
Google Cloud SQL Audit Trail

Introduction
A Google Cloud SQL Audit Trail is a database record of key events such as logins, data queries, and schema changes. It is a vital tool for detecting suspicious activity, meeting compliance requirements, and maintaining operational accountability.
When SQL Server runs on Google Cloud SQL, administrators can combine Microsoft’s native auditing capabilities with Google Cloud’s secure infrastructure. This enables detailed tracking of database activity while benefiting from managed backups, high availability, and network security features.
This guide explains how to configure a native Google Cloud SQL Audit Trail for SQL Server 2022 and shows how DataSunrise can extend those capabilities with real-time analysis, granular controls, and compliance-oriented reporting.
Native Auditing in SQL Server on Google Cloud SQL
SQL Server includes SQL Server Audit, a feature that writes audit records to a file or application log. In a Google Cloud SQL environment, these files can be stored on the local instance and then exported to Cloud Storage for retention and analysis.
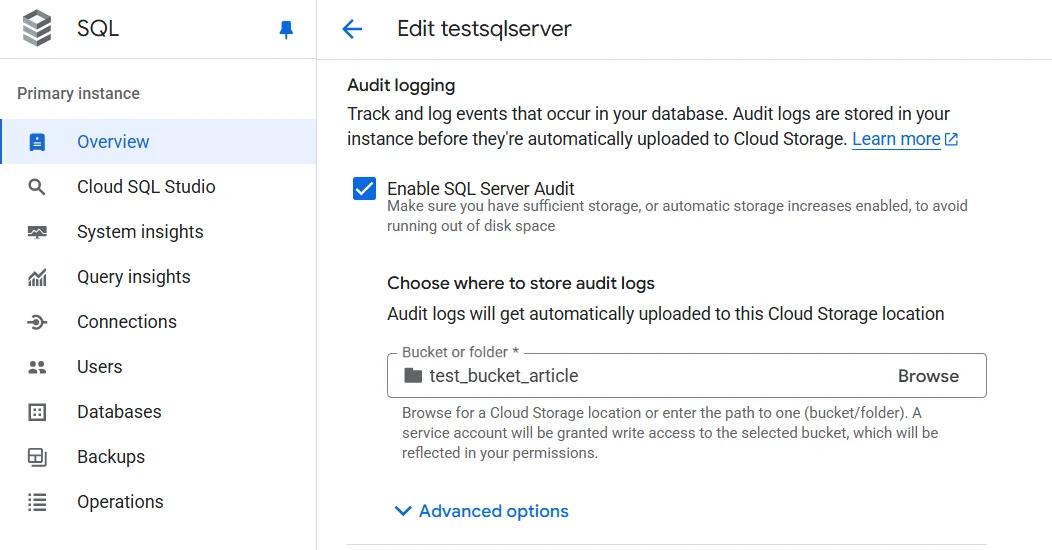
Creating a Server Audit
A server audit defines the destination and basic configuration for capturing audit data. In Google Cloud SQL for SQL Server, the TO FILE option stores events locally, which you can later export to Cloud Storage for persistence and analysis.
CREATE SERVER AUDIT GCloudAudit
TO FILE (FILEPATH = '/var/opt/mssql/audit', MAXSIZE = 10 MB);
ALTER SERVER AUDIT GCloudAudit WITH (STATE = ON);
The first statement creates the audit and specifies its file path and maximum size per file. The second statement activates the audit so it begins recording events immediately.
Server-Level Audit Specification
A server-level audit specification determines which high-level events to capture, such as login attempts or configuration changes. This example logs all failed login attempts to the previously created audit.
CREATE SERVER AUDIT SPECIFICATION AuditLoginFailures
FOR SERVER AUDIT GCloudAudit
ADD (FAILED_LOGIN_GROUP)
WITH (STATE = ON);
Here, FAILED_LOGIN_GROUP is a predefined audit action group that records unsuccessful authentication attempts — useful for detecting brute force or unauthorized access attempts.
Database-Level Audit Specification
A database-level audit specification focuses on events occurring within a specific database, such as reads, writes, or schema modifications.
CREATE DATABASE AUDIT SPECIFICATION AuditTransactions
FOR SERVER AUDIT GCloudAudit
ADD (SELECT ON dbo.transactions BY public)
WITH (STATE = ON);
In this example, any SELECT statements targeting the transactions table by public users will be recorded. This is helpful when monitoring access to sensitive data or verifying compliance with data protection policies.
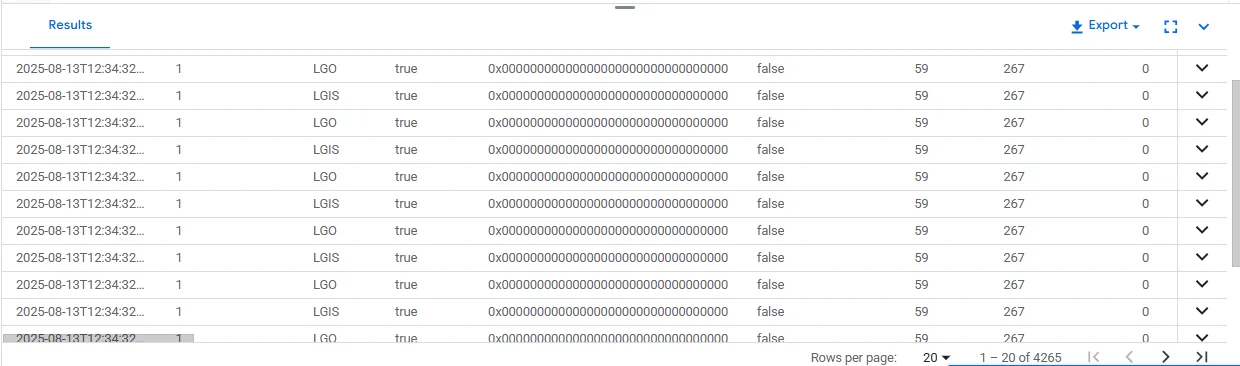
Reviewing Audit Data
Once events are recorded, you can query the audit logs directly from SQL Server.
SELECT *
FROM sys.fn_get_audit_file('/var/opt/mssql/audit/*.sqlaudit', NULL, NULL);
This function reads all .sqlaudit files from the specified path and returns their contents in tabular form. You can filter, join, or export this output for further analysis in tools like BigQuery or a SIEM platform.
Using Views and Procedures for Targeted Audits
While SQL Server Audit tracks defined events, you can supplement it with custom views and stored procedures to log business-specific activity.
CREATE VIEW RecentLogins AS
SELECT TOP 100 client_id, login_time, ip_address
FROM logins
ORDER BY login_time DESC;
CREATE PROCEDURE LogTransaction
@client_id INT, @amount DECIMAL(10,2), @type VARCHAR(20)
AS
BEGIN
INSERT INTO transactions (client_id, amount, transaction_type)
VALUES (@client_id, @amount, @type);
END
The view RecentLogins quickly retrieves the latest login events, while the procedure LogTransaction inserts new transactions with a built-in audit purpose, ensuring consistent tracking alongside native audits.
Where Native Auditing Falls Short
| Limitation | Impact |
|---|---|
| No native real-time alerting | Security teams must manually check logs, delaying response to threats |
| No built-in data masking in audit output | Sensitive data can appear in plain text, increasing compliance risk |
| Limited correlation across instances | Harder to track a user’s actions across multiple SQL Server databases |
| Minimal visual analytics | Lacks dashboards and interactive filtering for rapid investigation |
| Manual log review | Time-consuming to filter and extract meaningful insights |
Extending the Audit Trail with DataSunrise
While SQL Server Audit provides a reliable foundation, it was not designed for rapid incident response or multi-instance oversight. This is where DataSunrise fits in — enhancing audit trails with real-time monitoring, granular audit rules, and dynamic data masking.
With DataSunrise in place, Google Cloud SQL audit data becomes immediately actionable:
- Granular Audit Rules — Track only what matters: specific tables, query types, IP ranges, or users. This reduces log noise and focuses on security-relevant activity.
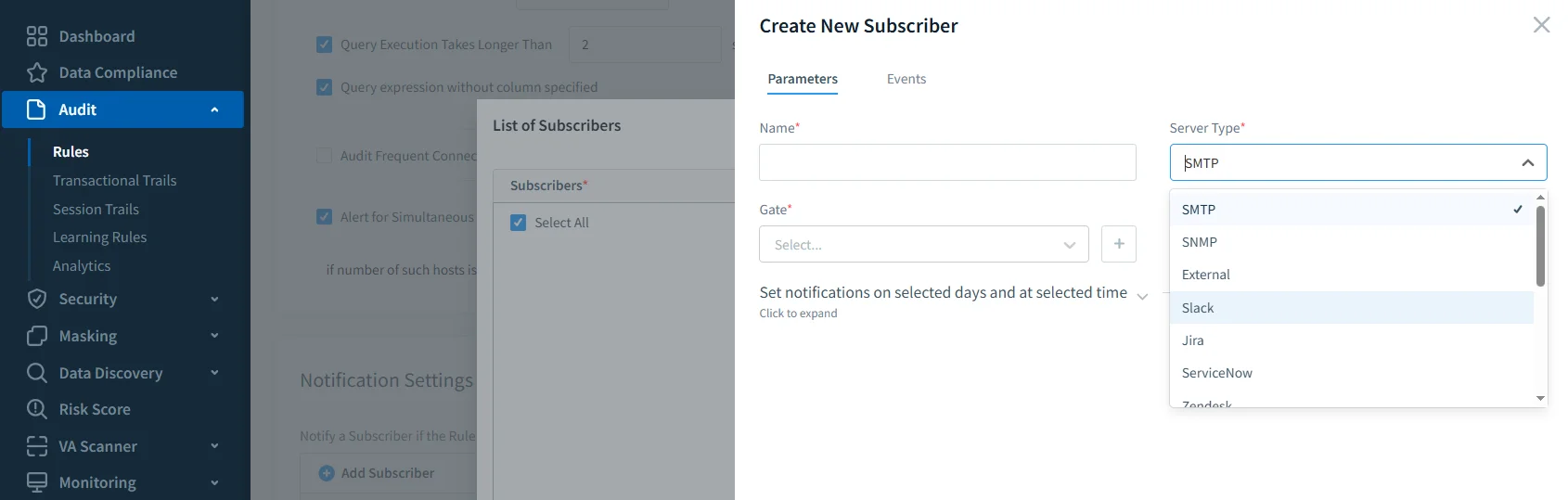
- Real-Time Alerts — Suspicious logins or unexpected query patterns can trigger instant notifications to your SOC team.
- Dynamic Data Masking — Sensitive fields such as PII, PHI, or financial data can be masked in query results, ensuring only authorized roles see actual values.
- Centralized Multi-Database View — Review audit trails from all monitored databases in a single interface, with filtering and correlation tools.
- Automated Compliance Reporting — Quickly generate auditor-ready reports for GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX.
When paired with screenshots of both SQL Server’s native audit configuration and DataSunrise’s audit rule creation interface, the contrast becomes clear: SQL Server’s logs are robust but static, while DataSunrise provides a dynamic, policy-driven security layer.
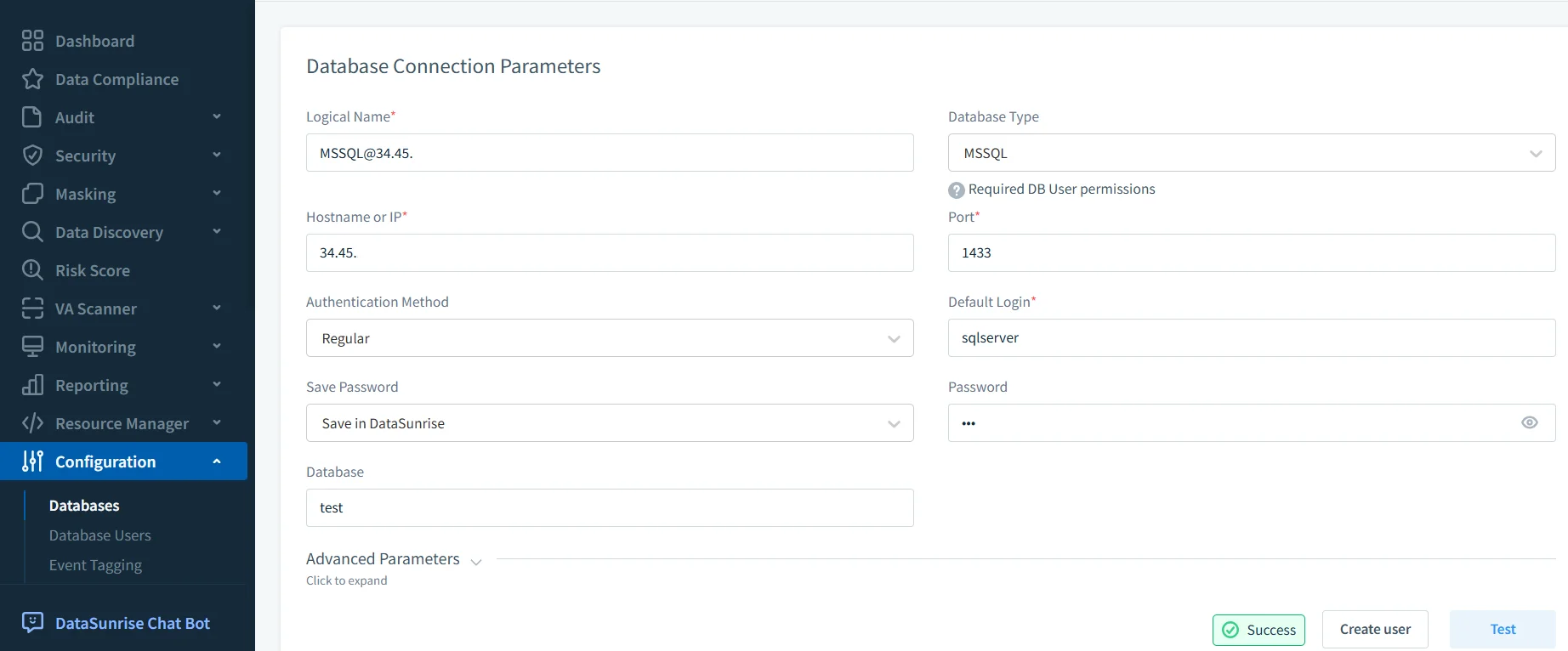
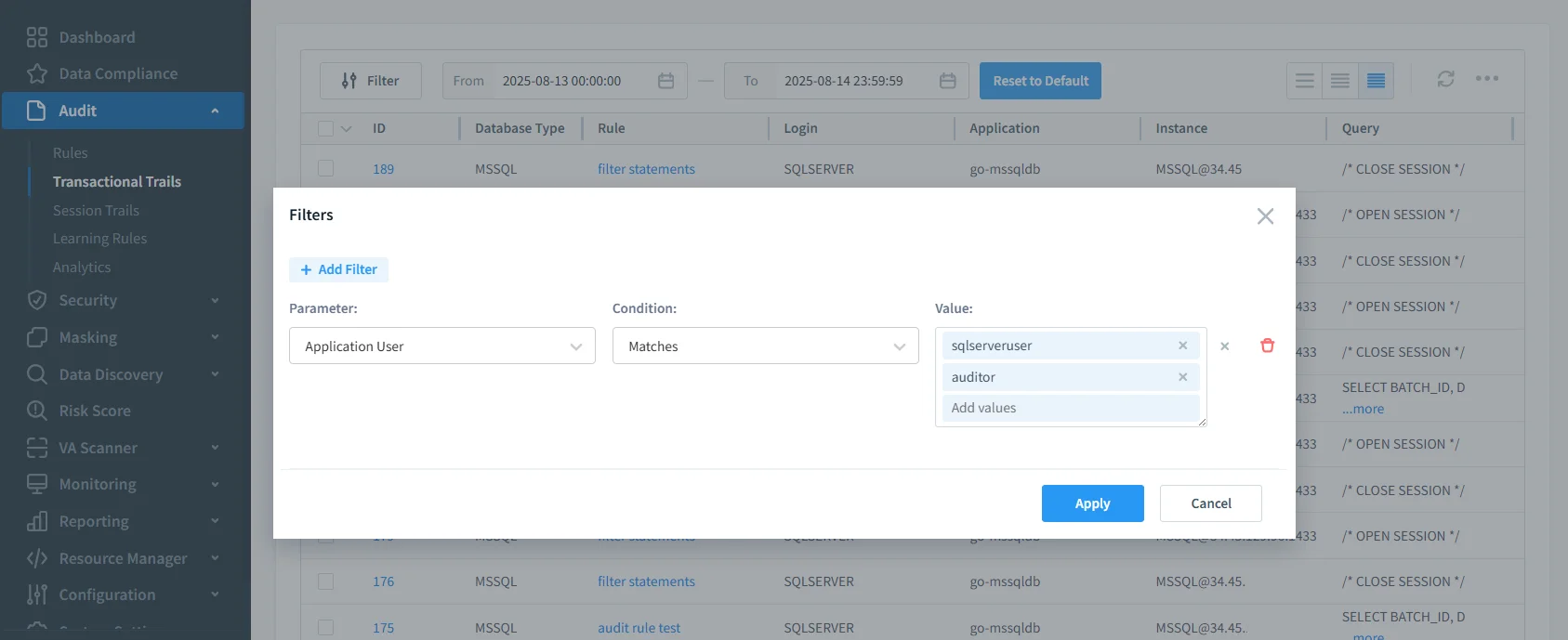
Example: Setting Up an Audit Rule in DataSunrise
- Connect Database — Add the Google Cloud SQL instance in the DataSunrise dashboard.
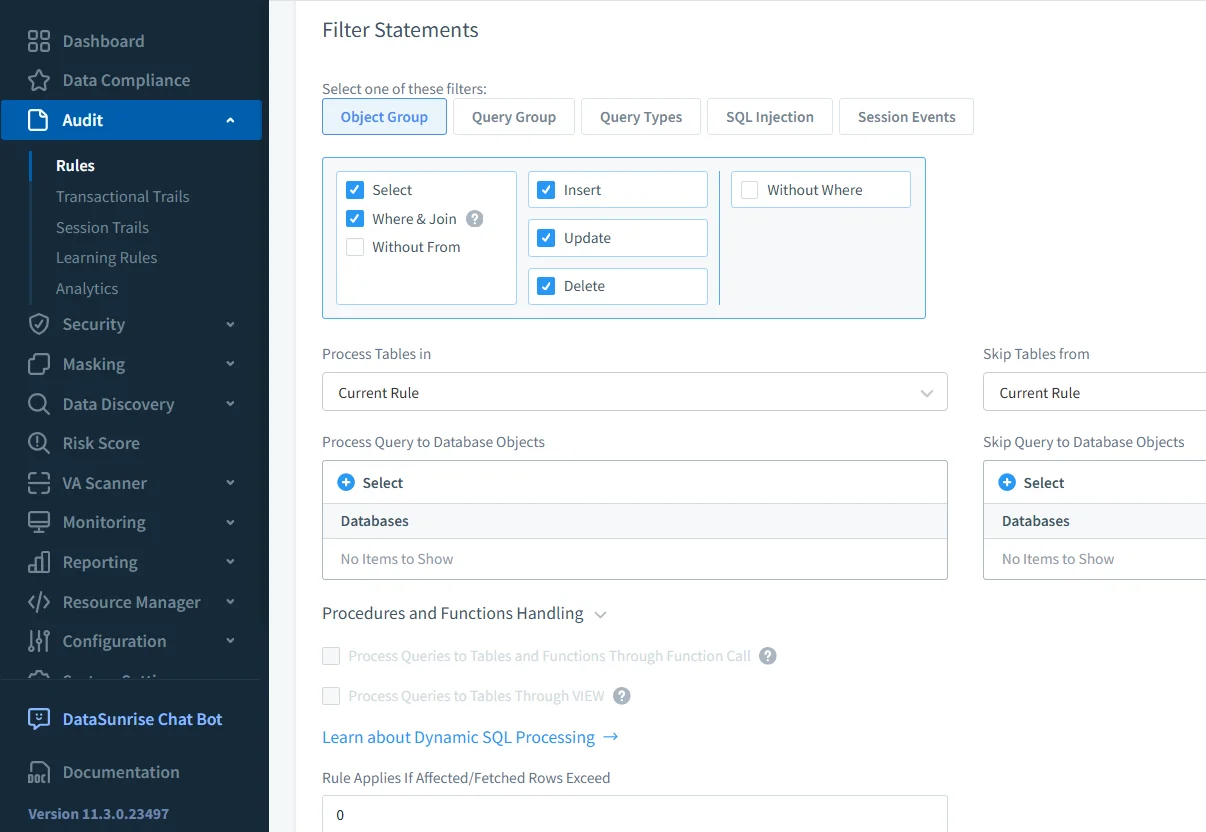
- Create an Audit Rule — Choose a target table (e.g.,
transactions) and select the event types (SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE, INSERT).
Sensitive Data Discovery and Masking
The built-in data discovery capability in DataSunrise scans your database to identify personally identifiable information (PII), protected health information (PHI), and other regulated data types. It automatically classifies columns containing sensitive content such as names, addresses, credit card numbers, or medical records, helping you understand where critical data resides.
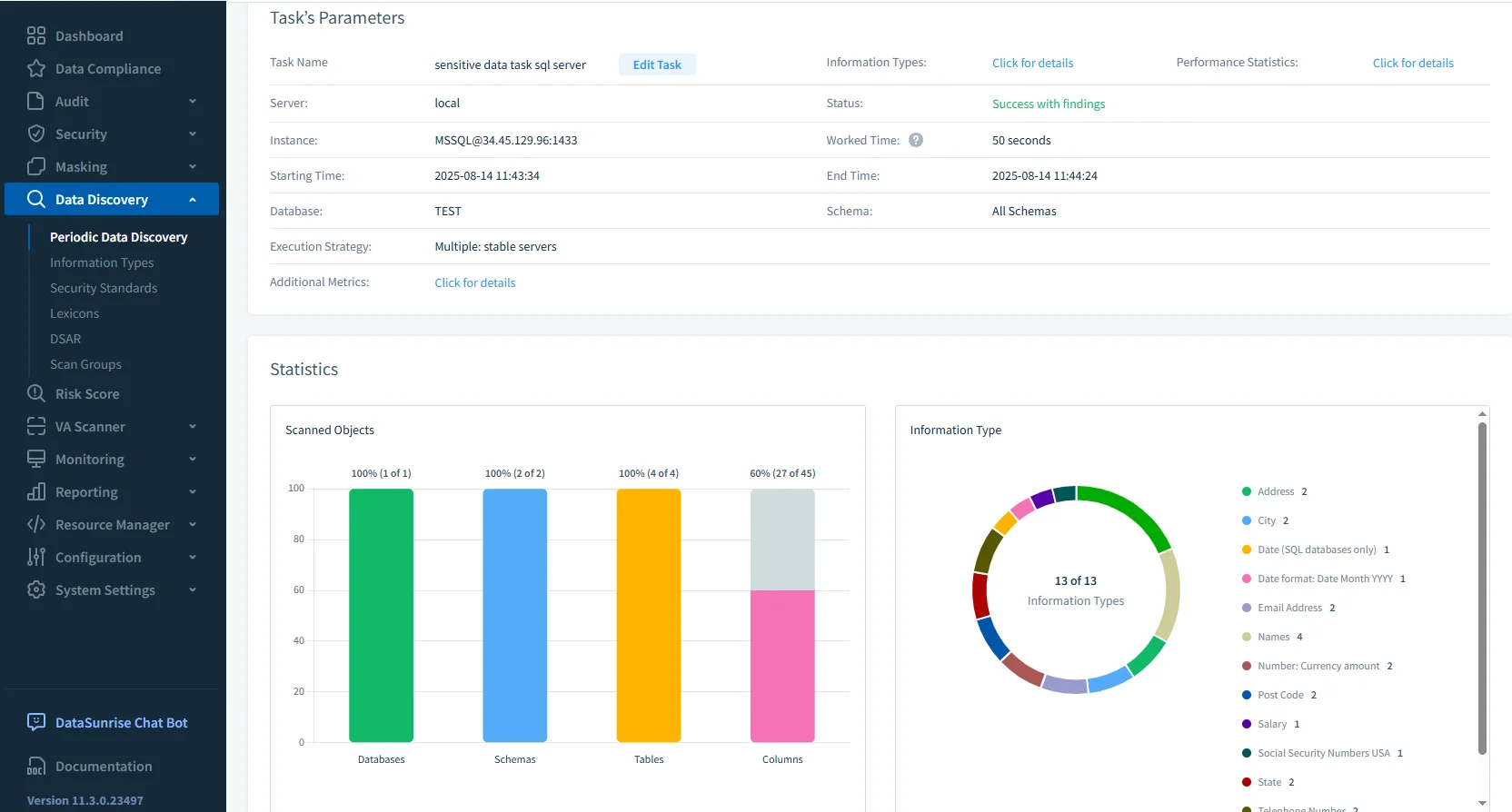
Once these assets are identified, you can apply dynamic data masking rules to protect them in real time. Masking policies are role-based, meaning that authorized users continue to see full values, while unauthorized users see masked or obfuscated data — for example, ********@example.com instead of an actual email address.
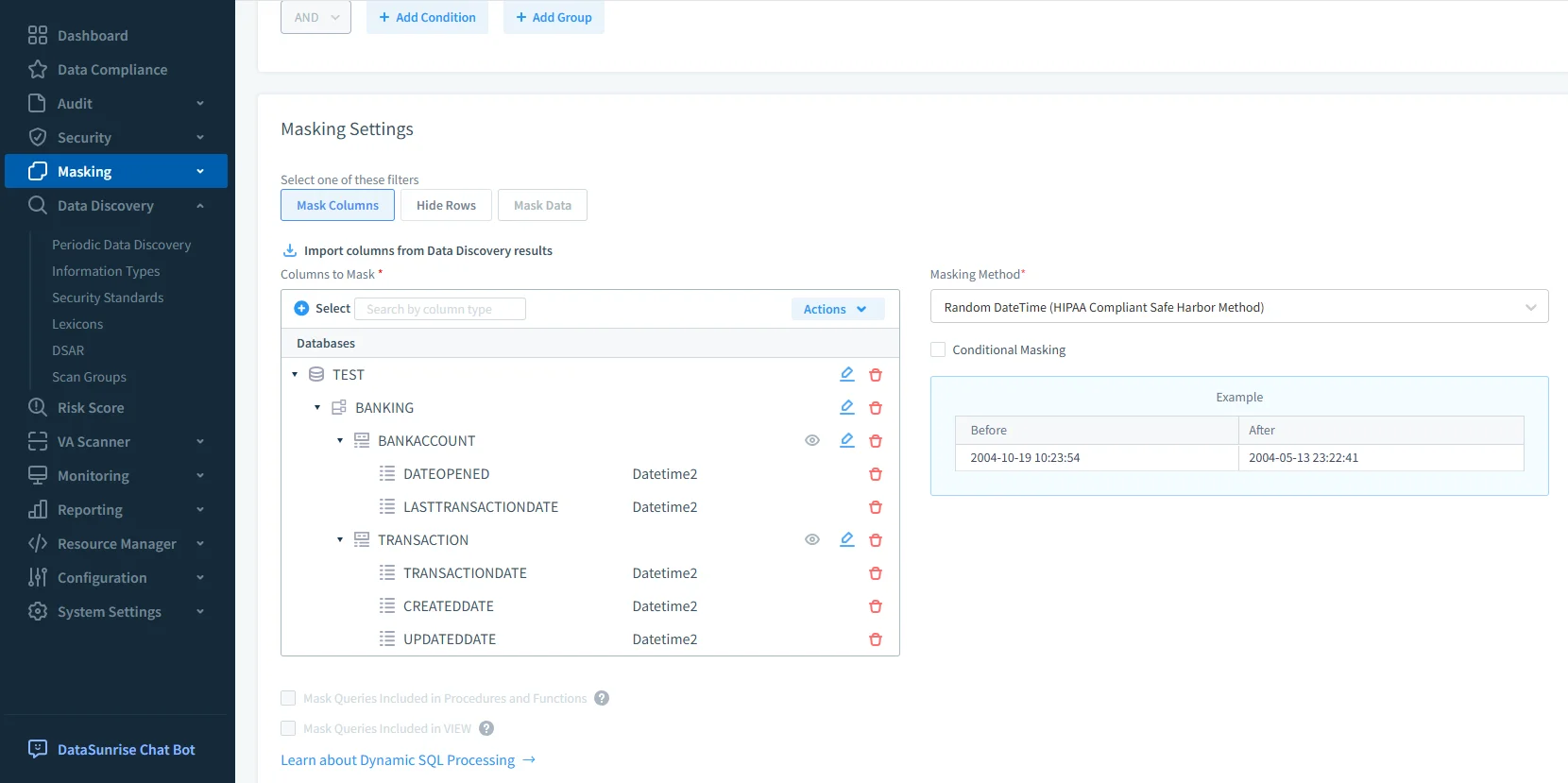
This approach ensures that sensitive information never leaves the database in clear form for unprivileged users, reducing the risk of accidental disclosure or insider threats. Because the masking occurs at the query-response level, there is no need to alter the underlying tables or duplicate datasets, which makes it easier to maintain consistent operations while meeting compliance regulations.
Best Practices for Google Cloud SQL Audit Trails
- Keep SQL Server and DataSunrise in the same VPC
- Store audit logs in Cloud Storage with lifecycle rules for automatic archiving
- Apply IAM roles to restrict audit log access
- Regularly refine audit rules to match evolving compliance needs
- Integrate with BigQuery or SIEM for advanced trend analysis
Conclusion
An effective Google Cloud SQL audit trail for SQL Server 2022 merges the detail of native SQL Server Audit with the flexibility of DataSunrise. By combining strong logging with real-time monitoring, masking, and centralized rule control, you can improve compliance readiness and security posture without overloading your team.
To learn more about why audit trails matter, see Audit Trails and explore how DataSunrise can enhance your Google Cloud SQL auditing workflow.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now