
Aim of a DB Audit Trail
In today’s regulatory environment, sectors like finance, government, healthcare, and education are required to implement rigorous measures to safeguard sensitive data. Conventional perimeter defenses such as firewalls are no longer sufficient to ensure accountability or traceability. Consequently, a dependable and tamper-resistant database audit trail has become a cornerstone of modern security architectures and compliance programs. According to a SANS security report, database-level auditing is one of the most effective methods for detecting misuse and maintaining compliance with industry standards.
Data Compliance Overview | Regulatory Frameworks
Modern data protection frameworks such as SOX, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and GDPR require organizations to maintain detailed and tamper-proof records of all data access and modification events. Comprehensive database audit trails not only demonstrate compliance but also play a crucial role in proactive threat detection and internal accountability. They provide a transparent view of who accessed which data, when the event occurred, what actions were performed, and under what context or authorization level. This level of traceability strengthens forensic analysis, supports incident response, and ensures that every interaction with sensitive information can be validated against security and governance policies.
Why Database Audit Trails Matter
Audit trails are more than a compliance formality—they provide valuable operational insights. When structured effectively, logs reveal user activities, confirm policy compliance, and highlight possible risks.
| Use Case | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Accountability | Trace data modifications to individual users |
| Policy Enforcement | Identify violations of access policies |
| Incident Response | Support investigations with granular logs |
| Intrusion Detection | Monitor for abnormal access behavior |
| Access Review | Spot inactive or over-privileged accounts |
Key questions a good audit trail should answer:
- Who accessed sensitive data and when?
- Were those actions authorized?
- Did the user operate within their assigned role?
- Can we trace specific security incidents back to the source?
Where Native Audit Tools Fall Short
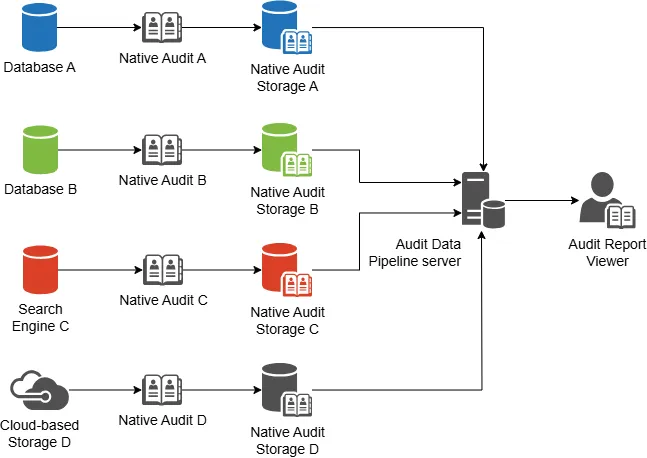
While most RDBMS platforms include some audit features, they are often verbose, inconsistent, or performance-draining. For example, PostgreSQL might require multiple triggers and manual log rotation just to get a basic row-level history.
-- PostgreSQL audit trigger example CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION log_update() RETURNS TRIGGER AS $$ BEGIN INSERT INTO audit_log(table_name, action, old_data, new_data, changed_at) VALUES (TG_TABLE_NAME, TG_OP, row_to_json(OLD), row_to_json(NEW), now()); RETURN NEW; END; $$ LANGUAGE plpgsql; CREATE TRIGGER audit_trigger AFTER UPDATE ON customer_data FOR EACH ROW EXECUTE FUNCTION log_update();
Native logging is useful but quickly runs into limitations. Typical challenges include:
Audit Trail Pain Points
- Raw logs are bulky and hard to query
- Storage pressure in production environments
- Inconsistent formats across database engines
- Slow investigations due to manual parsing
- Inability to track DDL changes or access context
| Domain | External Threat | Insider Threat | Compliance Risk |
|---|---|---|---|
| Customer PII | High | Med | High |
| Payment Data | High | High | High |
| Analytics Warehouse | Low | Med | Low |
| Source Code | Med | High | Low |
- 0 – 30 days: Hot storage → real-time investigations
- 1 – 12 months: Warm tier → compliance queries
- 1 – 7 years: Cold archive → legal / SOX evidence
Risks of Operating Without a Centralized Audit Trail
Native logs and ad‑hoc triggers create coverage gaps that show up the moment you need evidence. Without a unified audit layer, investigations drag on and compliance gets messy. The most common failure modes include:
- Silent data exposure — No cross‑engine correlation means suspicious access can hide in per‑node logs.
- Weak evidence chain — Inconsistent formats and retention policies make it hard to prove “who did what, when, and how.”
- Operational drag — Teams burn time normalizing logs instead of responding to incidents.
- Performance trade‑offs — DIY row‑level triggers add overhead and still miss session context.
- Regulatory risk — Auditors expect exportable, consistent trails aligned to frameworks like SOX and GDPR.
Centralizing audit across engines turns raw logs into answers—linking identities, sessions, and queries in one place. If you’re starting from scratch, begin with Database Activity Monitoring and plan for data discovery + dynamic masking to reduce alert noise and protect sensitive fields in transit and at rest.
What a Centralized Audit Platform Should Offer
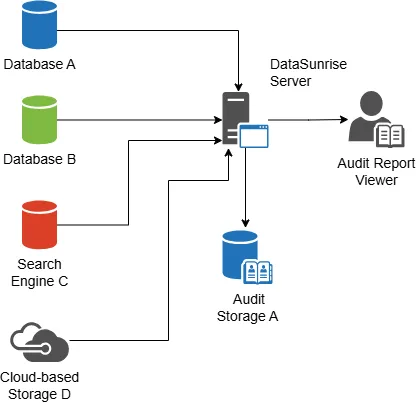
- Real-time visibility: Log every query, DDL change, or login as it happens
- Custom rule logic: Focus only on events that matter
- Searchable storage: Indexed logs ready for forensic analysis
- Compliance-friendly formats: Export PDFs, CSVs, or integrate into SIEMs
- Smart alerting: Get notified on policy violations or anomalies
2025 Cloud Audit Upgrades You Shouldn’t Ignore
| Cloud | 2025 Feature | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| AWS | CloudTrail Lake External Log Ingest | One pane for multi-cloud audit—ditch swivel-chair monitoring. |
| Azure | Enhanced Server Audit GA (July 2025) | 30–40 % lower CPU vs. per-DB auditing. |
| Multi-Cloud | DataSunrise vs. Guardium Connector | Policy-as-code beats plug-in sprawl—fewer moving parts to break. |
Native Database Audit vs DataSunrise: A Comparison
| Feature | Native Audit Tools | DataSunrise |
|---|---|---|
| Cross-DB Audit Policies | No — per-engine only | Yes — multi-DB support |
| Real-Time Rule-Based Logging | Limited, slow to customize | Yes — flexible GUI & CLI |
| Log Storage Control | Often local, difficult to scale | SQLite, Redshift, PostgreSQL, and more |
| Compliance Reporting | Manual or external tools | PDF, CSV exports built-in |
| Event Filtering & Analysis | Minimal session context | Session metadata, filters, roles |
Why Teams Choose DataSunrise
DataSunrise modernizes audit trails by offering a unified layer for query tracking, role-based enforcement, and reporting—across PostgreSQL, Oracle, SQL Server, MySQL, Redshift, and more.
- Create audit rules by table, user, role, or action type
- Store logs locally or externally in performance-optimized formats
- Generate reports via GUI or CLI—PDFs, CSVs, filtered views
- Use session metadata to narrow down exact query chains
- Protect sensitive fields with masking and anomaly detection
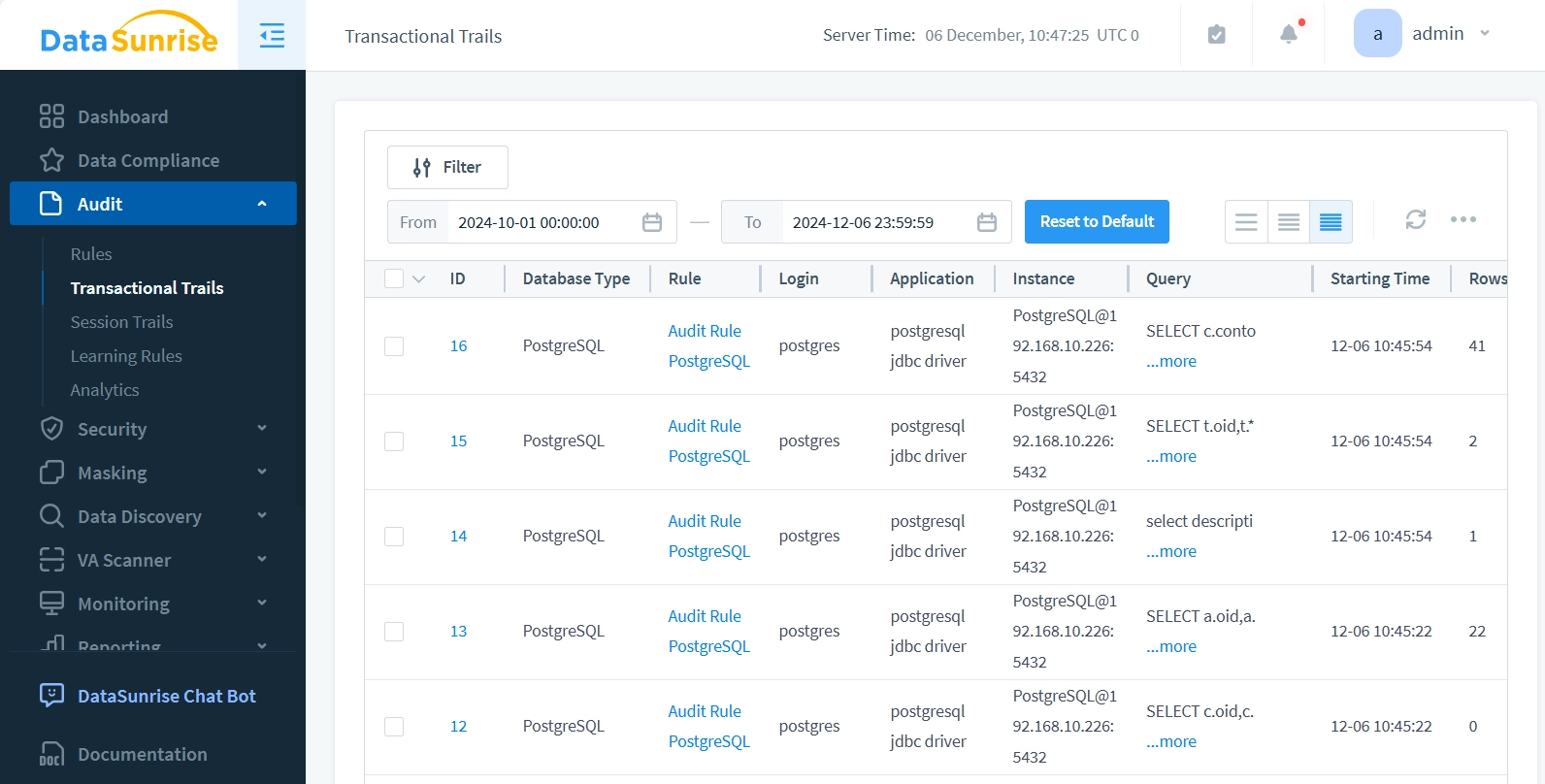
Real-World Scenario: Why Audit Trails Are Critical
Consider a situation where a privileged administrator is suspected of exfiltrating confidential customer information. Without a centralized audit system, piecing together the incident could require days of manual log collection — and even then, the results might be incomplete or inconclusive. However, with a unified monitoring platform such as DataSunrise, security teams can immediately replay the user’s session, review executed queries, and pinpoint precisely which records were viewed, altered, or exported.
In this context, the audit trail transforms from a simple historical log into a proactive security mechanism. Instead of merely documenting activity for compliance purposes, it enables rapid incident response, supports legal investigation, and helps identify whether the event was accidental, negligent, or malicious. Moreover, detailed audit visibility strengthens accountability across the organization and discourages insider misuse before it occurs.
Additionally, centralized audit trails bridge visibility gaps across hybrid environments — including cloud databases, on-premise systems, and distributed data stores. When activity is captured consistently across SQL, NoSQL, and cloud-native services, security teams can correlate events, detect lateral movement, and uncover multi-stage attacks that would otherwise remain hidden. This level of transparency is especially important when organizations rely on third-party contractors, shared administrative accounts, or DevOps teams with elevated privileges.
Audit trails also prove indispensable during compliance assessments. Regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX require organizations to demonstrate who accessed sensitive data, when they accessed it, and what actions were performed. A robust auditing solution allows teams to generate reports instantly, avoiding the costly and time-consuming process of reconstructing evidence manually.
Finally, audit analytics can reveal long-term behavioral patterns — unusual query frequency, off-hours access, privilege creep, or repeated attempts to bypass masking policies. By integrating audit intelligence with anomaly detection and SIEM systems, organizations evolve from reactive troubleshooting to predictive security, stopping incidents before they escalate.
Common Questions About Database Audit Trails
Understanding how audit trails work helps both security teams and compliance officers make informed decisions. Below are some frequently asked questions we encounter when helping organizations implement database auditing at scale.
- What should be included in a database audit trail?
User identity, timestamps, executed SQL statements, affected tables or rows, client IPs, and roles should all be logged. - How long should audit logs be retained?
Log retention depends on regulatory requirements. For example, SOX and GDPR may require logs to be kept from 1 to 7 years depending on industry and data type. - Can native audit tools meet compliance alone?
Rarely. Native tools offer basic logging, but they often lack real-time analysis, centralized management, or exportable compliance reports. - Do audit trails impact database performance?
They can—especially if poorly configured. That’s why platforms like DataSunrise use optimized logging engines and storage backends like SQLite or Redshift. - Is masking part of the audit trail?
It should be. Sensitive data like PII should be masked in logs or excluded entirely. DataSunrise applies masking rules before the audit event is stored.
This kind of detailed logging and reporting not only helps with regulatory audits, but also strengthens overall database security posture.
How Audit Trails Transform Daily Operations
In the financial sector, a unified audit trail revolutionizes the speed and accuracy of investigations by correlating user identities, session data, and SQL query histories across payment and transaction systems. What once required days of manual review can now be completed within hours, helping institutions rapidly detect and contain potential fraud or policy violations. Healthcare organizations apply the same principle to maintain precise records of every access to electronic health data—verifying who viewed, modified, or exported patient information. This automation eliminates the need for manual log correlation while providing real-time proof of HIPAA and GDPR compliance during audits and internal reviews.
Government and public sector entities depend on centralized auditing to ensure accountability among privileged users, prevent data leaks, and preserve the integrity of evidentiary chains for legal or disciplinary investigations. By enabling detailed visibility into administrative actions and policy enforcement, these systems significantly reduce insider threat dwell time and reinforce trust in institutional transparency.
Cloud-native and SaaS environments benefit equally from advanced audit trail systems. Suspicious cross-tenant access attempts or privilege escalations are detected instantly, noisy or inactive service accounts are flagged for review, and performance bottlenecks are traced to specific queries or workloads instead of guesswork. In e-commerce and fintech operations, automated anomaly detection highlights abnormal login attempts, data export patterns, or order manipulation behaviors, allowing teams to respond with precision rather than resorting to disruptive system-wide shutdowns.
Ultimately, audit trails have evolved from passive recordkeeping tools into active operational controls—enabling continuous monitoring, faster incident response, and repeatable compliance. By integrating with broader security ecosystems such as SIEM, DAM, and behavioral analytics platforms, they now serve as a foundation for proactive defense and intelligent data governance.
Conclusion
Comprehensive audit trails have become a cornerstone of modern cybersecurity and data governance strategies. As organizations navigate increasingly demanding regulatory requirements and face more advanced cyber threats, maintaining full visibility into every user action is more vital than ever. An effective auditing system tracks not only who accessed what data and when, but also the purpose and context of each operation—providing invaluable forensic insights when investigating incidents. Yet, native database logging tools often fall short, lacking scalability, centralized management, and real-time analytics, which limits their efficiency in complex or hybrid infrastructures.
Advanced solutions such as DataSunrise address these challenges through an integrated, policy-based framework capable of capturing and correlating activities across diverse databases and cloud environments. They empower security teams to convert raw log data into actionable intelligence, simplify regulatory reporting, and enhance access control governance. With built-in automation, intelligent alerts, and fully customizable dashboards, DataSunrise provides comprehensive oversight of both internal and external data operations—enabling rapid incident response and ensuring continuous compliance readiness.
Beyond meeting regulatory requirements, a strong audit trail acts as an active defense against insider risks, data misuse, and unauthorized activities. It enables early threat detection, strengthens accountability, and establishes a strategic foundation for trust, transparency, and long-term operational resilience across the organization.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now