures that MongoDB deployments maintain a structured compliance posture across jurisdictions and industry standards.
The platform enables Continuous Regulatory Calibration, ensuring that policies adapt to evolving requirements. It supports Compliance Drift Detection, identifies gaps in enforcement, and generates one-click compliance evidence for auditors.
This structured automation eliminates compliance gaps while reducing manual oversight and reporting burden.
Unified Security Framework Across MongoDB Ecosystems
DataSunrise acts as a Centralized Data Compliance Platform across MongoDB, traditional SQL databases, data warehouses, data lakes, and cloud storage systems. This unified framework enables consistent security governance across heterogeneous infrastructures.
By providing Cross-Database Visibility and Vendor-Agnostic Protection, organizations gain centralized control over data protection policies across all storage environments.
Business Impact of Sensitive Data Protection in MongoDB
| Business Outcome | Impact on Organization |
|---|---|
| Quantifiable Risk Reduction | Minimizes sensitive data exposure through continuous database activity monitoring and proactive threat controls, reducing breach probability and impact. |
| Significant Reduction in Manual Effort | Automates discovery and protection workflows using sensitive data discovery and centralized policy enforcement. |
| Streamlined Compliance Workflows | Aligns MongoDB protection policies with regulatory requirements through integrated compliance management capabilities. |
| Enhanced Audit Preparation | Generates structured, audit-ready evidence using detailed audit logs and automated reporting mechanisms. |
| Optimized Total Cost of Compliance | Reduces operational overhead by consolidating protection, masking, and monitoring into a unified database security framework. |
| Measurable Compliance Acceleration | Accelerates readiness for GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX through continuous policy calibration and automated governance. |
By enforcing Zero-Trust Data Access and maintaining a Continuous Compliance Posture, MongoDB environments become resilient against both insider misuse and external threats while sustaining operational efficiency.
Conclusion
MongoDB provides strong native security features, including authentication, encryption, and role-based access controls. These capabilities establish a solid security baseline. However, enterprise-grade Sensitive Data Protection requires more than encryption and role assignment. Modern environments demand automated discovery, runtime protection, centralized governance, and continuous regulatory alignment supported by a mature database security strategy.
DataSunrise extends MongoDB security with Zero-Touch Data Masking, automated Sensitive Data Discovery, Compliance Autopilot, Continuous Regulatory Calibration, and a Unified Security Framework aligned with comprehensive data security principles. The platform operates seamlessly across on-premise deployments, cloud platforms, and hybrid architectures without configuration complexity or application rewrites.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now