Amazon OpenSearch Data Audit Trail
Amazon OpenSearch data audit trail is essential for organizations whose search, log analytics, and observability workloads rely on OpenSearch. These environments analyze large volumes of operational and customer data. Therefore, they retain log events, identifiers, IP addresses, and application content that must remain continuously visible and traceable.
In practice, teams increasingly use OpenSearch Service for security analytics, application monitoring, and even audit logging itself. However, this creates a structural paradox. The same platform can store security-relevant data while also becoming a sensitive target. Without a trusted OpenSearch audit trail, organizations cannot establish access accountability, investigate incidents effectively, or demonstrate compliance during audits.
This article describes how an Amazon OpenSearch data audit trail works in real deployments where native visibility has limits, and how DataSunrise enhances OpenSearch auditing using centralized logging, transaction correlation, and compliance-focused controls built around Data Audit and audit trails.
The Core Audit Challenges in Amazon OpenSearch
OpenSearch workloads differ from traditional relational databases. They expose REST APIs, accept JSON input, and often run behind application services and analytics pipelines. As a result, these architectural traits introduce several audit-specific problems that affect both data security and database security.
- REST-based access without query context
OpenSearch operations rely on HTTP requests rather than SQL sessions. Native logs capture request metadata, but they do not provide structured visibility into query intent, affected indices, or payload content. As a result, forensic analysis becomes slower and less accurate. Centralized audit logs reduce this gap by normalizing access records. - High volume of write and search operations
Logging and analytics pipelines can generate thousands of index and search requests per second. Without selective controls, raw log storage grows quickly and introduces operational noise. A targeted auditing approach aligned with audit storage performance reduces cost while preserving evidence. - Limited transaction correlation
OpenSearch does not group related requests into logical transactions. Consequently, tracing a single application action across multiple API calls requires a separate correlation layer. This is exactly where database activity history and cross-request tracking become useful. - Compliance visibility gaps
Environments processing GDPR-controlled or PCI DSS-controlled data must demonstrate continuous enforcement of access controls. Native OpenSearch logs alone typically do not meet audit and compliance requirements. Pairing audit controls with Compliance Manager strengthens evidence generation.
Native Amazon OpenSearch Audit Capabilities
Amazon OpenSearch Service provides basic audit logging through its security plugin. Administrators can enable audit logs to record authentication events, REST requests, and index-level operations. These logs can be stored in CloudWatch or indexed directly in OpenSearch. For native references, see the AWS Amazon OpenSearch security overview and the audit logging guide.
Although this strategy provides baseline visibility, it comes with limitations. Audit records remain low-level, lack transaction awareness, and stay tightly coupled to the OpenSearch cluster. Consequently, retention management, filtering, and compliance reporting require additional tooling and a broader database activity monitoring approach.
The OpenSearch Audit Trail Built by DataSunrise
To overcome these weaknesses, DataSunrise introduces a separate audit layer that operates independently of the OpenSearch cluster. By inspecting traffic between clients and OpenSearch endpoints, DataSunrise builds a structured OpenSearch audit trail without modifying OpenSearch internals. This architecture also aligns with reverse proxy deployment patterns often used for security enforcement.
This design follows established monitoring principles and complements additional controls such as role-based access control and policy governance.
OpenSearch Audit Rule Configuration
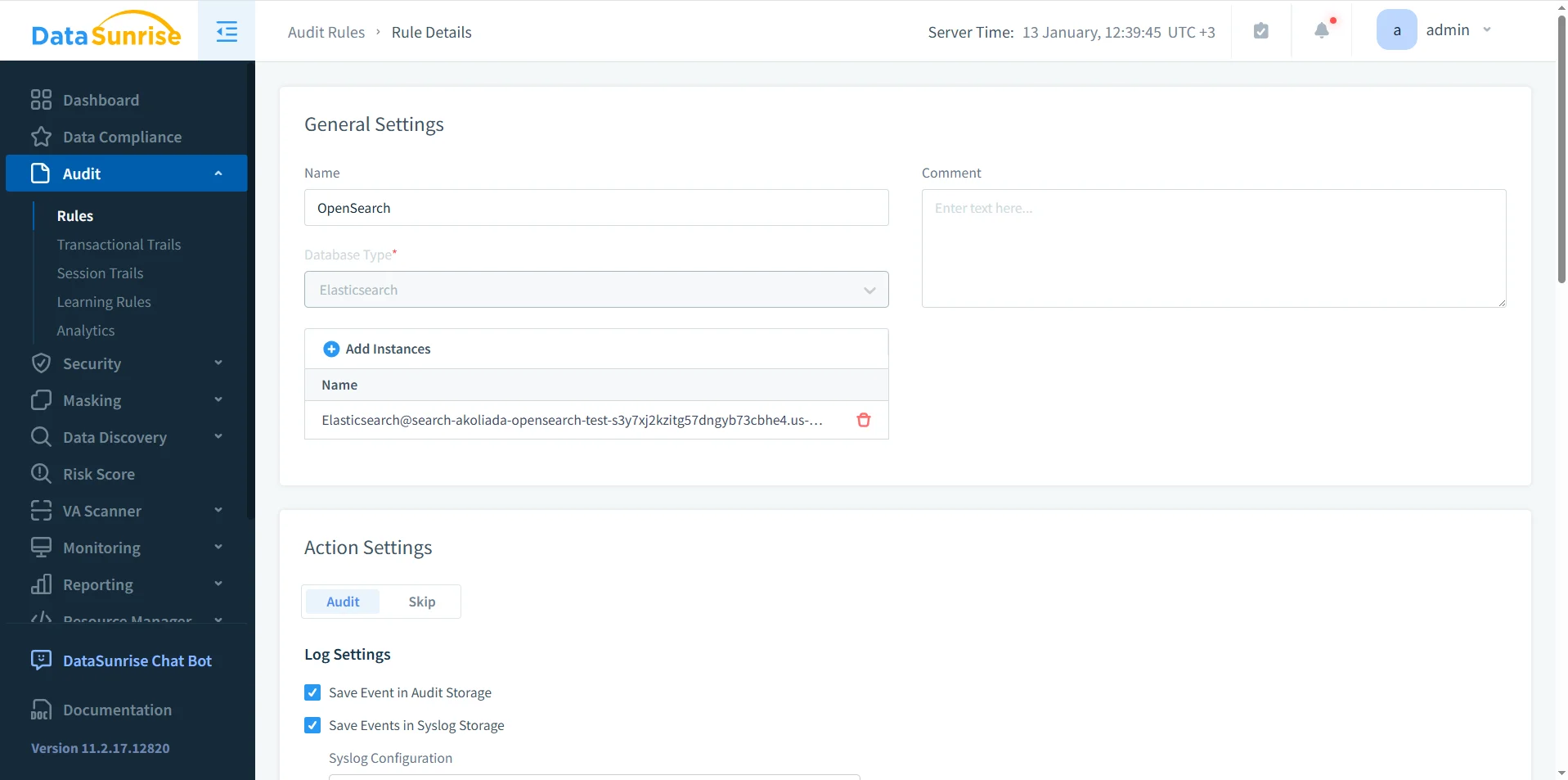
DataSunrise audit policies specify which OpenSearch instances, users, APIs, and operations must be logged. Rules can target index patterns, request types, or client sources. As a result, teams reduce audit noise while preserving accountability and aligning to audit rule priority behavior.
DataSunrise Amazon OpenSearch audit rule configuration
Audit rule configuration with OpenSearch instance selection, audit actions, and centralized log storage.
Transactional Trails and Session Awareness
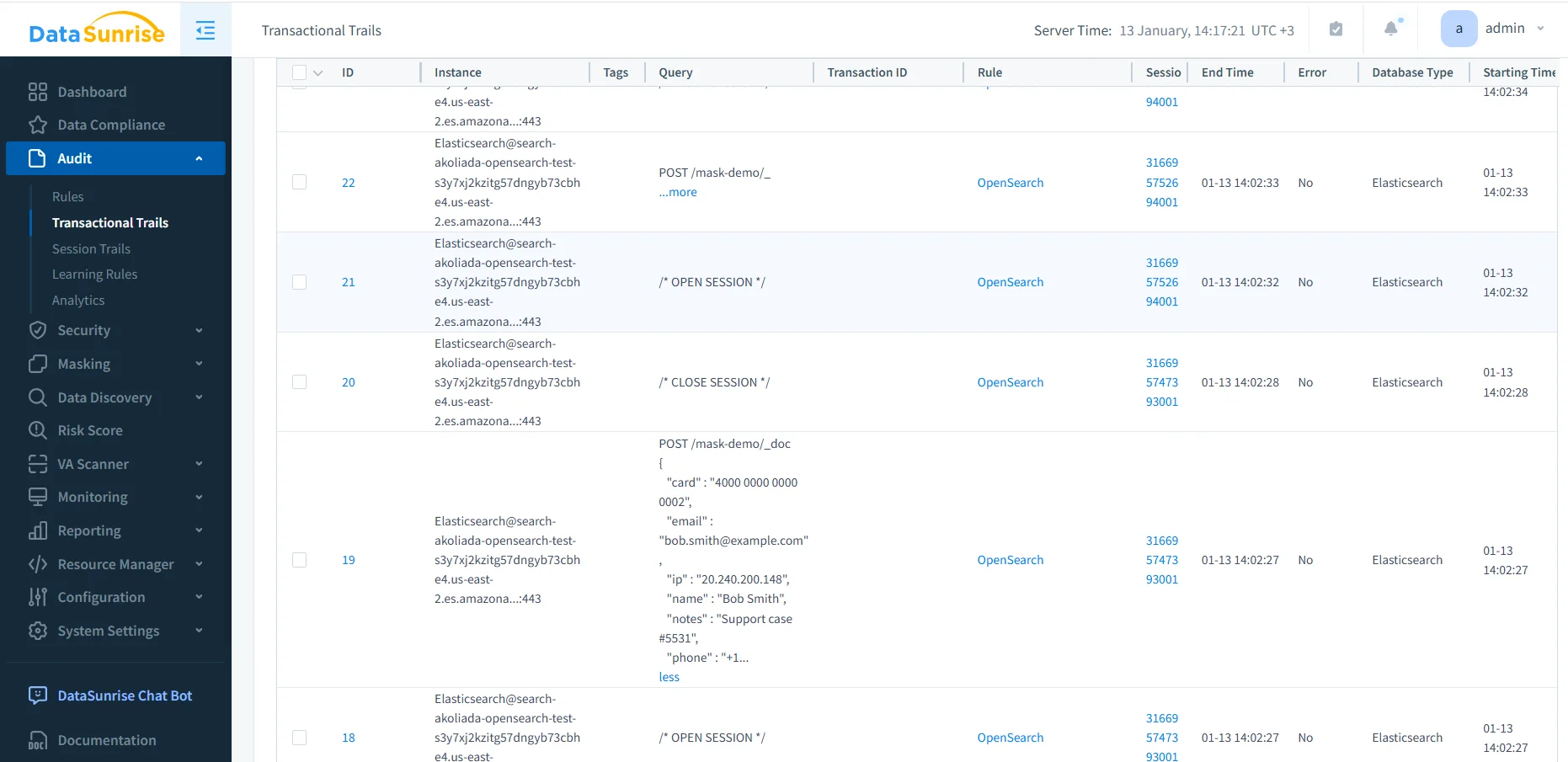
Unlike native OpenSearch logs, DataSunrise correlates related REST requests into logical sessions and transactional trails. Therefore, security teams can follow a full interaction from session setup through document indexing and search execution. This workflow also supports continuous auditing with consistent evidence collection.
Amazon OpenSearch transactional trails in DataSunrise
View of transactional trails with correlated OpenSearch operations, timestamps, session identifiers, and request details.
DataSunrise stores these records in dedicated audit storage optimized for retention, investigation, and reporting. In addition, organizations can connect audit evidence to broader detection workflows using threat detection concepts and security analytics.
Security and Governance Advantages
DataSunrise expands OpenSearch auditing beyond native logs and improves security posture and governance maturity. It also supports broader controls such as data discovery to identify where sensitive fields exist before you enforce policy.
- Centralized auditing across cloud and hybrid environments through audit logs
- Better incident response using data activity history
- Alignment with RBAC strategies
- Reduced exposure to security threats and unauthorized access
These capabilities integrate naturally with broader security and compliance programs, including compliance regulations mapping and automated reporting workflows.
Operational Audit Coverage Comparison
| Audit Aspect | Native OpenSearch | DataSunrise |
|---|---|---|
| Request-level logging | Basic REST metadata | Full request context with payload visibility |
| Transaction correlation | Not available | Session-based transactional trails |
| Centralized retention | Cluster-dependent | External audit storage with retention policies |
| Compliance reporting | Manual | Automated, audit-ready reporting via Compliance Manager |
The Compliance Imperative
Regulatory frameworks increasingly demand around-the-clock audit coverage, including non-relational platforms such as OpenSearch. In practice, that means organizations must combine audit evidence with enforceable policy and reporting workflows for GDPR, HIPAA technical safeguards, and PCI DSS.
These controls support the goals described in the aim of a database audit trail and enable automated evidence generation through automated compliance reporting.
To handle high-volume OpenSearch clusters, start with narrowly scoped audit rules focused on sensitive indices and administrative APIs. Then expand coverage gradually to prevent unnecessary storage growth while preserving compliance-critical visibility.
Conclusion: Building a Workable OpenSearch Audit Trail
Amazon OpenSearch provides baseline logging, but it was not designed to operate as a standalone audit platform. Therefore, organizations that rely on OpenSearch for security analytics, observability, or customer data processing usually need stronger guarantees.
DataSunrise adds an external audit layer and provides transaction-aware audit trails that integrate OpenSearch into a wider compliance architecture. As a result, teams support investigations, regulatory inspections, and long-term operational accountability without disrupting existing pipelines.
As OpenSearch usage continues to grow, organizations should treat audit trails as infrastructure, not as an afterthought. A platform that combines monitoring, auditing, and compliance controls makes it far easier to scale analytics safely and consistently.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now