
Get Started with SQL Plus

Introduction
Working with Oracle often requires command-line precision. That’s where SQL Plus comes in. It’s Oracle’s command-line interface for executing SQL statements, managing schema objects, and running scripts. Whether you’re an admin or a developer, knowing how to use this tool efficiently can greatly improve your productivity.
What Is SQL Plus?
SQL Plus is a terminal-based utility bundled with Oracle Database. It provides an interactive shell for running SQL and PL/SQL statements. You can use it for reporting, automation, and direct database control—all without relying on a GUI.
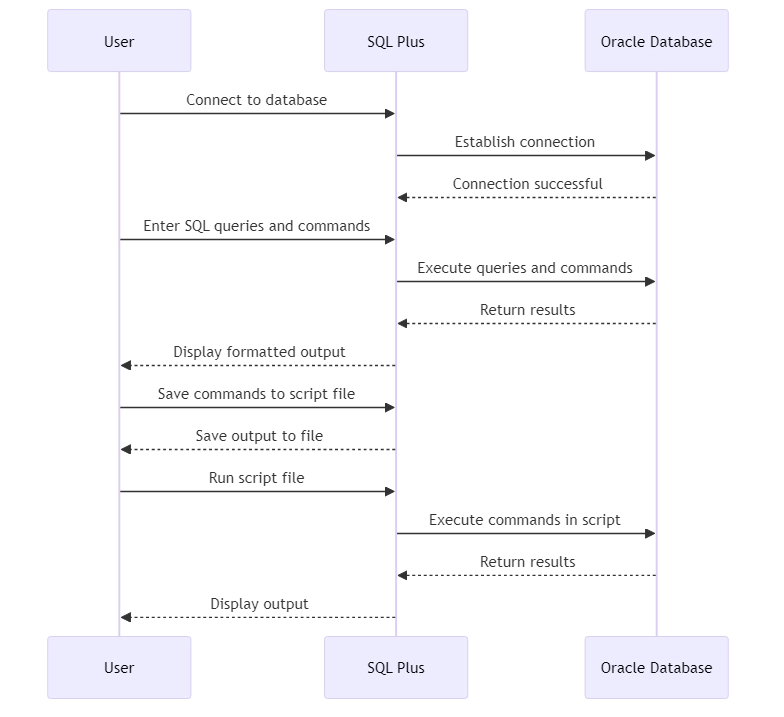
Core features include:
- Executing SQL statements and viewing results
- Running PL/SQL blocks and scripts
- Formatting query results
- Performing database administration tasks
- Automating tasks through scripting
- Interacting with the operating system
Users can quickly and efficiently manage their databases, run queries, load data, and automate routine tasks.
SQL Plus Installing
If you have Oracle Database installed, you probably already have SQL Plus because it comes with the software package. Nonetheless, if there is a need to set up Plus individually, the following are the broad steps:
- Download the Oracle Instant Client package for your operating system from the Oracle website. Choose the version that matches your Oracle Database.
- Extract the downloaded package to a directory of your choice.
- Set the required environment variables:
- Set the PATH variable to include the directory where SQL Plus is located.
- Set the ORACLE_HOME variable to the directory where you extracted the Instant Client package.
- Set the TNS_ADMIN variable to the location of your tnsnames.ora file (if using one).
- Verify the Plus installation by running the sqlplus -version command in your terminal. It should display the SQL Plus version information.
For example, on Linux or macOS, you can set the environment variables in your .bash_profile file:
export PATH=/path/to/instantclient_directory:$PATH export ORACLE_HOME=/path/to/instantclient_directory export TNS_ADMIN=/path/to/tnsnames.ora
Now you’re ready to start connecting to your Oracle databases and running commands.
Connecting to a Database
To start using SQL Plus, you first need to connect to an Oracle database. Here’s how:
- Open a terminal or command prompt.
- Run the sqlplus command followed by your username and password:
sqlplus username/password@connect_identifier
Replace username, password, and connect_identifier with your actual database credentials and connection details.
For example, to connect as the system user with “password” password to a local database with SID “orcl”, the command would be:
sqlplus system/password@orcl
If the connection is successful, you’ll see the prompt, which looks like this:
SQL>
You are now connected to the database and can start running SQL and PL/SQL commands.
Example: Creating a Test User
Let’s create a test user called testuser with the password testpass to use for our examples. Connect to your database as a user with administrative privileges (e.g., system) and run the following commands:
CREATE USER testuser IDENTIFIED BY testpass; GRANT CONNECT, RESOURCE TO testuser;
The CREATE USER command creates a new user. The GRANT command gives the user permissions to connect to the database and create things.
Now you can connect to the database as testuser:
sqlplus testuser/testpass@connect_identifier
With the test user created and connected, we’re ready to explore some basic SQL Plus commands.
Basic SQL Plus Commands
SQL Plus has various commands for managing the database, formatting query results, and customizing the environment. Here are some basic commands to get you started:
To run a SQL query, simply enter the query at the Plus prompt and end it with a semicolon (;). For example:
SELECT * FROM employees;
This query selects all rows and columns from the employees table. SQL Plus will display the query results in a formatted table.
Most Common SQLPlus Commands You Should Know
Understanding each core SQLPlus command helps database administrators and developers streamline their daily operations. From formatting output to scripting automation, here are some widely used SQLPlus commands:
SELECT– Executes a SQL query.TTITLE,BTITLE– Add report headers and footers.COLUMN FORMAT– Format the width and alignment of columns.SPOOL– Save session output to a text file.@script.sql– Run a SQL script.SHOW ALL– Display current settings and environment.
Formatting Query Results
SQL Plus provides several commands to format query results. Here are a few common ones:
- COLUMN column_name FORMAT format: Sets the display format for a specific column.
- TTITLE text: Sets the title for the top of each report page.
- BTITLE text: Sets the title for the bottom of each report page.
- BREAK ON column: Creates a break group on a specified column, which inserts a blank line and repeats column values when the value changes.
For example, to format the salary column as currency and add a title to the report:
COLUMN salary FORMAT $99,999 TTITLE 'Employee Salaries' SELECT first_name, last_name, salary FROM employees;
This report will show the names and salaries of employees. The system will display salaries in currency format with a title. This output customization is made possible by SQLPlus commands like COLUMN FORMAT and TTITLE, which are widely used in reporting workflows.
Saving and Running Scripts
SQL Plus allows you to save a series of commands into a script file and run them later. To save your current Plus session to a file, use the SPOOL command:
SPOOL output.txt SELECT * FROM departments; SPOOL OFF
This will save the output of the SELECT statement to a file named output.txt.
To run a script file, use the @ command followed by the script filename:
@myscript.sql
This will execute the commands in the myscript.sql file. This is a common SQLPlus command used to execute predefined SQL scripts stored in files. It allows you to automate long sequences of statements, such as table creation and permission management.
Example of Using SQL Plus: Creating a Table and Inserting Data
Let’s create a simple products table and insert some sample data using SQL Plus:
CREATE TABLE products ( product_id NUMBER PRIMARY KEY, product_name VARCHAR2(100), price NUMBER(10,2) ); INSERT INTO products VALUES (1, 'Laptop', 999.99); INSERT INTO products VALUES (2, 'Smartphone', 499.99); INSERT INTO products VALUES (3, 'Headphones', 99.99); COMMIT;
Now, let’s format and query the data:
COLUMN product_name FORMAT A20 COLUMN price FORMAT $999.99 SELECT * FROM products;
The output should look something like this:
PRODUCT_ID PRODUCT_NAME PRICE
---------- ---------------- -------
1 Laptop $999.99
2 Smartphone $499.99
3 Headphones $99.99SQL Plus vs. Other Oracle Tools
SQL Plus is widely used, but it’s not the only option for command-line or GUI interaction with Oracle databases. Here’s how it compares to other common Oracle tools:
| Tool | Interface | Best For | Scriptable |
|---|---|---|---|
| SQL Plus | Command-line | Low-level access, legacy scripting, automation | ✅ Yes |
| SQL Developer | GUI | Visual schema design, query testing, data modeling | ⚠️ Limited |
| SQLcl | CLI with scripting enhancements | Modern CLI alternative to SQL Plus with scripting, JSON, Liquibase integration | ✅ Yes |
Automating SQL Plus in Real Environments
SQL Plus scripts are often used in batch jobs, compliance checks, and nightly database tasks. Here’s an example of running a scheduled SQL Plus script from a shell:
#!/bin/bash sqlplus -s testuser/testpass@orcl <<EOF SPOOL audit_report.txt SELECT username, account_status FROM dba_users; SPOOL OFF EXIT EOF
This script runs silently (-s), queries user statuses, and saves the output to a text file. It’s ideal for automated audits or daily checks in secure environments.
Auditing and Compliance with SQL Plus + DataSunrise
When integrated with DataSunrise, SQL Plus becomes part of a broader enterprise audit strategy. You can:
- Run masking test cases via SQL Plus scripts
- Execute role audits and capture activity logs in real-time
- Verify DDL operations and access changes from the command line
This hybrid approach lets teams manage Oracle databases efficiently while maintaining full audit coverage and regulatory alignment.
Conclusion
SQL Plus continues to be a go-to utility for Oracle professionals. Whether you’re running quick queries, scripting tasks, or generating reports, it offers the control and flexibility needed for everyday database work. Mastering its commands makes every session faster and more productive.
To strengthen your Oracle security posture, consider DataSunrise. With real-time monitoring, data masking, and compliance automation, we help protect Oracle databases from top to bottom. Request a demo to see it in action.
