How to Audit Amazon OpenSearch
How to audit Amazon OpenSearch becomes a critical question once Amazon OpenSearch is used beyond simple search workloads. In many production environments, Amazon OpenSearch stores security logs, operational telemetry, application events, and user-related data. As a result, organizations must track who accessed the system, what actions were performed, and whether those actions complied with internal security policies.
Auditing Amazon OpenSearch is not only about visibility. It is also about accountability, investigation readiness, and regulatory compliance. Without a structured audit process, security teams struggle to reconstruct incidents, while compliance teams lack defensible evidence during reviews.
This article explains how to audit Amazon OpenSearch effectively, outlines the limitations of native logging, and shows how DataSunrise provides centralized audit controls for OpenSearch environments using data audit practices.
What Auditing Means in Amazon OpenSearch
Auditing in Amazon OpenSearch refers to recording and reviewing database-level activity rather than system performance metrics. Specifically, auditing focuses on how users and applications interact with indices, documents, and administrative APIs.
An effective audit process captures:
- User authentication and access attempts
- Index creation, deletion, and configuration changes
- Document indexing, updates, and deletions
- Administrative and security-related REST API calls
These records support database security and data security by making activity transparent and reviewable. In addition, audit records establish accountability by linking actions to specific users, roles, or service accounts.
From a governance perspective, audit data also enables organizations to demonstrate that access controls and operational procedures are enforced consistently across environments.
Limitations of Native Amazon OpenSearch Logging
Amazon OpenSearch includes built-in logging and security plugins that capture request metadata. While these logs help with troubleshooting and diagnostics, they do not provide a complete audit trail.
Native limitations include:
- REST requests recorded as isolated events
- No session or transaction correlation
- Retention tied to cluster configuration
- Manual reconstruction of audit evidence
Because of these constraints, native logs rarely satisfy audit requirements defined by data compliance regulations. When auditors request a clear sequence of events or proof of access accountability, teams often need to correlate multiple log sources manually.
Native Logging vs Centralized Audit Approach
| Audit Capability | Native OpenSearch Logging | Centralized Audit with DataSunrise |
|---|---|---|
| User access visibility | Basic request metadata | Full user and source attribution |
| Request correlation | Not available | Transactional and session-based trails |
| Audit data retention | Cluster-dependent | Centralized, policy-driven storage |
| Audit evidence readiness | Manual reconstruction | Searchable, audit-ready records |
| Tamper resistance | Limited | External, protected audit storage |
How DataSunrise Audits Amazon OpenSearch
DataSunrise audits Amazon OpenSearch by acting as an external security and monitoring layer. Instead of relying on OpenSearch internals, DataSunrise observes database traffic and records audit events in a centralized repository supported by database activity monitoring.
This design ensures that audit records remain independent of the OpenSearch cluster. Consequently, database users cannot modify or delete audit data, preserving evidentiary value during investigations and compliance reviews supported by Compliance Manager.
By separating audit storage from the database itself, organizations also reduce the risk of log tampering or accidental data loss during maintenance operations.
Audit Rule Configuration
The first step to audit Amazon OpenSearch with DataSunrise is defining audit rules. Audit rules specify which OpenSearch instances are monitored, which operations are logged, and where audit records are stored using centralized audit logs.
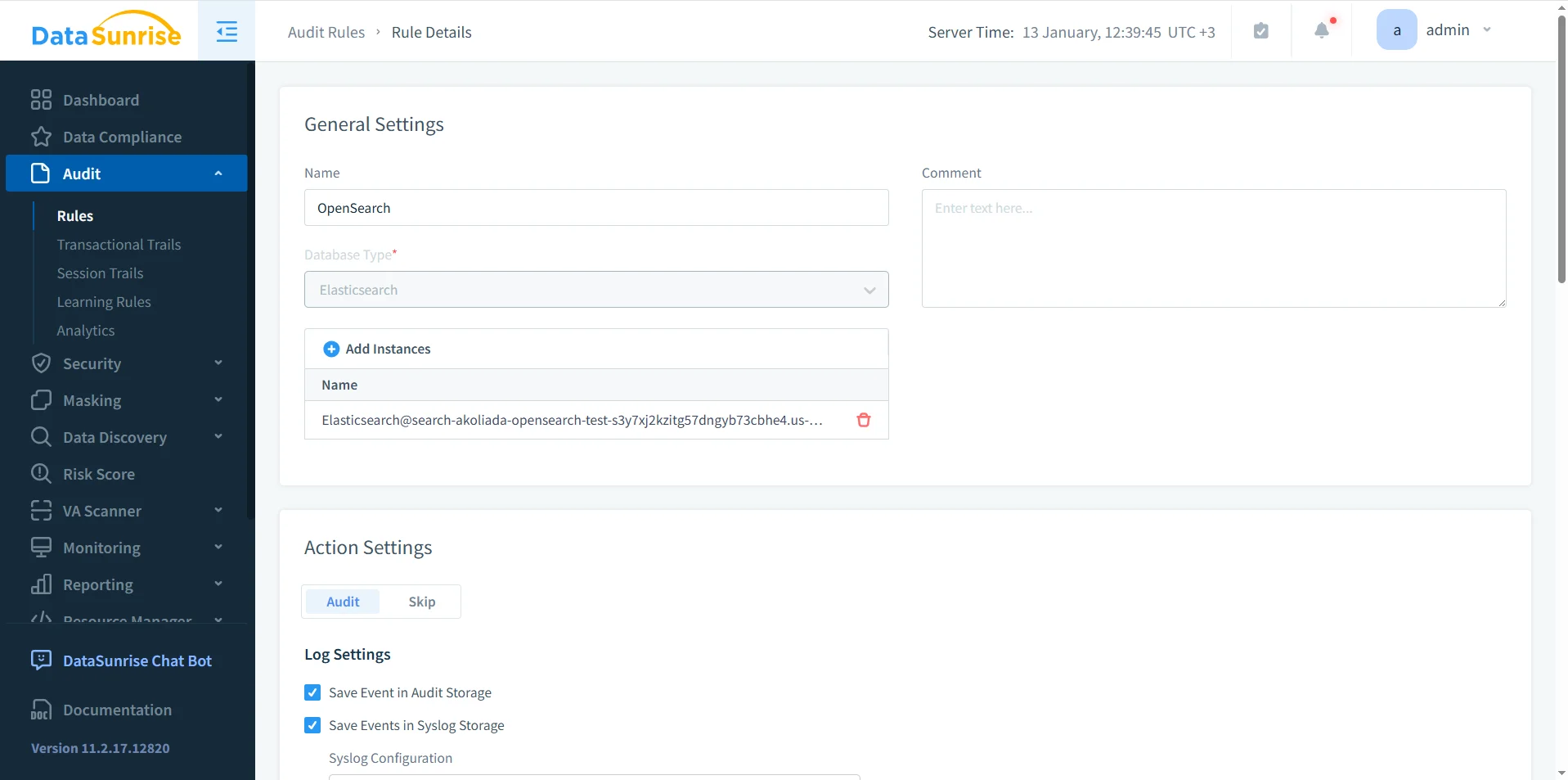
Using audit rules, teams can focus on high-risk actions such as data modification, index management, and administrative access. This selective approach reduces audit noise while preserving forensic value.
Transactional Trails and Session Context
OpenSearch processes each REST request independently. As a result, native logs fragment user activity into disconnected events.
DataSunrise correlates related requests into transactional audit trails. These trails group operations into a single logical sequence that reflects real user or application behavior, supporting database activity history.
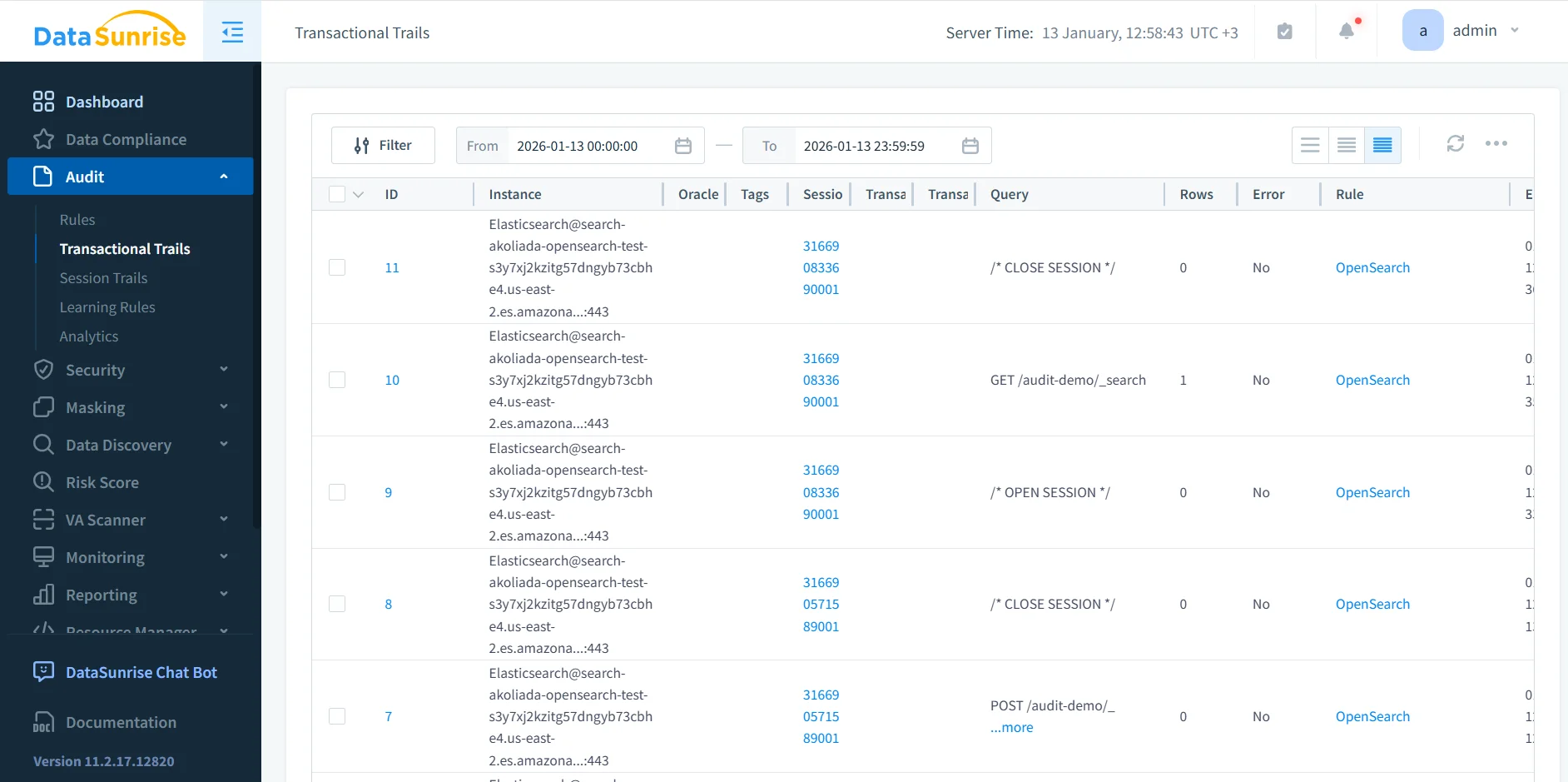
Transactional trails significantly simplify investigations by presenting a clear timeline of activity. Instead of reviewing dozens of isolated log entries, auditors can analyze a single session-level record.
Centralized Audit Architecture
DataSunrise captures OpenSearch traffic using traffic inspection and reverse proxy techniques.
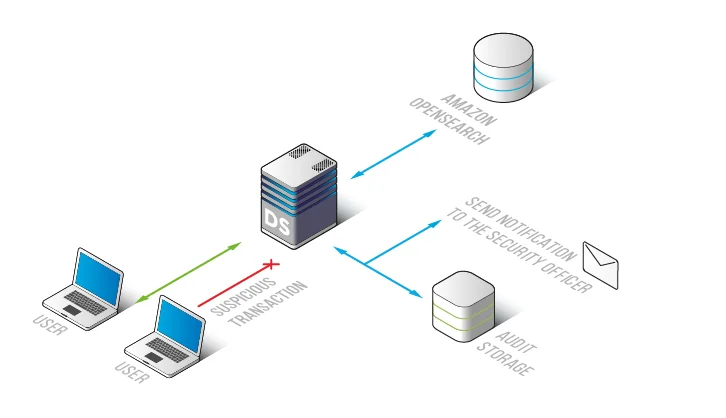
Centralized storage integrates with optimized audit storage and supports long-term retention. This design is especially important for organizations that must retain audit evidence for months or years.
Operational and Compliance Benefits
Auditing Amazon OpenSearch delivers value beyond investigations. Audit data helps organizations validate access models, review automation behavior, and analyze administrative changes.
Over time, audit trails reveal risky patterns such as excessive privilege usage, repeated failed access attempts, or unexpected configuration changes. These insights support continuous improvement of security controls through user behavior analysis.
Security and Compliance Use Cases
Organizations typically audit Amazon OpenSearch to support:
- Incident response and forensic investigations
- Access accountability enforced through RBAC
- Audit evidence for GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and SOX
- Centralized audit logs and reporting
When auditing Amazon OpenSearch, start with administrative actions and data modification operations. Expand audit coverage gradually to control volume while preserving forensic value.
Conclusion
So, how do you audit Amazon OpenSearch? The answer lies in combining structured audit rules, transactional trails, and centralized storage.
While native OpenSearch logging offers basic visibility, it does not deliver a complete audit solution. By implementing DataSunrise, organizations gain a centralized, tamper-resistant way to audit Amazon OpenSearch, enabling investigations, audits, and long-term governance.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now