How to Apply Dynamic Masking in Amazon OpenSearch
How to apply dynamic masking in Amazon OpenSearch becomes a real question the moment your “just logs” cluster starts holding customer emails, phone numbers, IP addresses, session identifiers, or support notes. Amazon OpenSearch is a workhorse for observability, security analytics, and incident response—exactly the kind of pipelines that accidentally ingest regulated data. Dynamic masking is the fastest way to reduce exposure without breaking dashboards, search relevance, or operational workflows.
AWS provides the managed platform for Amazon OpenSearch Service, but compliance accountability remains with the organization operating the data. OpenSearch access control can decide who may query an index; masking decides what those users are allowed to see in the results.
This guide explains how to apply dynamic masking in Amazon OpenSearch using DataSunrise—starting from discovery, moving through rule configuration, and finishing with monitoring and audit-ready evidence.
Why Dynamic Masking Is the Right Control for OpenSearch
OpenSearch clusters are designed for speed and flexibility, not for “least data exposure.” Teams often broaden read permissions to keep Kibana/OpenSearch Dashboards, alerting, or SOC investigations working. That’s how you end up with too many users pulling raw identifiers from indices—especially when documents include nested JSON payloads or free-text message fields.
Dynamic masking reduces risk by transforming sensitive values at query time, before they reach the user. It’s a practical complement to identity controls and an excellent match for OpenSearch workloads where people need search capability but not raw values. If you need a baseline definition of the approach, see What is Data Masking and the dedicated overview of dynamic data masking.
Dynamic masking is particularly valuable when OpenSearch content includes PII or other sensitive elements embedded inside operational data that wasn’t built with compliance in mind.
Where Dynamic Masking Fits in the OpenSearch Access Path
The most important implementation detail is simple: masking must sit on the access path. If users can query OpenSearch directly, they can bypass masking entirely. That’s why deployment architecture matters.
DataSunrise supports multiple deployment modes so you can position enforcement in a way that matches your OpenSearch topology—whether you’re protecting a shared domain, multiple environments, or segmented teams. Once traffic consistently flows through the control point, policies can be enforced centrally through access controls and governed per role.
Prerequisites: Make Masking Predictable and Auditable
Before you create rules, make sure these basics are in place:
- Scope clarity: which indices and fields are considered sensitive, and why.
- Role model: who should see full values vs. masked values using RBAC.
- Least visibility: align masking outcomes with the principle of least privilege.
- Evidence: ensure you can prove policies were applied using centralized audit logging.
When these are defined up front, dynamic masking becomes a stable operational control instead of a fragile “it works on my dashboard” feature.
Step 1: Discover Sensitive Data in OpenSearch
You cannot mask what you cannot find. In OpenSearch, sensitive data often appears in unexpected places: nested attributes, payload fields, or log “message” strings. Manual reviews do not scale.
Start with automated data discovery to identify sensitive fields and patterns across indices. Discovery outputs help you build a defensible inventory and avoid blind spots, especially in fast-moving environments where schemas evolve and indices are created automatically by pipelines.
Discovery-driven scope is also the cleanest way to keep masking tight—protect what matters without turning your OpenSearch environment into a usability disaster.
Step 2: Define Scope and Ownership for Masking
After discovery, decide what gets masked and for whom. Good masking design focuses on role-based outcomes:
- SOC / incident response: needs search and correlation, rarely needs raw identifiers for every hit.
- Support / ops: needs confirmation and troubleshooting context, not full sensitive values.
- Privileged roles: may require full visibility under strict justification and auditing.
To avoid rule sprawl, centralize governance with Compliance Manager and define how masking policies map to real operational responsibilities.
Step 3: Create a Dynamic Masking Rule
Now for the part everyone actually came here for: rule configuration. In DataSunrise, create a Dynamic Masking Rule, select the OpenSearch fields you want to protect, and choose a masking method that preserves the required operational meaning (full redaction, partial masking, or normalization depending on your policy model).
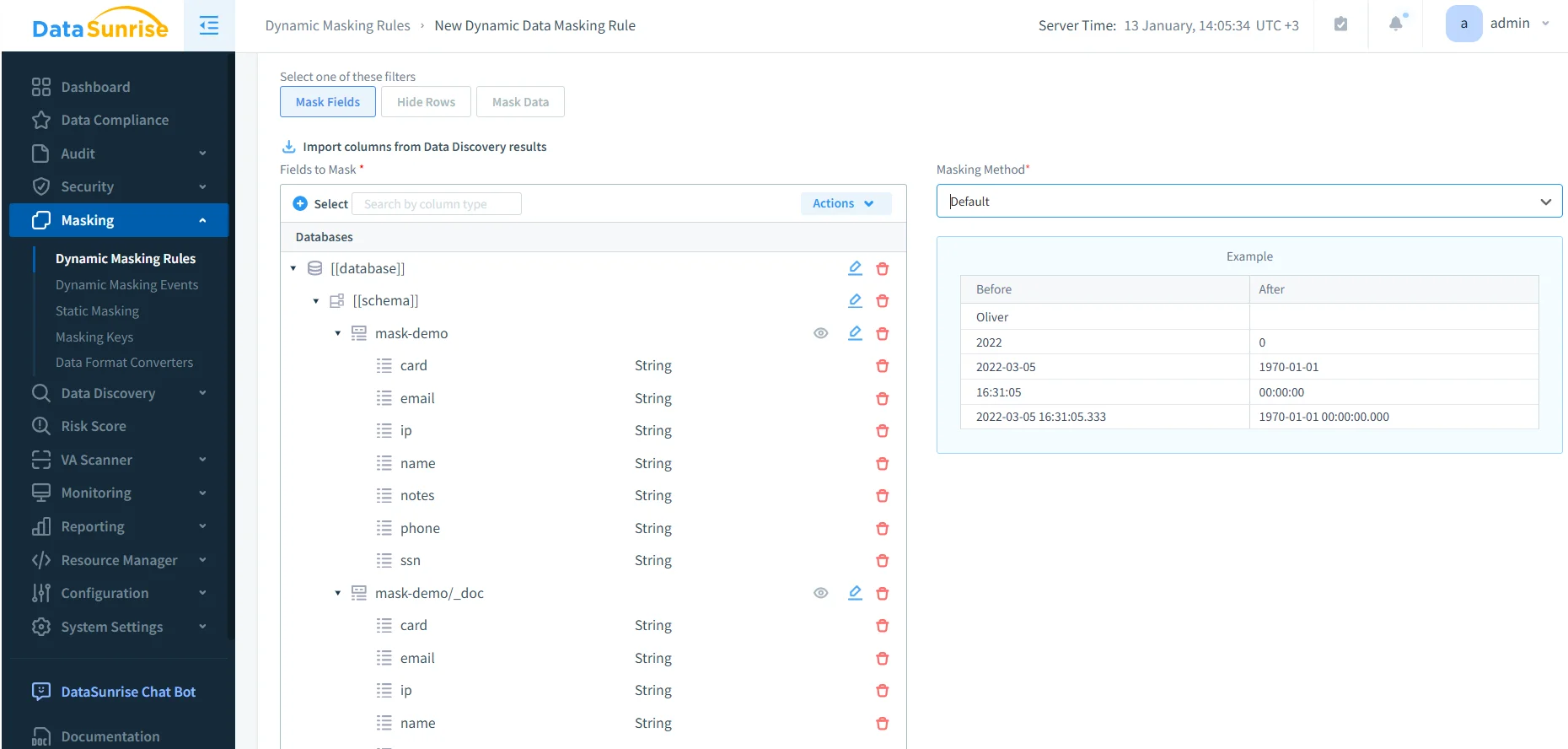
Practical rule design tips:
- Start with high-risk fields: emails, phone numbers, card-like fields, SSN-like identifiers, and IPs.
- Preserve utility: partial masking often keeps dashboards usable while reducing exposure.
- Keep policy deterministic: when multiple rules can match, resolve overlap with rules priority so outcomes remain predictable.
Step 4: Validate Masking Behavior (Don’t Skip This)
Validation isn’t optional. Run representative queries and confirm that:
- Search and aggregations still work as expected.
- Sensitive fields are masked for the intended roles.
- Privileged roles (if allowed) receive full visibility only under defined policy.
- No bypass path exists that lets users reach OpenSearch directly.
This step is where “dynamic masking” stops being a checkbox and becomes a reliable control. If you treat validation like a formality, you’ll eventually learn about your gaps from an auditor—or from an incident report.
Step 5: Monitor Dynamic Masking Activity
Once rules are active, you need operational visibility into enforcement. Monitoring helps you answer questions like:
- Which masking rule was applied to which query?
- Were there errors during enforcement?
- Which sessions and proxies were involved?
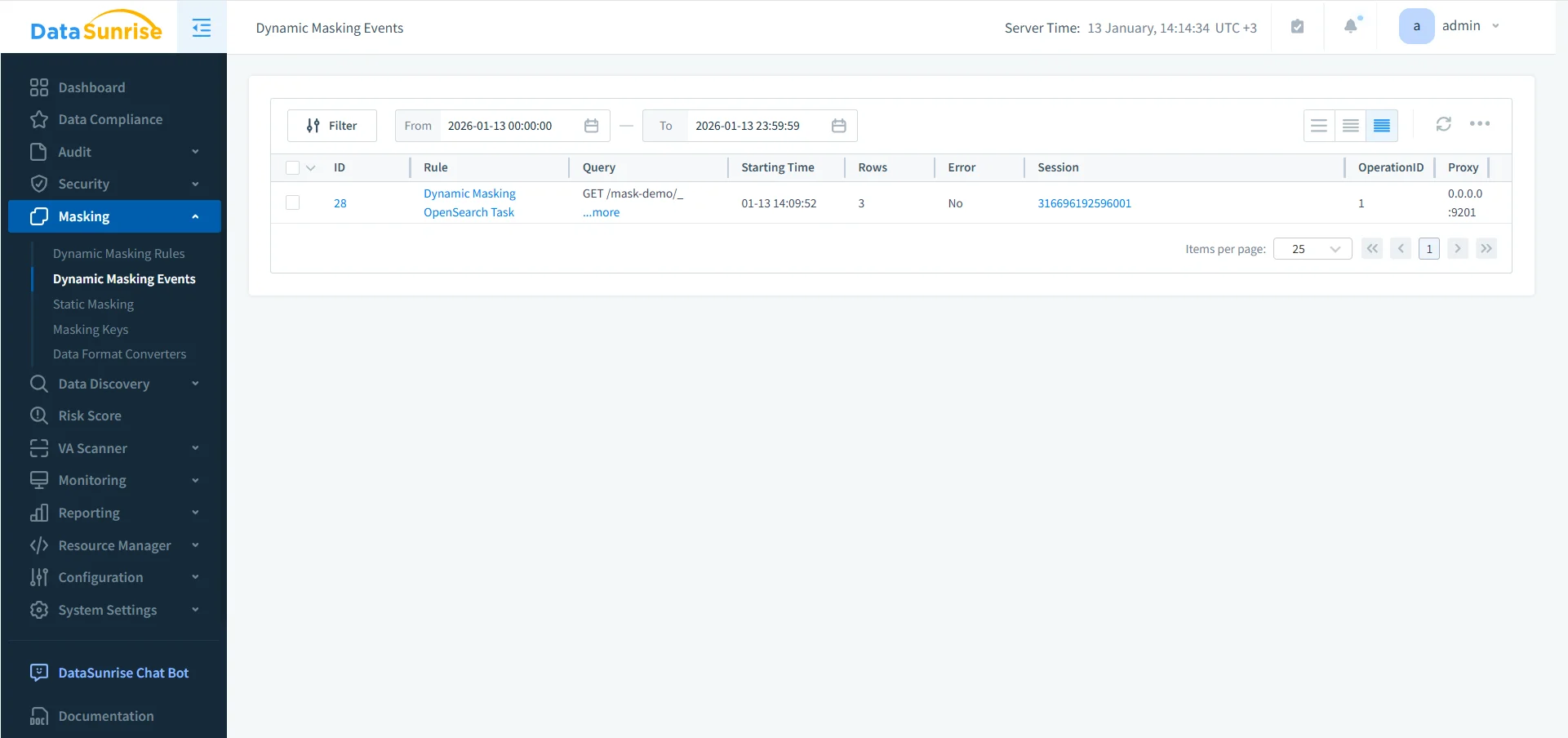
Treat these events as a live feedback loop. If you see unexpected activity spikes or repeated attempts to access sensitive fields, that’s a signal to refine role scope, adjust masking coverage, or tighten preventive controls.
Step 6: Capture Audit-Ready Evidence for Compliance
Masking lowers exposure, but compliance requires proof. You need to demonstrate that masking policies were enforced and that sensitive access is traceable.
DataSunrise provides centralized evidence through Data Audit, detailed audit logs, and immutable audit trails. For continuous oversight and anomaly detection, use database activity monitoring to identify suspicious patterns (bulk extraction attempts, unusual access sources, repeated sensitive lookups).
As a baseline reference for platform-native logging, AWS documents OpenSearch audit logs here: Amazon OpenSearch audit logs. In practice, centralized auditing is often easier to operationalize across multiple environments and access paths.
Step 7: Operational Hardening Around Masking
Masking is not a complete security strategy. Strong implementations pair masking with guardrails that reduce the chance of bypass, abuse, or drift:
- Database firewall rules to block abusive patterns and suspicious requests
- Continuous data protection to keep controls effective as indices and pipelines evolve
- Vulnerability assessment to detect configuration weaknesses and drift early
For audit packages and recurring reviews, consolidate evidence via report generation. This turns “we think masking is working” into “here’s the proof.”
Common Mistakes (That Make Masking Useless)
- Direct access bypass: if users can hit OpenSearch directly, masking won’t apply. Lock down routes.
- Over-broad scope: masking everything can break analytics. Start with sensitive indices and expand deliberately.
- No ownership: if nobody owns the policy, it will drift. Assign data owner and security owner.
- No evidence: masking without audit is a future audit finding waiting to happen.
Use discovery results to scope masking rules and start with the highest-risk fields first (email, phone, SSN-like identifiers, card-like fields, IPs). Expand coverage based on real usage and audit evidence—not guesswork.
Dynamic masking only protects what flows through the enforcement path. If clients can bypass the proxy/control point and query OpenSearch directly, sensitive values can leak. Enforce network controls, keep auditing always-on, and treat secrets in logs as a critical incident.
Conclusion
If you need to know how to apply dynamic masking in Amazon OpenSearch without breaking operations, the winning pattern is consistent: discover sensitive fields, scope policies to the right objects, apply dynamic masking by role, validate behavior with real queries, monitor masking events, and keep audit evidence continuously available. Done correctly, dynamic masking becomes a quiet control that reduces exposure every day—not a once-a-year compliance scramble.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now