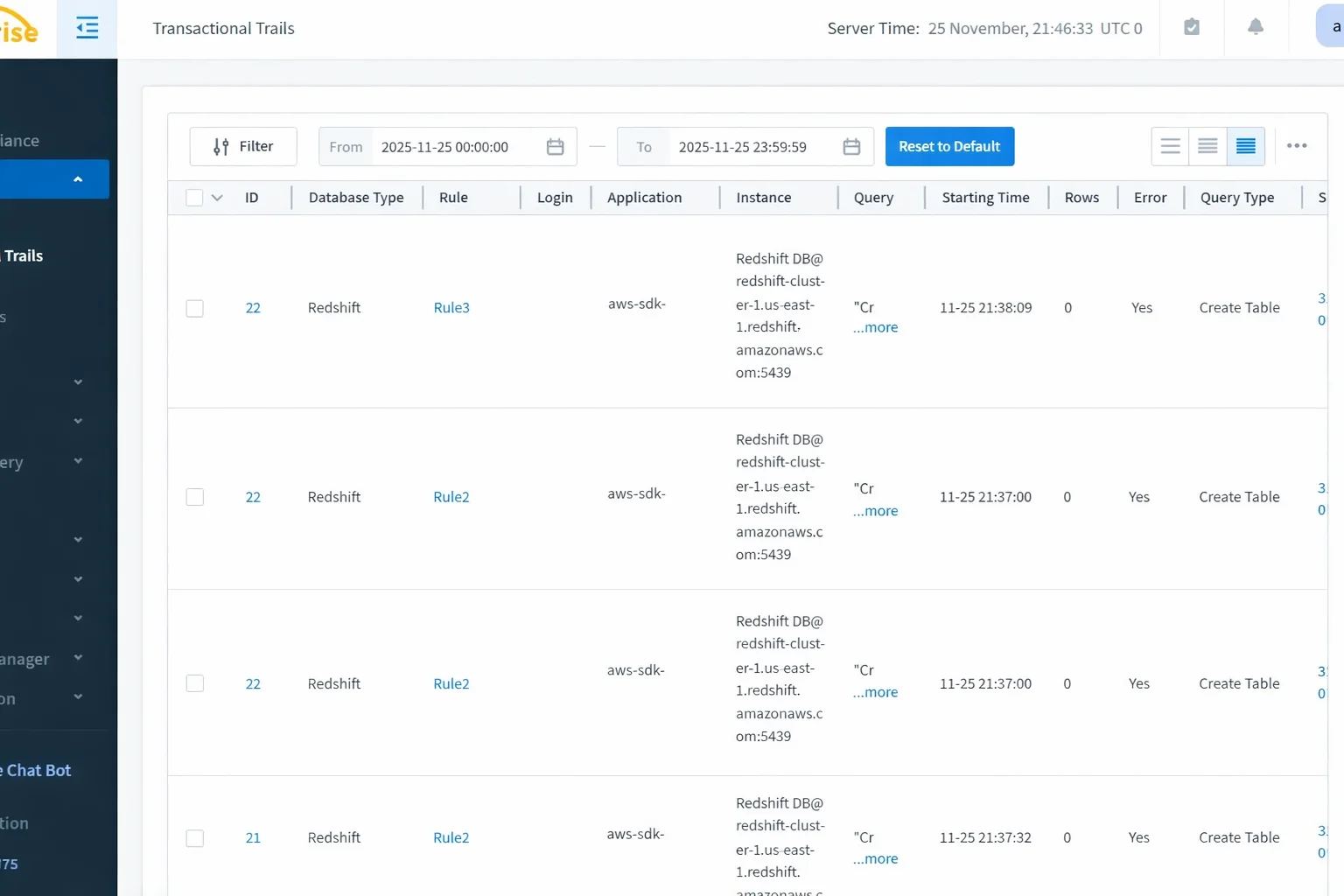
What Is Amazon Redshift Audit Trail
Modern analytics platforms concentrate massive volumes of sensitive business data into a single execution layer. In this context, an Amazon Redshift audit trail is not a logging feature—it is a governance mechanism closely tied to effective database activity monitoring.
Amazon Redshift is widely used for financial reporting, customer analytics, and operational intelligence. Queries executed against Redshift often involve regulated data, privileged users, automated pipelines, and external BI tools. Without a structured audit trail, organizations lack provable accountability for who accessed data, how it was used, and whether that access aligned with policy and regulation defined by modern data audit trails.
An Amazon Redshift audit trail provides chronological visibility into database activity, supporting security investigations, compliance validation, and operational oversight across distributed analytic workloads.
Importance of Audit Trail
In analytical environments, data access is rarely limited to a small group of database administrators. Business analysts, data scientists, reporting tools, ETL jobs, and automated services all interact with the same datasets. As a result, visibility into database activity becomes a foundational control rather than an optional security feature, especially in the context of database activity history.
An audit trail establishes accountability by recording how data is accessed and manipulated over time. It enables organizations to demonstrate control over sensitive information, investigate incidents, and verify that access patterns align with internal policies and regulatory expectations. These capabilities directly support structured database audit trails used during internal reviews and regulatory inspections. Without an audit trail, analytical systems operate as opaque execution engines where actions cannot be reliably attributed or reviewed.
For Amazon Redshift specifically, audit trails play a critical role in bridging the gap between high-performance analytics and governance. They provide the historical evidence required for compliance reviews, internal audits, and post-incident analysis, while also supporting operational transparency across teams and workloads governed by modern data compliance regulations.
Native Amazon Redshift Audit Data Sources
Amazon Redshift does not generate a single, consolidated audit log. Instead, audit-relevant signals are scattered across several native telemetry mechanisms, each designed for operational diagnostics rather than governance.
System Tables and Views
Redshift system tables and views capture low-level execution metadata generated during query processing. These internal tables are populated automatically by the Redshift engine and store detailed information about query execution across compute nodes.
Commonly used system tables include:
STL_QUERY— stores high-level query execution metadata such as start time, end time, execution status, and error flagsSTL_SCAN— records table scan operations, including scanned tables, row counts, and bytes processedSTL_DDLTEXT— captures Data Definition Language (DDL) statements, including schema changes and object creation or deletionSVL_USER_LOGINS— tracks authentication events, including successful and failed login attempts
These tables provide granular visibility into how queries are executed and which objects are touched. However, records are produced at the node level. A single SQL statement may generate multiple rows across different tables and nodes, representing execution fragments rather than a single logical operation.
Example: Reviewing Recent Query Activity
SELECT
q.query,
q.userid,
q.starttime,
q.endtime,
q.aborted,
q.text
FROM stl_query q
ORDER BY q.starttime DESC
LIMIT 10;
This query returns recent SQL statements executed in the cluster, along with execution timing and status. While useful, it does not show which tables were accessed or how data was scanned.
Example: Identifying Tables Scanned by Queries
SELECT
s.query,
s.tbl,
s.rows,
s.bytes
FROM stl_scan s
ORDER BY s.query DESC
LIMIT 20;
This output shows table-level scan activity, but it must be manually correlated with STL_QUERY using the query ID. In distributed workloads, this correlation becomes increasingly complex as query concurrency increases.
Example: Tracking Schema Changes
SELECT
ddl.userid,
ddl.starttime,
ddl.text
FROM stl_ddltext ddl
ORDER BY ddl.starttime DESC
LIMIT 10;
This query exposes recent DDL operations, allowing teams to identify schema changes. However, DDL statements are stored as text fragments and may require reconstruction for complete visibility.
Exported Audit Logs
Redshift supports exporting audit logs to Amazon S3 to support longer retention periods and offline analysis. These logs are typically enabled at the cluster level and written asynchronously.
Exported audit logs include:
- Connection logs — record database connection attempts
- User activity logs — capture executed SQL statements
- Authentication logs — track login successes and failures
Once exported, logs can be processed by external systems such as SIEM platforms, log analytics tools, or custom processing pipelines.
Example: Enabling Audit Log Export (Conceptual)
While audit log export is configured at the Redshift cluster level, the resulting files in S3 typically contain entries similar to the following:
2025-01-18T09:42:11Z user=reporting_user db=analytics pid=12345 LOG: statement: SELECT * FROM sales_data;
These records provide useful raw signals but lack structured context. Object-level access, query lineage, and user intent are not explicitly captured.
Characteristics of Exported Logs
- Logs are asynchronous, not real-time
- Entries are unstructured or semi-structured
- Query context and execution details are limited
- Object sensitivity and schema relationships are not preserved
As a result, exported audit logs primarily serve as raw inputs for downstream processing rather than a complete audit narrative. Meaningful audit trails require additional parsing, correlation, and enrichment before they can support investigations or compliance reviews.
Centralized Amazon Redshift Audit Trails with DataSunrise
DataSunrise extends Redshift’s native telemetry into a unified, investigation-ready audit trail. Instead of relying on post-processing of exported logs, the platform correlates Redshift activity in real time using non-intrusive deployment modes. This approach preserves execution context while eliminating fragmentation across compute nodes, parallel execution paths, and service boundaries. Audit records remain consistent regardless of whether activity originates from BI tools, automated pipelines, applications, or administrative sessions.
How DataSunrise Builds a Redshift Audit Trail
To construct a coherent audit trail, DataSunrise aggregates system table data, authentication events, and query execution signals into a single logical activity record. Distributed execution fragments are normalized into a chronological timeline, while full SQL context is preserved together with user identity, role information, and source attribution. Audit events are further enriched with object awareness and sensitivity classification, allowing the audit trail to reflect governance-relevant actions rather than low-level execution artifacts. As a result, investigation, reporting, and long-term governance become possible without manual reconstruction or custom correlation logic.
Compliance and Governance Benefits
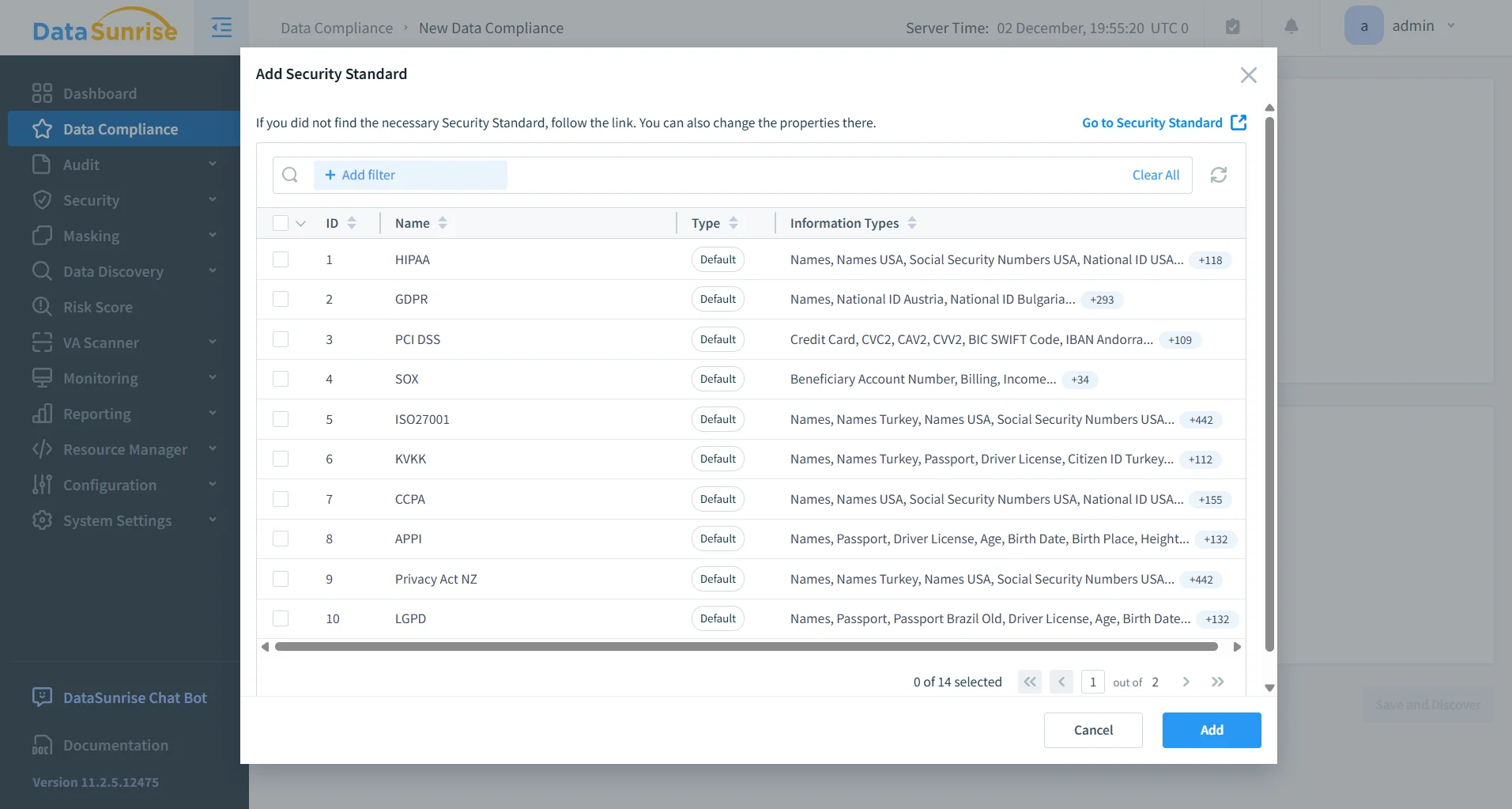
A structured Amazon Redshift audit trail directly supports regulatory and internal governance requirements by providing verifiable, time-ordered evidence of database activity. Such audit records enable accountability for financial data access under SOX, transparency for personal data processing under GDPR, monitoring of analytical access to cardholder data under PCI DSS, and auditability for healthcare analytics environments under HIPAA. Because audit data is centralized and normalized, organizations no longer need to assemble evidence retroactively. Instead, they maintain continuous audit readiness with consistent records across environments and workloads.
Operational and Security Value
Beyond compliance, a complete audit trail delivers tangible operational benefits. Preserved execution context allows security teams to investigate incidents more efficiently, correlate activity across sessions, and distinguish between human-driven actions and automated workloads. This clarity is especially important in analytical environments where scheduled jobs, dashboards, and interactive queries coexist. Clear attribution of actions to users, roles, and services improves accountability, simplifies internal reviews, and reduces ambiguity during incident analysis. Over time, audit trails evolve from a compliance requirement into an operational asset that supports security monitoring, governance enforcement, and informed oversight of analytical workloads.
Key Advantages of DataSunrise
| Advantage | What It Means for Amazon Redshift Auditing |
|---|---|
| Centralized Audit Trail | Correlates Redshift queries, sessions, DDL, and access events into a single, searchable audit history |
| Real-Time Visibility | Captures and analyzes database activity as it happens, not hours later via exported logs |
| Granular Audit Rules | Audits specific users, roles, schemas, tables, columns, or query types without noise |
| Compliance-Ready Reporting | Generates structured audit evidence for GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX |
Conclusion
Amazon Redshift provides foundational telemetry for observing database activity, but a complete audit trail requires structure, context, and correlation. Native system tables and exported logs capture valuable signals, yet they represent individual execution artifacts rather than a unified historical record required for effective database activity history analysis.
By centralizing, normalizing, and enriching Redshift activity, platforms like DataSunrise transform distributed signals into a coherent Amazon Redshift audit trail. This structured approach enables data audit alignment, security investigations, and operational clarity across modern analytics environments.
For organizations treating analytics platforms as regulated infrastructure rather than reporting engines, a robust audit trail becomes a core element of database security rather than a secondary reporting feature.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now