Amazon OpenSearch Database Activity History
Amazon OpenSearch Database Activity History provides a critical audit capability for organizations that use Amazon OpenSearch to store, search, and analyze operational telemetry, application logs, and event-driven records. In modern architectures, teams often use OpenSearch to handle data that is security-relevant by default, including user identifiers, IP addresses, timestamps, request metadata, and support-related content.
Because OpenSearch frequently stores this type of information, it quickly falls within audit and compliance scope. Every indexing operation, search request, or document update represents a database interaction that auditors and security teams may later need to reconstruct.
Unlike relational databases, OpenSearch does not rely on persistent SQL sessions or transactional query contexts. Instead, it exposes REST endpoints that accept stateless HTTP requests. Consequently, applications, log shippers, and automation tools can generate thousands of requests per minute on behalf of users and backend services. As a result, traditional database activity tracking models fail to preserve sufficient context or continuity.
Amazon OpenSearch Database Activity History addresses this gap by recording how systems write, query, and access data over time while preserving execution order and request context. This article explains how DataSunrise implements database activity history for OpenSearch, focusing on data audit, database activity monitoring, transactional correlation, centralized storage, and audit-ready evidence generation.
Why Native OpenSearch Logs Fall Short for Auditing
Amazon OpenSearch generates internal logs that capture request handling, system events, and error conditions. While operators use these logs for troubleshooting and diagnostics, they do not satisfy audit or governance requirements defined by modern data compliance regulations.
From an audit perspective, native OpenSearch logs introduce several limitations. First, the platform records requests as isolated technical events rather than correlated user actions. Second, OpenSearch does not track sessions or transactions across related requests. Third, retention policies often depend on cluster lifecycle and storage constraints. Finally, security teams struggle to map business actions to multiple underlying OpenSearch operations.
Consequently, when auditors ask who accessed specific data, what actions occurred, and when those actions took place, native logs rarely provide reliable answers. To close this gap, organizations need a dedicated database activity history layer.
Audit Rule Configuration for Amazon OpenSearch
DataSunrise builds database activity history through explicit audit rules. These rules define the monitoring scope and control how the system records OpenSearch activity.
Specifically, audit rules determine which OpenSearch instances DataSunrise monitors, which operations trigger audit events, and where the platform stores audit records. As a result, teams can focus on security-relevant database activity instead of collecting every low-value request. Rule behavior follows the rules priority model, ensuring consistent enforcement.
Security teams commonly audit document writes, updates, deletions, and administrative API calls while excluding routine read-only traffic. This selective approach aligns with data security and database security best practices.
Transactional Trails and Database Activity Correlation
OpenSearch processes each REST request independently. Although this design improves scalability, it complicates audit analysis because related operations appear disconnected.
In real workflows, a single user action often triggers multiple OpenSearch requests. For example, an application may index a document, update related records, and then execute a verification query. Native logs record these steps separately, which makes reconstruction difficult.
DataSunrise resolves this challenge by correlating individual requests into transactional database activity trails. Correlation relies on timing, connection attributes, and request metadata, allowing auditors to trace complete activity sequences.
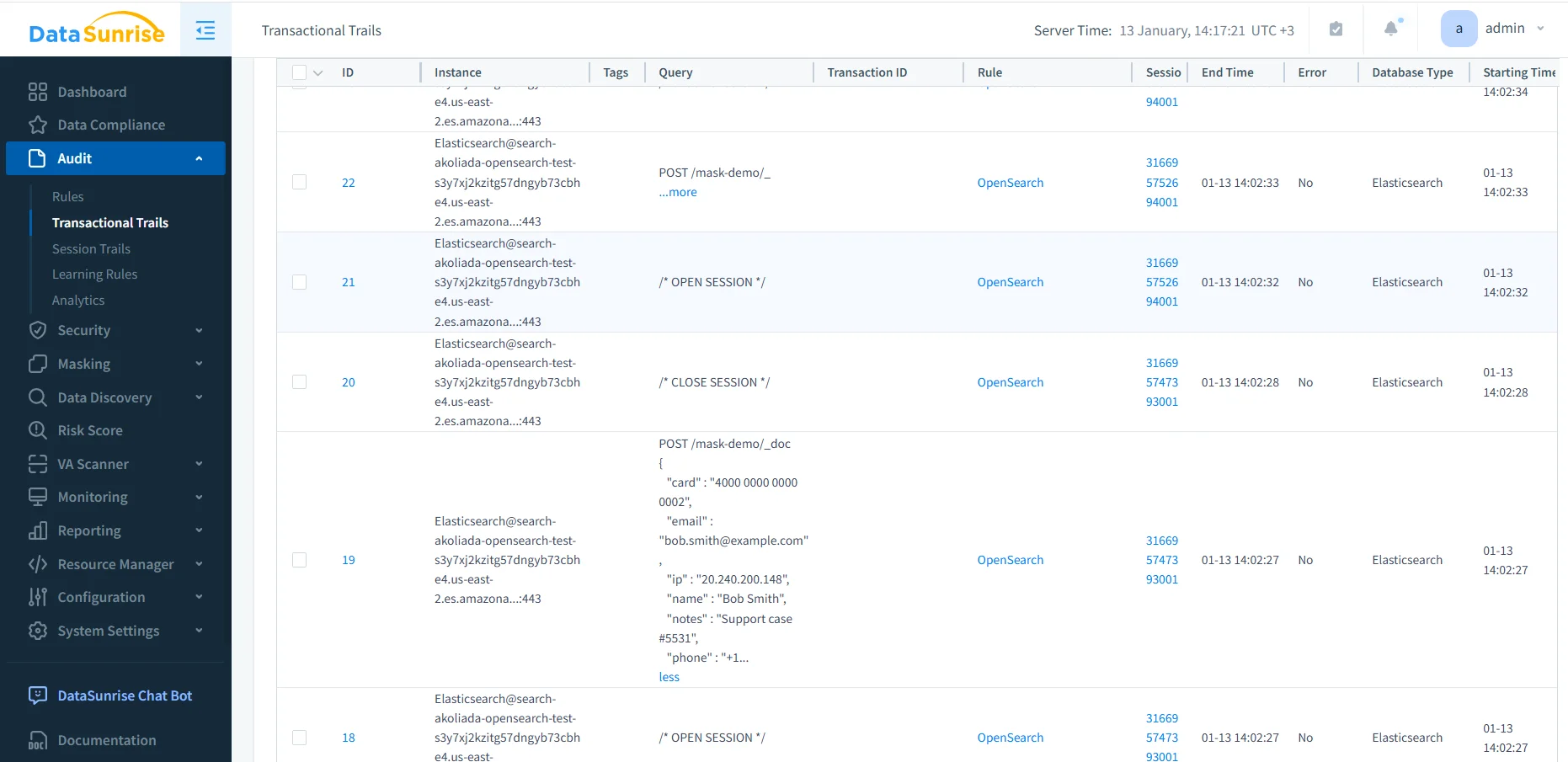
From an audit standpoint, transactional trails provide context that isolated logs cannot. They show how users and applications interacted with the database over time.
Centralized Database Activity Monitoring Architecture
Rather than relying on OpenSearch internals, DataSunrise implements database activity history as an external audit layer using reverse proxy or traffic inspection techniques.
This architecture offers several advantages. Audit records remain independent from the OpenSearch cluster, users cannot tamper with audit data, and teams can enforce centralized retention policies using optimized audit storage.
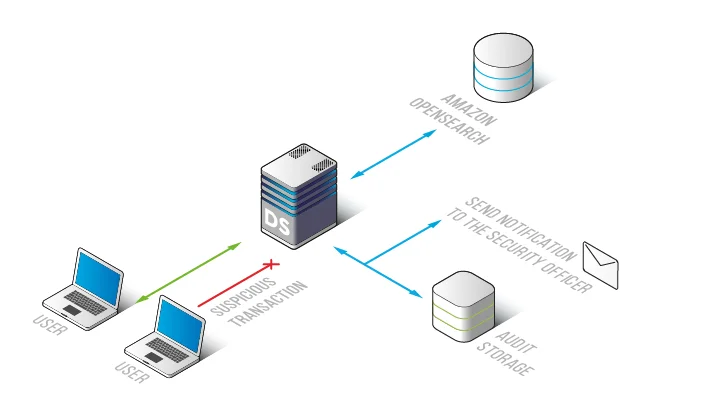
This approach supports long-term governance, investigations, and integration with automated compliance reporting.
Example: Audited OpenSearch Operation
The following example shows a document indexing request that becomes part of the OpenSearch database activity history. The request structure follows standard OpenSearch REST APIs documented in the OpenSearch indexing API.
curl -X POST "http://localhost:9201/audit-demo/_doc" \
-H "Host: search-your-opensearch-domain.us-east-2.es.amazonaws.com" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"user": "bob.smith",
"action": "support_case_update",
"ip": "220.240.200.148",
"timestamp": "2026-01-13T14:02:27Z"
}'
DataSunrise records this operation as an auditable database activity event. The audit record includes client identity, source address, operation type, execution timing, and the applied audit rule, supporting audit logs and investigations.
Audit and Compliance Use Cases
Maintaining complete database activity history enables several audit-driven use cases:
- Reconstructing access patterns during security investigations
- Demonstrating accountability for role-based access control
- Tracking actions by privileged or support accounts
- Detecting anomalous behavior using behavior analytics
These capabilities help organizations meet requirements for GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX using centralized data security policies and continuous audit enforcement.
Conclusion: Building an Auditable OpenSearch Environment
Amazon OpenSearch delivers powerful search and analytics functionality. However, it does not provide an audit-grade database activity history by default.
By deploying DataSunrise as an external audit layer, organizations gain a centralized, transaction-aware, and tamper-resistant view of OpenSearch database activity. This approach strengthens security posture, simplifies compliance, and enables reliable audit evidence without disrupting existing workflows.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now