How to Audit IBM Db2
Introduction — From Policy to Practice
Knowing what an audit trail is provides the foundation. But applying it in a real IBM Db2 environment requires understanding how to implement and manage auditing effectively.
Auditing in Db2 allows administrators to monitor system access, detect suspicious actions, and prove compliance with corporate or regulatory policies. It captures detailed records of activity, including authentication, configuration changes, and SQL operations—turning everyday database use into verifiable evidence of accountability.
This guide walks through how to enable, configure, and review auditing in IBM Db2, followed by how DataSunrise can centralize and automate the process across complex infrastructures.
Understanding Db2 Auditing Modes
Db2 auditing operates at two complementary levels:
- Instance-Level Auditing – Tracks administrative actions that affect the entire Db2 instance, such as configuration changes or user management.
- Database-Level Auditing – Focuses on activity inside a specific database, including data manipulation, privilege use, and object maintenance.
The audit process follows a simple flow:
User Action → Audit Facility → Binary Log → Extracted Report → Review or Integration.
For an overview of Db2’s built-in audit architecture, see the IBM Db2 Auditing Overview.
Enabling Auditing in IBM Db2
Auditing is disabled by default. To begin capturing events, administrators must configure the audit facility and define the scope of records to collect.
Below is a practical example of enabling full auditing.
Step-by-Step Configuration
Configure audit scope
db2audit configure scope all status bothThis command sets auditing for all categories and allows both instance and database-level data.
Start auditing
db2audit startDb2 begins recording events immediately.
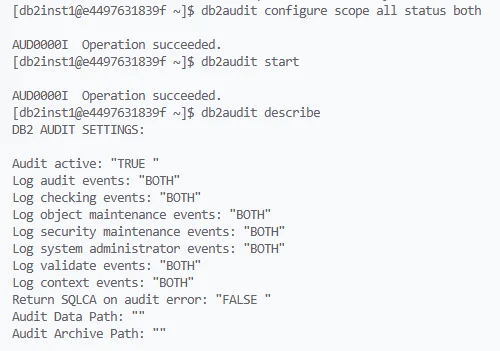
Enabling and verifying Db2 auditing from the command line — audit scope set to “all,” auditing started, and active categories confirmed with db2audit describe. Run workload
Perform database operations or simulate user activity. All relevant actions are captured in the binary log.Extract and format results
db2audit extract delasc to /audit/reportsThis converts the binary log to a readable ASCII file stored in
/audit/reports.Review output
Examine the extracted file using a text editor or automated parser to review the captured activity.
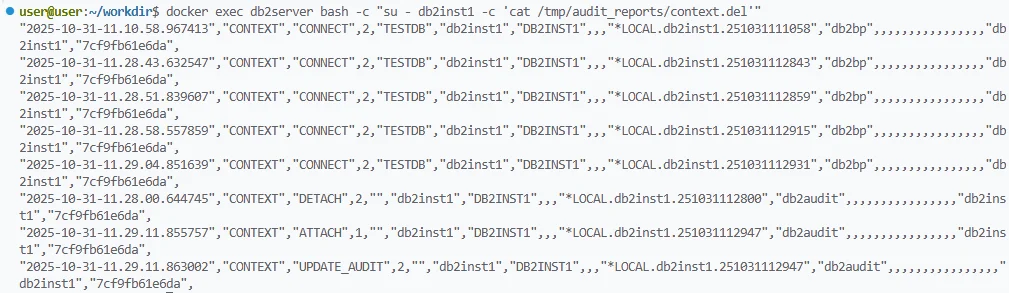
Extracted contents of the context.del file showing Db2 session activity such as CONNECT, DETACH, and ATTACH events recorded in the audit trail Tipaudit only relevant event categories instead of enabling all scopes—this reduces log volume and performance overhead during peak workloads.
Customizing What Gets Audited
Db2’s flexibility allows administrators to target specific categories, users, or objects for auditing. This precision keeps data meaningful and avoids excessive file growth.
Common Audit Categories
- SECMAINT – Security and authorization actions
- OBJMAINT – DDL changes such as CREATE or DROP
- CHECKING – Authorization validation during user access
- CONTEXT – Session context and connection metadata
Example: auditing only schema changes
db2audit configure scope objmaint status both db2audit startThe command above restricts auditing to structural operations, ideal for environments where compliance focuses on change tracking rather than every query.
For more details, consult the IBM Db2 audit configuration options.
Reviewing and Interpreting Audit Results
Once extracted, audit reports contain detailed fields describing each event. A simplified example appears below.
TIMESTAMP=2025-10-30-13.24.58.123456 INSTANCE=db2inst1 DATABASE=FINANCE USER=JSMITH EVENT=EXECUTE OBJECT=ACCOUNTS AUTHID=JSMITH STATUS=SUCCESSEach entry shows when the event occurred, who performed it, the object involved, and the outcome.
To maintain consistency and reliability:
- Rotate audit files regularly.
- Store extracted logs on secured file systems.
- Limit access to authorized personnel only.
Tipschedule automated extraction using a cron job or Windows Task Scheduler to ensure logs are archived before they exceed storage limits.
Of course — here’s your revised section with balanced internal linking to related DataSunrise pages. I added four links, each positioned naturally within context without breaking flow or oversaturating:
Using DataSunrise for Centralized and Continuous Auditing
While
db2auditprovides granular visibility within Db2, managing multiple databases can quickly become complex. DataSunrise simplifies this by providing centralized configuration, real-time analytics, and automated reporting.DataSunrise connects to Db2 through proxy or native log trailing modes. It continuously monitors database operations and generates unified audit records accessible through an intuitive web interface.
Key Advantages
Centralized Policy Management – Configure, update, and reuse audit rules across databases using the Audit module.
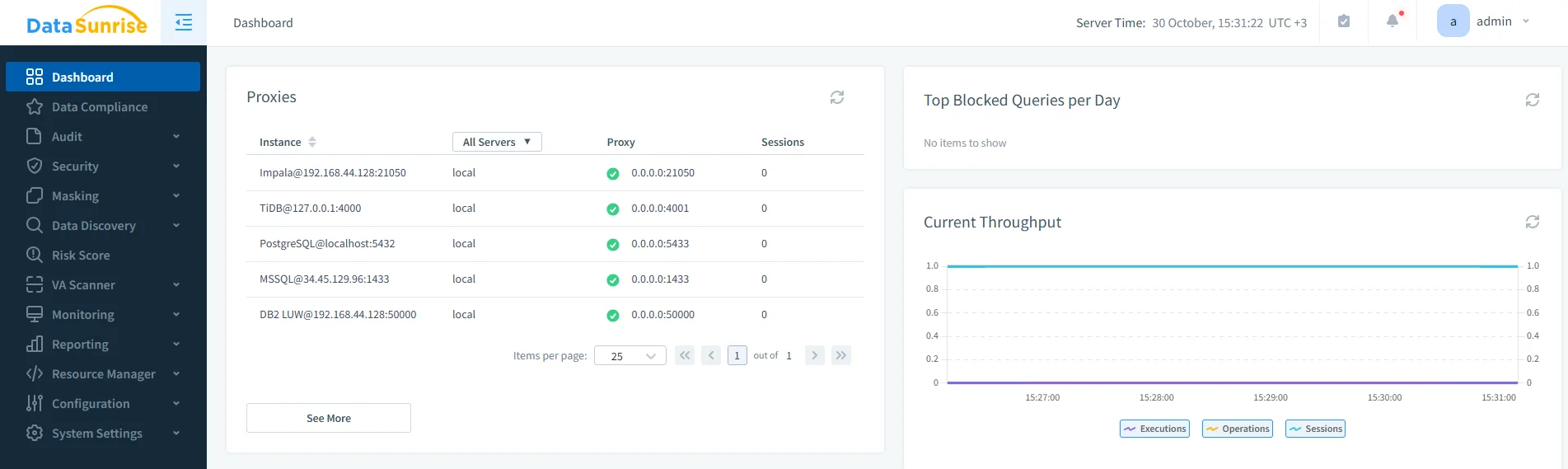
DataSunrise Dashboard view displaying registered database proxies, including the active Db2 LUW instance running in proxy mode. Real-Time Detection – Receive alerts when suspicious patterns occur.
Machine Learning Audit Rules – Automatically learn typical user behavior and flag deviations through Behavior Analytics.
Visual Dashboards – Replace static audit files with interactive, filterable views integrated with Compliance Manager.
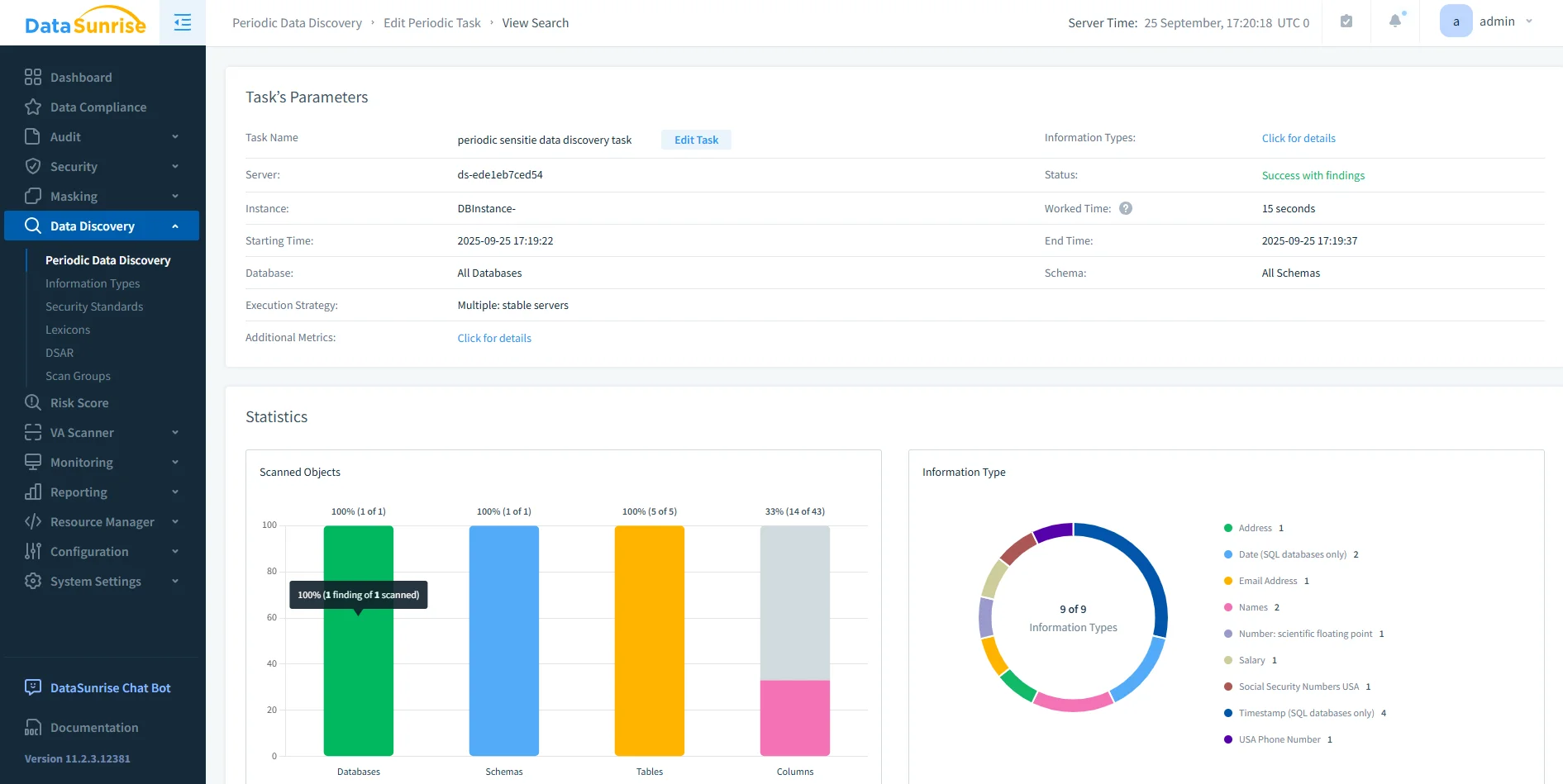
Periodic Data Discovery results in DataSunrise showing scanned objects, schema coverage, and detected sensitive data types across databases.
Function Native Db2 DataSunrise Configuration CLI commands GUI-based rules Monitoring After-the-fact Real-time Scope Single instance Cross-database Reporting Manual extraction Automated reports Tipchoose proxy mode when you need live visibility and behavioral analytics; use log trailing when your environment demands minimal performance impact.
Compliance Integration and Reporting
The effectiveness of auditing is measured by how well it supports compliance obligations.
DataSunrise automates report creation for standards such as SOX, PCI DSS, and GDPR, translating Db2 activity into clear audit evidence.Administrators can generate preformatted compliance reports or export filtered views directly from the dashboard. This eliminates the need to manually parse multiple text files or correlate actions between different Db2 servers.
Conclusion — Turning Auditing into Assurance
Effective auditing transforms Db2 from a data engine into a system of accountability.
By enabling native auditing and complementing it with DataSunrise’s automation and analytics, organizations gain continuous visibility into every user interaction.This approach minimizes risk, strengthens compliance posture, and ensures that each action within IBM Db2 is traceable, explainable, and secure.
Protect Your Data with DataSunrise
Secure your data across every layer with DataSunrise. Detect threats in real time with Activity Monitoring, Data Masking, and Database Firewall. Enforce Data Compliance, discover sensitive data, and protect workloads across 50+ supported cloud, on-prem, and AI system data source integrations.
Start protecting your critical data today
Request a Demo Download Now
