
Audit Trails

Introduction
Human error remains one of the most persistent drivers of data breaches across modern organizations. Numerous industry reports indicate that nearly two-thirds of security incidents stem from unintentional insider actions rather than deliberate attacks. According to the latest IBM Data Breach Report, mistakes made by authorized users continue to be a major factor in data exposure as well as rising remediation expenses. These lapses typically involve misconfigured databases, inadequate access controls, accidental disclosure of confidential records, or the unintended sharing of sensitive information. In today’s distributed cloud and hybrid ecosystems, even a single misconfiguration can instantly expose critical data to the public internet.
To effectively mitigate these risks, organizations must adopt strong data governance frameworks supported by ongoing employee awareness programs and role-based security training. Implementing detailed audit trails and automated monitoring systems is essential for ensuring visibility and accountability across the data landscape. Such tools provide security teams with real-time insights into every query, change, and access request, enabling rapid detection of unusual patterns and swift investigation of potential incidents. When combined with robust access controls, masking techniques, and user-behavior analytics, audit trails significantly reduce the likelihood and impact of human errors while improving compliance posture and enhancing the resilience of the entire data environment.
What Is an Audit Trail in a Database?
A database audit trail is a comprehensive, time-ordered log that captures every action carried out within a database environment. It records both user-initiated operations—including authentication attempts, executed queries, and data modifications—and system-generated events such as automated tasks, backup routines, and background processes. Each log entry generally includes details about who executed the action, which object or dataset was involved, when the event occurred, and often where the activity originated (for example, an IP address or specific application).
These detailed logs help organizations maintain strong data accountability and end-to-end visibility across their database operations. Audit trails play a crucial role in detecting abnormal behavior, preserving data integrity, and meeting regulatory requirements set by frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX. They also support broader security controls like User Behavior Analysis (UBA), enhancing an organization’s ability to identify risks proactively.
Core Purposes of an Audit Trail
- Detecting unauthorized access: Helps identify suspicious logins or privilege escalations that may indicate a security breach.
- Tracking data modifications: Records changes made to tables, schemas, or configuration parameters—allowing administrators to reconstruct the exact sequence of actions.
- Investigating security incidents: Provides verifiable evidence for forensic analysis and supports root-cause investigations during audits.
- Ensuring regulatory compliance: Demonstrates adherence to data protection and financial accountability standards through reliable, tamper-resistant logs.
Ultimately, audit trails serve as a critical foundation for transparency, accountability, and trust in data management. Whether used for real-time monitoring or retrospective analysis, they reinforce the integrity and security of your database systems—helping teams detect threats early, verify compliance, and build resilient data governance frameworks.
Approaches to Database Audit Trails
There are two main approaches to implementing audit trails in databases:
Native Tools
Many database management systems (DBMS) offer built-in auditing capabilities. These native tools provide a straightforward way to enable basic auditing functions. For example, Oracle has its Audit Trail feature, while Microsoft SQL Server includes SQL Server Audit.
Third-Party Tools
Third-party audit trail solutions, like DataSunrise, offer more advanced features and centralized management. These tools often provide:
- Enhanced security controls
- Cross-platform compatibility
- Customizable reporting options
- Real-time alerting capabilities
Example: Audit Trail with pgAudit in PostgreSQL
To view the PgAudit log, you can use the ‘cat’ command as follows (more details here):
cat /var/log/postgresql/postgresql-16-main.log | more
Let’s look at a brief example of what an audit trail might look like using the pgAudit extension in PostgreSQL:
2024-09-17 10:15:23 UTC,AUDIT,SESSION,1,1,READ,SELECT,TABLE,public.users,,,SELECT * FROM users WHERE id = 123;
This log entry shows:
- Timestamp
- Audit type
- Session and user IDs
- Operation type (READ)
- SQL statement type (SELECT)
- Object type (TABLE)
- Schema and table name
- The actual SQL query executed
Native audit capabilities often fall short in advanced features. While they provide basic logging, they typically lack data tagging, built-in analytics, and automated rule application. Transforming raw log files, like the example shown earlier, into actionable insights requires significant additional effort and processing.
Audit Trail Quick Start (Step-by-Step)
Enable pgAudit on PostgreSQL
# postgresql.conf
shared_preload_libraries = 'pgaudit'
pgaudit.log = 'read,write,ddl'
pgaudit.log_parameter = on
-- in each database:
CREATE EXTENSION pgaudit;
-- restart PostgreSQL after editing shared_preload_libraries
Verify logging:
cat /var/log/postgresql/postgresql-16-main.log | moreSignals to Watch
- Off-hours reads on tables with PII/PHI
- Spikes in SELECT volume by a single user/session
- Role changes followed by DDL or large exports
Creating a DataSunrise Instance for Audit Trail
Assuming DataSunrise is already installed, here’s how to create an instance and view an audit trail:
- Log in to the DataSunrise web interface
- Navigate to “Instances” and click “+ Add New Instance”
- Configure the connection details for your database. DataSunrise consolidates all database connections in one location.
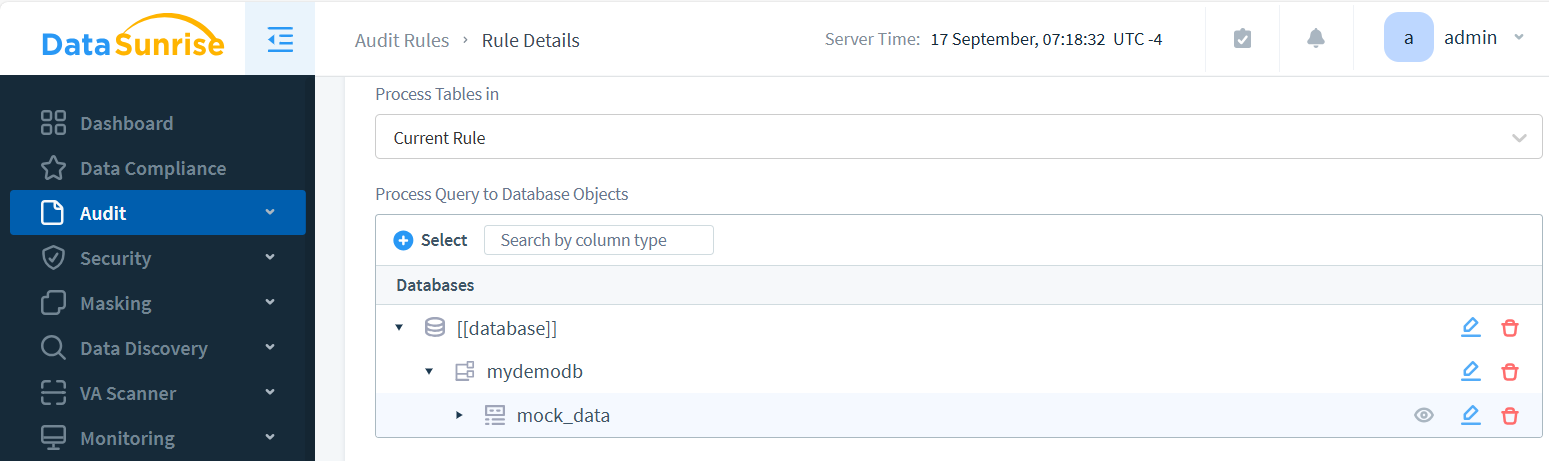
- Create Audit Rule in Audit – Rules and enable auditing for the desired objects.
- Access the “Audit – Transactional Trails” section to view and analyze the generated trails.
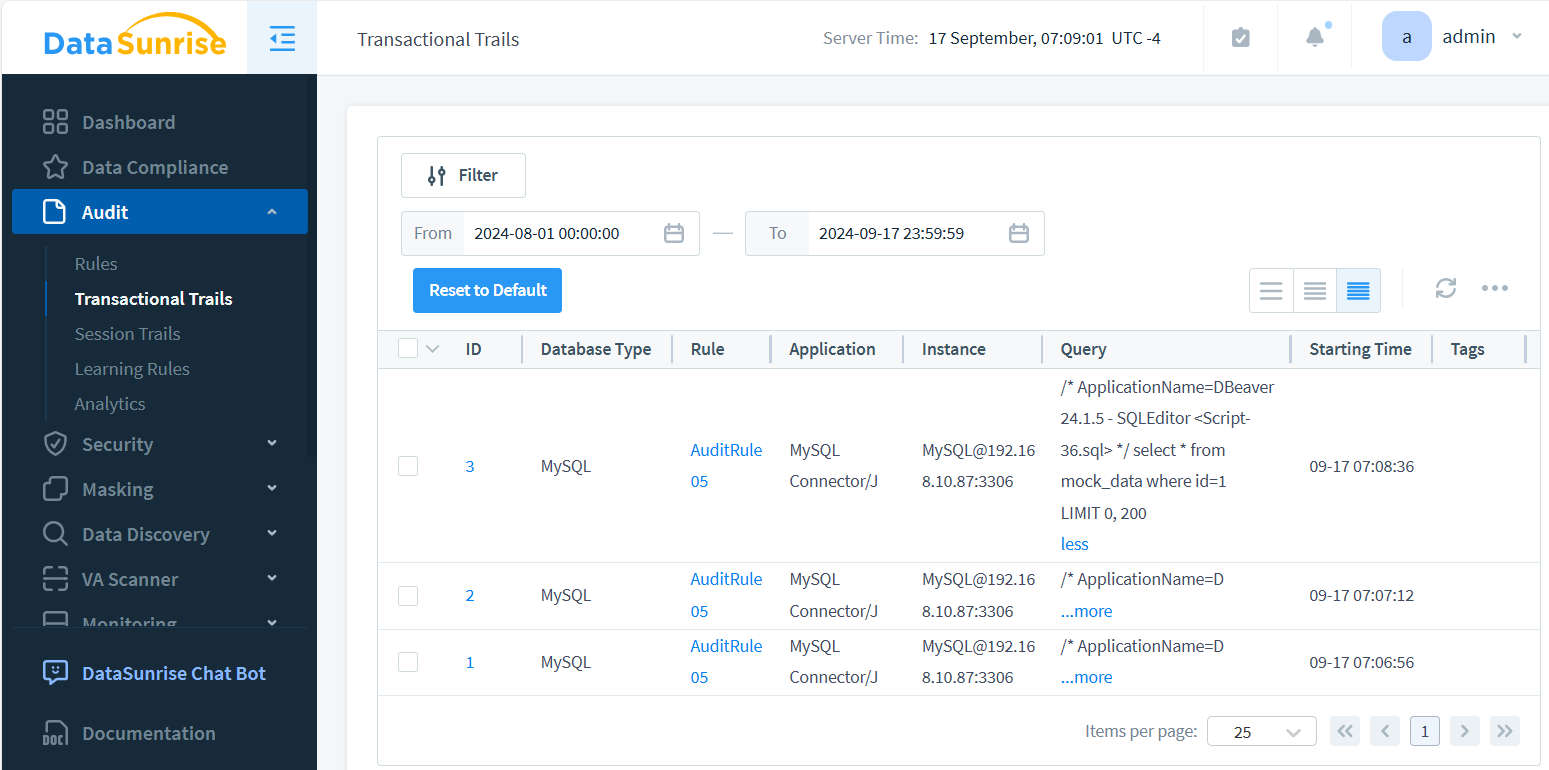
DataSunrise makes it easy to set up comprehensive auditing across multiple database platforms. The image above showcases key audit trail components: instance details, timestamps, and logged queries. Optionally, query results can be captured as well. Each event in the Audit Trail is interactive, allowing users to drill down and view detailed database query outcomes with a simple click.
Benefits of DataSunrise for Centralized Audit Control
DataSunrise offers several advantages for managing audit trails:
- Unified Interface: Control audit rules across various database types from a single dashboard
- Customizable Policies: Create tailored audit policies based on your specific security requirements
- Real-time Monitoring: Detect and alert on suspicious activities as they occur
- Compliance Support: Meet regulatory requirements with pre-configured compliance reports
- Scalability: Easily manage audit trails for large, complex database environments
Quick Comparison: Native vs. DataSunrise Audit Trails
| Feature | Native Tools | DataSunrise |
|---|---|---|
| Setup & Configuration | Manual, DB-specific | Centralized, cross-DB |
| Analytics & Alerts | Limited or none | Real-time, customizable |
| Compliance Reporting | Basic exports | Pre-built SOX, HIPAA, GDPR templates |
Industry Use Cases
- Finance: Detect unauthorized account access quickly.
- Healthcare: Monitor PHI access for HIPAA audits.
- SaaS: Track tenant-level activity for customer trust.
Business Impact at a Glance
| Investigation time | Cut from hours to minutes |
| Audit readiness | Always-on compliance reporting |
| Storage efficiency | Centralized, compressed logs |
The Importance of User Behavior Monitoring
Tracking user behavior is critical for maintaining database security. Comprehensive audit trails serve as vigilant watchdogs, helping organizations identify a range of suspicious activities. These include unusual access patterns that deviate from normal user behavior, unauthorized data modifications that could compromise integrity, attempts to escalate privileges beyond assigned roles, and potential insider threats that often go unnoticed. By meticulously analyzing these patterns, organizations can proactively address security risks, implement targeted countermeasures, and effectively protect sensitive data from both external and internal threats.
Best Practices for Implementing Audit Trails
To maximize the effectiveness of your audit trail system, it’s crucial to adopt a comprehensive approach. Start by defining clear auditing objectives that align with your organization’s security goals. Implement least privilege access to minimize potential risks. Regularly review and analyze audit logs to detect anomalies and potential threats promptly. Establish a robust retention policy for audit data to ensure compliance and historical analysis. Safeguard the integrity of your audit trails through secure storage mechanisms. Lastly, conduct periodic audits of the auditing system itself to ensure its reliability and effectiveness. By diligently following these practices, you’ll significantly enhance your overall database security posture and create a more resilient defense against potential threats.
Audit Trails in Compliance Frameworks
Different regulations outline specific expectations for database audit trails. Mapping your audit strategy to these frameworks ensures you meet mandatory controls and avoid penalties:
| Framework | Audit Trail Requirements | How DataSunrise Helps |
|---|---|---|
| GDPR | Log access to personal data and prove lawful processing. | Centralized tracking of queries involving PII with automated reports. |
| HIPAA | Record all PHI access and provide tamper-proof audit evidence. | Granular audit rules on PHI fields with integrity-checked logs. |
| PCI DSS | Track payment data access and monitor unusual activity. | Real-time monitoring and alerts for cardholder data queries. |
| SOX | Maintain accountability for financial record changes. | Role-based auditing and scheduled compliance-ready reports. |
This mapping highlights how DataSunrise bridges the gap between raw database logs and auditor-ready compliance evidence, reducing manual effort while strengthening security.
Audit Trail Standards & Compliance References
Audit trails are not only best practices — they are explicitly tied to compliance frameworks. Below are resources on how DataSunrise helps organizations meet these standards:
- Data Compliance Overview — Central resource on aligning database controls with major regulations
- Regulatory Compliance Knowledge Center — Detailed coverage of GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX
- How to Comply with GDPR, HIPAA, and SOX — Practical guidance on audit trail alignment
- Database Security — Foundations for audit logging and access control
- Database Activity Monitoring — Continuous oversight of user behavior and audit events
Mapping your audit trail strategy against these resources ensures your controls are aligned with compliance demands while leveraging DataSunrise automation to reduce overhead.
Challenges in Audit Trail Management
While trails are invaluable, they come with challenges:
- Performance Impact: Extensive auditing can affect database performance
- Storage Requirements: Audit logs can grow rapidly, requiring significant storage
- Data Privacy: Audit trails may contain sensitive information, requiring careful handling
- Analysis Complexity: Large volumes of audit data can be overwhelming to analyze
Practical Example: Querying Audit Logs Directly
For administrators working without third-party tools, analyzing native audit logs often means writing queries against system catalog views or log tables. For instance, in SQL Server you can pull recent audit events like this:
SELECT event_time, server_principal_name, database_name, statement
FROM sys.fn_get_audit_file('C:\SQLAudits\*.sqlaudit', DEFAULT, DEFAULT)
WHERE event_time > DATEADD(HOUR, -2, GETDATE())
ORDER BY event_time DESC;
This query retrieves audit events from the past two hours, including who ran the query, which database they accessed, and the executed statement. While informative, scaling this kind of manual log analysis across multiple databases quickly becomes a heavy lift—highlighting the value of centralized solutions such as DataSunrise for correlation, alerting, and compliance reporting.
DataSunrise can help address these challenges through efficient automated log management and advanced analytics capabilities.
Real-World Applications of Database Audit Trails
Audit trails move beyond theory when applied to industry-specific challenges. They ensure accountability, transparency, and compliance in environments where sensitive data drives critical operations:
- Financial Services: Track every transaction detail to comply with SOX and PCI DSS while detecting fraud in real time.
- Healthcare: Protect patient records (PHI) under HIPAA by logging access and modifications to clinical data.
- Government: Provide tamper-proof evidence of database activity to support audits and transparency initiatives.
- SaaS and Cloud Platforms: Monitor multi-tenant environments, ensuring customer data isolation and trust.
- Retail and eCommerce: Maintain visibility into sensitive customer and payment data for GDPR and PCI DSS compliance.
By connecting audit trails to specific industry requirements, organizations not only strengthen database security but also simplify regulatory alignment and reduce risk exposure.
The Future of Audit Trails
As data security threats evolve, so too must audit trail technologies. Future trends include:
- AI-powered anomaly detection
- Blockchain-based immutable audit logs
- Integration with threat intelligence platforms
- Enhanced visualization and reporting tools
Staying ahead of these trends will be crucial for maintaining robust database security.
Audit Trail FAQ
What is a database audit trail?
A database audit trail is a chronological record of user and system actions. It provides verifiable evidence of who accessed or changed data, when the action occurred, and the scope of the activity. This record supports accountability, security investigations, and regulatory compliance.
How is an audit trail different from system logs?
System logs primarily track operational health and performance. Audit trails directly associate events with users and data objects, making them suitable for compliance validation and forensic analysis.
Which regulations require audit trails?
Audit trails are explicitly required or strongly recommended under frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX. They demonstrate control effectiveness and support external audits.
How can performance impact be minimized?
- Apply auditing selectively to sensitive objects and critical actions.
- Filter unnecessary parameters and reduce event noise.
- Export and centralize audit data outside the transactional system.
- Implement retention, rotation, and compression policies.
What metrics indicate an effective audit trail?
- Coverage of sensitive objects monitored.
- Mean time to detect and respond to incidents.
- Accuracy of alerts (true vs. false positives).
- Integrity verification success rate of stored logs.
- Audit data growth and retention compliance.
Conclusion
Audit trails are a fundamental component of strong database security. They capture and document every relevant action within the system, providing full visibility, accelerating threat detection, and simplifying compliance with regulatory standards. While native auditing tools often deliver only basic functionality, enterprise-grade platforms like DataSunrise offer centralized oversight, deeper analytics, and more granular control over user activities.
By combining structured auditing with behavioral analysis and dedicated governance capabilities, organizations can significantly enhance the protection of sensitive data, quickly identify anomalies, and maintain system integrity across hybrid, multi-cloud, and distributed environments.
DataSunrise delivers flexible and intuitive solutions for comprehensive database security, including intelligent activity monitoring and advanced data masking. Request a demo to see how the platform streamlines compliance, strengthens data protection, and reduces operational overhead without disrupting your workflows.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now